
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of 1-Hexanol with chromic acid has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohols: Oxidation of primary alcohol gives an
Chromic acid Oxidation of an Alcohol:
Step 1: Reaction of alcohol and chromic acid gives an alkyl chromate. No change in oxidation state of both Carbon and Chromium.
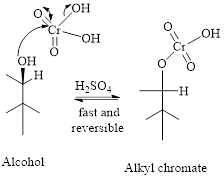
Step 2: Take a proton away and simultaneously break bonds to give stable molecules or ions. Reaction of the alkyl chromate with a base (here water molecule) results in cleavage of a
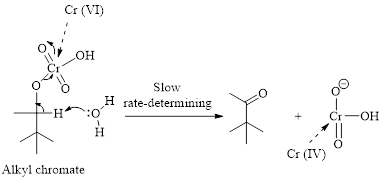
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of 2-Hexanol with chromic acid has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohols: Oxidation of primary alcohol gives an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid, depending on experimental conditions.
Chromic acid Oxidation of an Alcohol:
Step 1: Reaction of alcohol and chromic acid gives an alkyl chromate. No change in oxidation state of both Carbon and Chromium.

Step 2: Take a proton away and simultaneously break bonds to give stable molecules or ions. Reaction of the alkyl chromate with a base (here water molecule) results in cleavage of a

(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of Cyclohexanol with chromic acid has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohols: Oxidation of primary alcohol gives an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid, depending on experimental conditions.
Chromic acid Oxidation of an Alcohol:
Step 1: Reaction of alcohol and chromic acid gives an alkyl chromate. No change in oxidation state of both Carbon and Chromium.

Step 2: Take a proton away and simultaneously break bonds to give stable molecules or ions. Reaction of the alkyl chromate with a base (here water molecule) results in cleavage of a

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- Curved arrows were used to generate the significant resonance structure and labeled the most significant contribute. What are the errors in these resonance mechanisms. Draw out the correct resonance mechanisms with an brief explanation.arrow_forwardWhat are the: нсе * Moles of Hice while given: a) 10.0 ml 2.7M ? 6) 10.ome 12M ?arrow_forwardYou are asked to use curved arrows to generate the significant resonance structures for the following series of compounds and to label the most significant contributor. Identify the errors that would occur if you do not expand the Lewis structures or double-check the mechanisms. Also provide the correct answers.arrow_forward
- how to get limiting reactant and % yield based off this data Compound Mass 6) Volume(mL Ben zaphone-5008 ne Acetic Acid 1. Sam L 2-propanot 8.00 Benzopin- a col 030445 Benzopin a Colone 0.06743 Results Compound Melting Point (°c) Benzopin acol 172°c - 175.8 °c Benzoping to lone 1797-180.9arrow_forwardAssign ALL signals for the proton and carbon NMR spectra on the following pages.arrow_forward7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forward
- Assign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

