
For a mixture of n-butane (1) + n-pentane (2) at 25°C, what would be the predicted bubble-point pressure using Raoult’s Law if your mixture was 20% n-butane by mole? Would you expect Raoult’s Law to be a good model for this system? Why or why not?
Interpretation:
To obtain the bubble-point pressure using Raoult’s Law and to predict if the Raoult’s law be expected to be a good model for this system.
Concept Introduction:
The Antoine equation for the 1st component
Here, Antoine constants or coefficients are A, B, and C, vapor pressure is
The Antoine equation for the 2nd component
Here, vapor pressure is
The expression of system pressure using Raoult’s Law is,
Here, liquid phase mole fraction of components 1 and 2 is
The expression to obtain the vapor phase mole fraction
Here, vapor phase mole fraction of component 1 is
The expression to obtain the liquid phase mole fraction
The expression to obtain the liquid phase mole fraction
Here, liquid phase mole fraction of component 1 is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Temperature is
Write the Antoine equation for the 1st component
Refer Appendix E, “Antoine Coefficients”; obtain the constants A, B, and C for
Substitute
Write the Antoine equation for the 2nd component
Refer Appendix E, “Antoine Coefficients”; obtain the constants A, B, and C for
Substitute
The mixture of n-butane (1) + n-pentane is at the temperature of 25°C. Hence, consider the system pressure is the pressure of corresponding to the temperature of 25°C of steam.
Refer Appendix A-2, “Saturated steam-temperature increments”; obtain the pressure corresponding to temperature of
Here, pressure at temperature of
Write the expression to obtain the vapor phase mole fraction
It is given that the mixture is composed of 20% of n-butane by mole. It not clear that the given mole fraction is corresponded to liquid phase or vapour phase. Hence, consider that the vapour mole fraction of n-butane is,
Substitute 0.20 for
Write the expression to obtain the liquid phase mole fraction
Substitute
Write the expression to obtain the liquid phase mole fraction
Substitute
Write the expression of system pressure using Raoult’s Law.
Substitute
Similarly using excel spread sheet, calculate the values of
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 70.7 |
| 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.00131 | 0.99869 | 70.9244 |
| 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.00262 | 0.99738 | 71.1488 |
| 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.00393 | 0.99607 | 71.3732 |
| 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.00524 | 0.99476 | 71.5976 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.00655 | 0.99345 | 71.8219 |
| 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.00786 | 0.99214 | 72.0463 |
| 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.00917 | 0.99083 | 72.2707 |
| 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.01048 | 0.98952 | 72.4951 |
| 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.01179 | 0.98821 | 72.7195 |
| 1 | 0 | 0.0131 | 0.9869 | 72.9439 |
Table 1
The plot of P versus
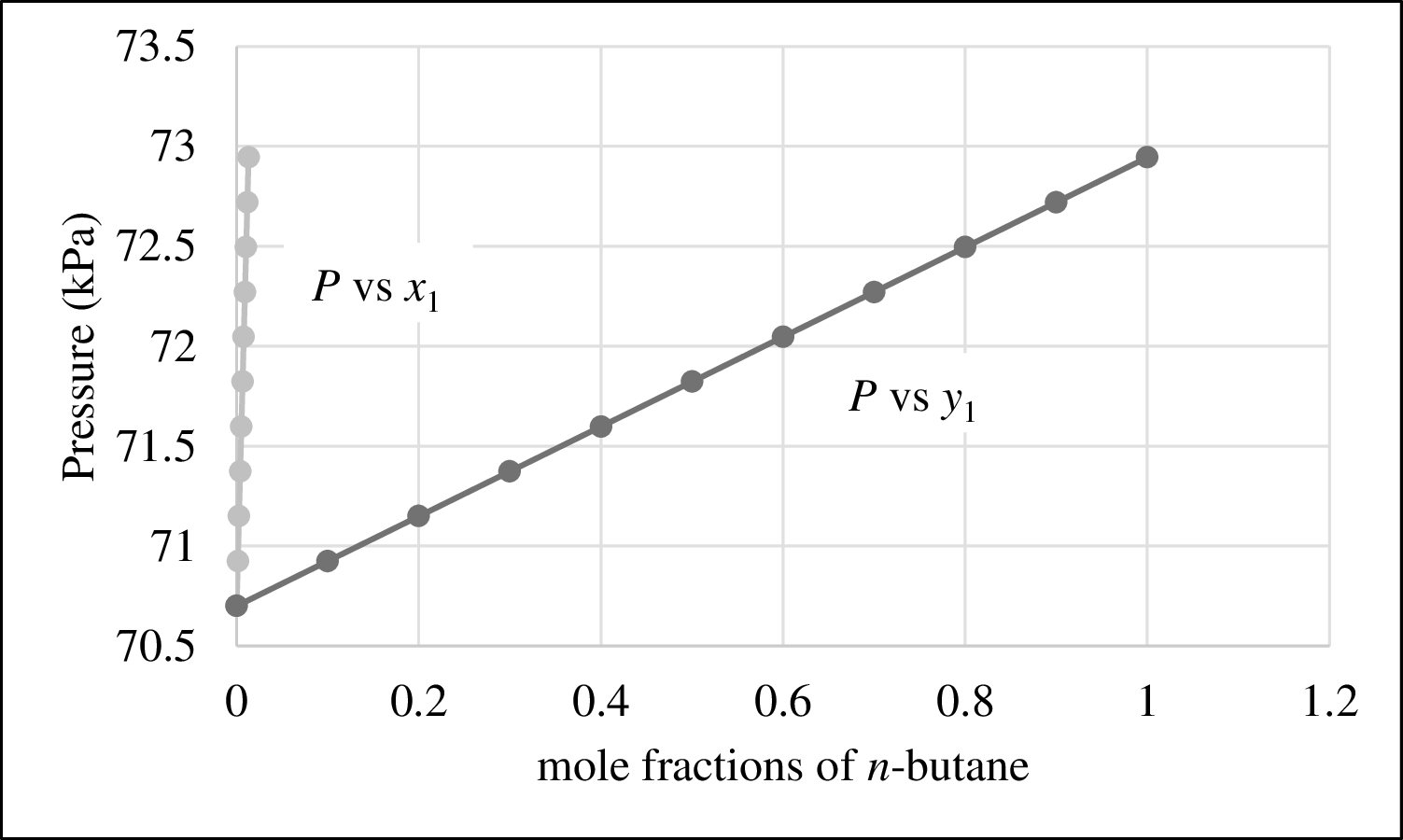
Figure 1
From Figure 1,
The bubble point curve and dew point curve are not meet anywhere. Hence Raoult’s Law is not a good model for this system and the bubble point pressure cannot be predicted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (MindTap Course List)
- A passive solar house was determined to lose heat to the outdoors at an average rate of 50,000 kJ/h during a typical 10-hour winter night. The house is to be maintained at 22°C at all times. Passive heating is accomplished by 50 glass containers each containing 20 L of water that is heated to 80°C during the day by absorbing solar energy. A 15-kW back-up electric resistance heater turns on whenever necessary to keep the house at 22°C. (a) How many hours does the electric heating system run during a typical winter night? (b) How many hours would the electric heater run during a typical winter night if the house did not have passive solar heating? For the density and specific heat of water at room temperature, use p = 1 kg/L and cp = 4.18 kJ/kg.°Carrow_forwardA well-insulated rigid tank contains 3 kg of a saturated liquid-vapor mixture of water at 200 kPa. Initially, three-quarters of the mass is in the liquid phase. An electric resistance heater placed in the tank is now turned on and kept on until all the liquid in the tank is vaporized. Determine the entropy change of the water during this process.arrow_forwardHeat in the amount of 100 kJ is transferred directly from a hot reservoir (heat source) at 1200 K to a cold reservoir (heat sink) at 600 K. Calculate the entropy change of the two reservoirs and determine if the second law of thermodynamics is satisfied.arrow_forward
- The following chemical reaction takes place at 500K and 1 atm and the products leaves at 1000K aCH4 + b(O2 + 3.76N2)=7.7CO2 + 0.5CO + 2CH4+2.95O2 + 86.85N2 + cH2O use the specific heat capacity given in Table A-21 (Moran and Shapiro, page 755) and the heat of formation given in Tabble A-25 (Moran and Shapiro, page 763) determine: 1. The stoichiometric coefficients (a, b, and c) 2. The air-fuel ratio on a molar basis 3. The air-fuel ratio on a mass basis 4. The stoichiometric air fuel ratio 5. The excess air (%) 6. The lower heating value 7. The rate of heat transfer from the combustion chamber.arrow_forward3. Nitric oxide is produced in the body by several different enzymes and acts as a signal that controls blood pressure, long-term memory, and other critical functions. The major route for removing NO from biological fluids is via reaction with O2 to give NO₂ 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) The following table lists kinetics data for the reaction of NO with O2 at 25°C: Experiment 1 [NO] (M) 0.0235 2 0.0235 3 0.0470 4 0.0470 (a) Determine the rate law for the reaction (b) calculate the rate constant. [02]0 (M) Initial Rate (M/s) 0.0125 7.98 × 10-3 0.0250 15.9 × 10-3 0.0125 32.0 × 10-3 0.0250 63.5 x 10-3 5:32arrow_forwardA closed system of 122 moles of an ideal gas with constant-pressure heat capacity of cp = 2.5R expands isobarically from 52°C and 4.9 bar to 137°C, with a thermodynamic efficiency of 0.74. How much total work is involved in this process? Please report your answer to the nearest whole kJ and don't forget the sign: "-" if the work is negative, no sign if the work is positive.arrow_forward
- Liquid toluene at 20°C is reversibly and isothermally compressed from 2.94 bar to 7.7 bar. What is the specific work, in J/kg, required to accomplish this? Some properties of liquid toluene at 20°C: β = 1.05 x 10-3 ºC-1 , κ = 8.96 x 10-5 bar-1 , V = 1154 cm3 kg-1. Please report your answer to 3 SF. Be very, very careful of units!arrow_forward132 kJ of work is transferred from a system to its surroundings in a reversible process to get it from state A to state B. If a similar but irreversible process is performed from state A to state B with a thermodynamic efficiency of 0.73, how much work will be transferred, in kJ? Be sure to include the correct sign on your answer: if it is positive, do NOT include a "+", but if it is negative you MUST include a "−" sign.arrow_forward2- What will be the power required to crush 150 tonnes per hour of limestone if 80 percent of the feed passes 50 mm screen and 80 percent of the product a 3.125 mm screen? Work index of limestone 12.74.arrow_forward
- 3- A certain crusher accepts a feed material having a volume-surface mean diameter of 19 mm and gives a product of volume-surface mean diameter of 5 mm. The power required to crush 15 tonnes per hour is 7.5 kW. What will be the power consumption if the capacity is reduced to 12 tonnes per hour?arrow_forwardCR = CAOK1 K2-K1 - Cs CAO CR - CA = [e-k₁t + e-k₂t] --(6) Cs = Cao CAO 1+ K₂e-kit K₁e-k2t + K1-K2 K₂-K1 By differentiating eq (6) and set to zero (dCR = 0), the time at which concentration of R occurs is thus: dT K2 1 In Ki K1 tmax K₂-K1 Klogmean (7) Equation 7. Prove that?arrow_forwardQuestion #6 a) Draw a simple block flow diagram of a petroleum refinery consisting of following sections. 1. Atmospheric and vacuum distillation 2. Hydrotreating of diesel steam 3. Hydrocracking of LVGO Show main product streams from each unit. (8)arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





