
A steam power plant operates on an ideal reheat–regenerative Rankine cycle with one reheater and two open feedwater heaters. Steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 1500 psia and 1100°F and leaves the low- pressure turbine at 1 psia. Steam is extracted from the turbine at 250 and 40 psia, and it is reheated to 1000°F at a pressure of 140 psia. Water leaves both feedwater heaters as a saturated liquid. Heat is transferred to the steam in the boiler at a rate of 4 × 105 Btu/s. Show the cycle on a T-s diagram with respect to saturation lines, and determine (a) the mass flow rate of steam through the boiler, (b) the net power output of the plant, and (c) the thermal efficiency of the cycle.
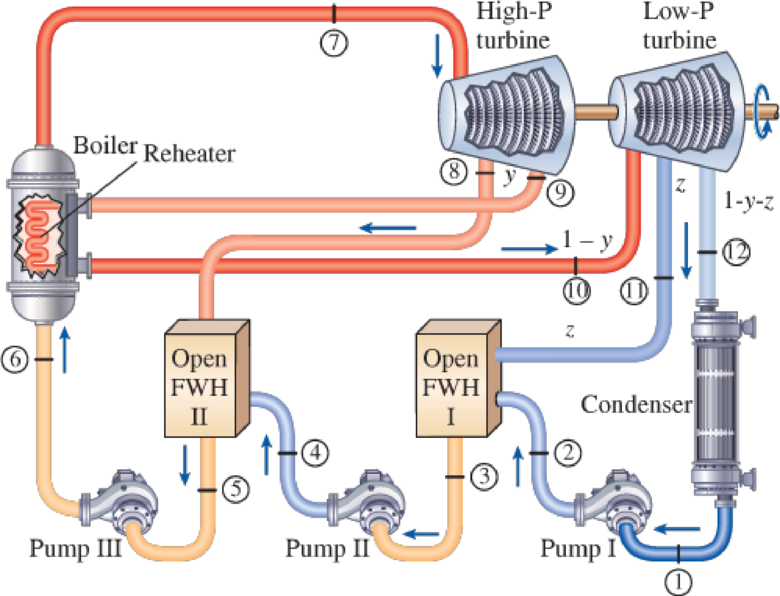
FIGURE P10–62E
(a)
The mass flow rate of steam flowing through the boiler.
Answer to Problem 62P
The mass flow rate of steam flowing through the boiler is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the schematic layout of the given power plant that operates on an ideal reheat-regenerative Rankine cycle as shown in Figure 1.
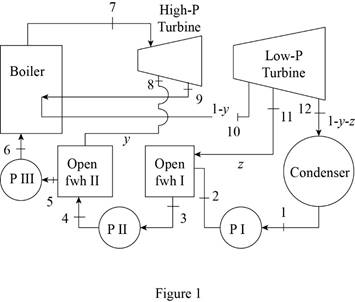
Draw the
Figure 2.
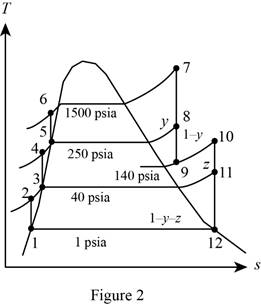
Here, water (steam) is the working fluid of the ideal regenerative Rankine cycle. The cycle involves three pumps.
Write the formula for work done by the pump during process 1-2.
Here, the specific volume is
Write the formula for enthalpy
Write the formula for work done by the pump during process 3-4.
Here, the specific volume is
Write the formula for enthalpy
Write the formula for work done by the pump during process 5-6.
Here, the specific volume is
Write the formula for enthalpy
Before reheating.
At state 9:
The steam expanded to the pressure of
After reheating.
At state 10:
The steam is reheated to the temperature of
At state 12:
The steam enters the condenser at the pressure of
The quality of water at state 12 is expressed as follows.
The enthalpy at state 12 is expressed as follows.
Here, the enthalpy is
Write the formula for heat in
Here, the mass fraction steam extracted from the turbine to the feed water entering the boiler via feed water heater-II
Write the general equation of energy balance equation.
Here, the rate of net energy inlet is
At steady state the rate of change of net energy of the system
Refer Equation (XI).
Write the energy balance equation for open feed water heater-II.
Rewrite the Equation (XII) in terms of mass fraction
Refer Equation (XI).
Write the energy balance equation for open feed water heater-I.
Rewrite the Equation (XIV) in terms of mass fraction
Write the formula for mass flow rate.
Here, the rate of heat input is
At state 1:
The water exits the condenser as a saturated liquid at the pressure of
Refer Table A-5E, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 3: (Pump II inlet)
The water exits the open feed water heater-I as a saturated liquid at the pressure of
Refer Table A-5E, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 5: (Pump III inlet)
The water exits the open feed water heater-II as a saturated liquid at the pressure of
Refer Table A-5E, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 7: (H.P. Turbine inlet)
The steam enters the turbine as superheated vapor.
Refer Table A-6E, “Superheated water”.
The enthalpy
Refer Figure 2.
At state 8:
The steam is extracted at the pressure of
Refer Table A-6E, “Superheated water”.
The enthalpy
At state 9:
The steam is expanded at the pressure of
Refer Table A-6E, “Superheated water”.
The enthalpy
At state 10:
The steam is reheated to the temperature of
Refer Table A-6E, “Superheated water”.
The enthalpy
Refer Figure 2.
At state 11:
The steam is expanded at the pressure of
Refer Table A-6E, “Superheated water”.
The enthalpy
At state 12: (Condenser inlet)
The steam enters the condenser at the pressure of
Refer Table A-5E, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following properties corresponding to the pressure of
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (III).
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (V).
Substitute
From Figure 2.
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (VIII).
Consider the open feed water heater-II alone.
Substitute
Equation (XIII).
Consider the open feed water heater-I alone.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the mass flow rate of steam flowing through the boiler is
(b)
The net power output of the plant.
Answer to Problem 62P
The net power output of the plant is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula for net power output of the cycle per unit mass.
Write the formula for net power output of the cycle.
Here, the mass flow rate is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the net power output of the plant is
(c)
The thermal efficiency of the cycle.
Answer to Problem 62P
The thermal efficiency of the cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula for thermal efficiency of the cycle
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of the cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERING APPR
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Prefferably handwritten solution pleasearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





