
Silicon used in computer chips must have an impurity level below 10−9 (that is, fewer than one impurity atom for every 109 Si atoms). Silicon is prepared by the reduction of quartz (SiO2) with coke (a form of carbon made by the destructive distillation of coal) at about 2000°C:
Next, solid silicon is separated from other solid impurities by treatment with hydrogen chloride at 350°C to form gaseous trichlorosilane (SiCl3H):
Finally, ultrapure Si can be obtained by reversing the above reaction at 1000°C:
(a) Trichlorosilane has a vapor pressure of 0.258 atm at −2°C. What is its normal boiling point? Is trichlorosilane’s boiling point consistent with the type of intermolecular forces that exist among its molecules? (The molar heat of vaporization of trichlorosilane is 28.8 kJ/mol.) (b) What types of crystals do Si and SiO2 form? (c) Silicon has a diamond crystal structure (see Figure 11.28). Each cubic unit cell (edge length a = 543 pm) contains eight Si atoms. If there are 1.0 × 1013 boron atoms per cubic centimeter in a sample of pure silicon, how many Si atoms are there for every B atom in the sample? Does this sample satisfy the 10−9 purity requirement for the electronic grade silicon?
Figure 11.28 (a) The structure of diamond. Each carbon is tetrahedrally bonded to four other carbon atoms. (b) The structure of graphite. The distance between successive layers is 335 pm.
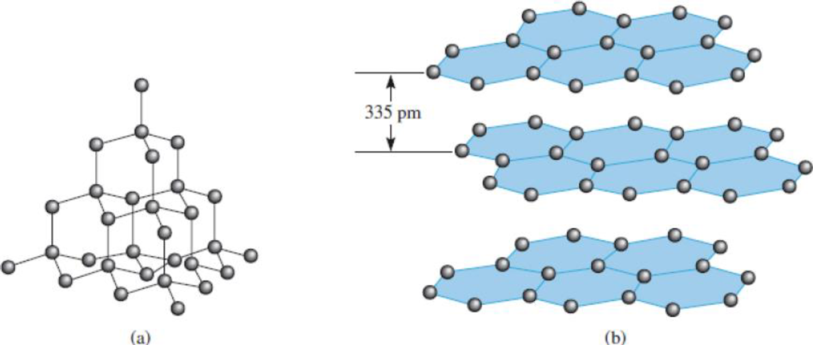
(a)
Interpretation:
The normal boiling point of trichlorosilane and its adherence to its intermolecular forces have to be found out and discussed.
Concept Introduction:
Boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure will be in equilibrium with the external pressure which is normally
Vapour pressure: It is the pressure developed on the vapor when it is in contact with its liquid form or solid form. So, it is also known as equilibrium vapor pressure which establishes equilibrium between its gaseous vapor state and liquid state or solid state.
The trends of boiling points are only due to the strength of the intermolecular forces that are acting between the molecules of the given compounds.
Intermolecular forces are the forces existing between molecules, atoms, ions or dipoles and hence binds all the molecules of a definite physical state such as solid, liquid or gas state.
Explanation of Solution
The normal boiling point of trichlorosilane can be calculated using the Clausisus-Clapeyron equation:
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
Given:
Converting kilojoules into joules:
Converting temperature from Celsius to kelvin:
Substituting all these values in the Clausius-Clapeyron equation:
Converting the normal boiling point temperature from Kelvin into Celsius:
Therefore, the normal boiling point of trichlorosilane is
Intermolecular forces existing in trichlorosilane
There are three highly electronegative halogen atoms such as chlorine atoms in the trichlorosilane which are attached to the least electronegative atoms such as silicon and hydrogen atoms. So there will be permanent dipole moment in the molecule, due to the distinguishable electronegativity in it. Hence, the interactions between such molecules will be dipole-dipole interactions, which are strong intermolecular forces. Therefore, the normal boiling point is expected to be in positive integer, since more energy is required to break the strong intermolecular forces. The calculated boiling point of trichlorosilane is
(b)
Interpretation: The type of crystal formed by
Concept Introduction:
The major types of crystals are listed here:
- 1. Ionic crystals.
- 2. Covalent crystals.
- 3. Molecular crystals.
- 4. Metallic crystals.
Ionic crystals: The crystals that are composed of charged species such as anions and cations.
Covalent crystals: In covalent crystals, all the atoms will be connected in a three-dimensional network by covalent bonds.
Molecular crystals: In molecular crystal, the molecules occupying the lattice points will have attractive forces between them such as van der waals forces or hydrogen bonding.
Metallic crystals: All the lattice points are occupied by the same type of metal.
Explanation of Solution
(c)
Interpretation: The purity requirement for the electronic grade silicon, has to be checked out when boron atom is added to
Concept Introduction:
Silicon is being used in various electronic devices today, due its special and important properties such as superconducting property and electrical properties. Silicon can be doped which is a modification in its electrical properties. Silicon used in computer chips must have an impurity level below
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The edge length of cubic unit cell in the diamond structure of silicon is given as
Converting edge length from picometers into centimeters:
Calculating the volume of per unit cell:
The relation between edge length and volume is
So, the volume of per unit cell is
Calculating the number of unit cells per cubic centimetre:
Therefore, in the volume of
Calculating the number of
It is given that there are 8
So,
Thus, there will be
Calculating the purity of
Given that
It is now known that per centimetre sample of pure silicon have
So, per centimetre sample of pure silicon have
This implies that there will be fewer than one impurity atom for every
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H H CH3OH, H+ H Select to Add Arrows H° 0:0 'H + Q HH ■ Select to Add Arrows CH3OH, H* H. H CH3OH, H+ HH ■ Select to Add Arrows i Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
- What are examples of analytical methods that can be used to analyse salt in tomato sauce?arrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the relative stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts H Šali OH H OH Select to Edit Select to Draw 1. BH3-THF 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O =U= 2. H2O2, NaOH 2. NaBH4, NaOH + Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forwardWhat is the MOHR titration & AOAC method? What is it and how does it work? How can it be used to quantify salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction. Cl₂ hv ? Draw only the major product or products in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If there will be no products because there will be no significant reaction, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Note for advanced students: you can ignore any products of repeated addition. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 10 m 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility DII A F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 EO F11arrow_forwardGiven a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





