
i.
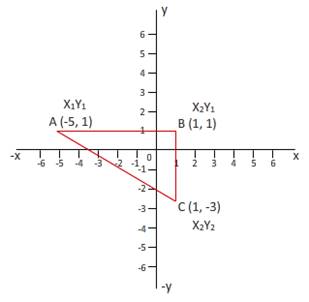
Plot the graph having points A(-5,1), B(1,1) and C(1,-3).
i.
Answer to Problem 33PPS
Following is the graph having points A(-5,1), B(1,1) and C(1,-3).
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Co-ordinates of graph: A(-5,1), B(1,1) and C(1,-3).
Calculations:
We have coordinates of graph.
A(-5,1), B(1,1) and C(1,-3).
After connecting points, we get right angle
Conclusion:
Therefore, we are able to plot given points on graph.
ii.
Calculate length of AC.
ii.
Answer to Problem 33PPS
Length of AC is 7.211unit
Explanation of Solution
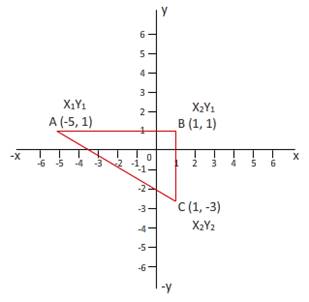
Given:
Calculation:
Here, we have to find value of hypotenuse that is length of AC.
From given figure, we have endpoints (x1,y1) and (x2y2). Thus, we can find distance between two points
Conclusion:
Therefore, we are able to calculate length of AC using distance formula.
iii.
Calculate sides of
iii.
Answer to Problem 33PPS
Length of AB =3.6055 unit
Length of BC =7.057 unit
Explanation of Solution
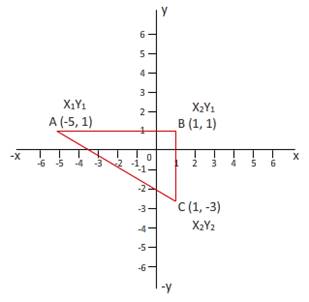
Given:
Length of AC =7.211 unit
Calculation:
Here, we have to find value of each side of triangle ABC.
Given triangle is right angle triangle. Lengths of triangle are different. Thus, we can say that triangle may be
Therefore, applying trigonometry, we get length of AB and BC.
Now applying Pythagoras theorem to calculate length of BC,
Conclusion:
Therefore, we are able to calculate length of AB and BC using trigonometry and Pythagoras theorem.
iv.
Calculate area and perimeter of
iv.
Answer to Problem 33PPS
Area of
Perimeter of
Explanation of Solution
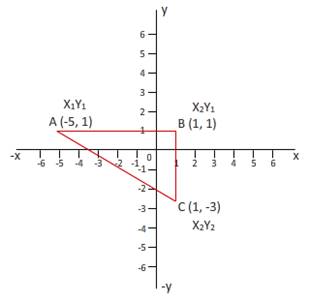
Given: From sub part (iii) Length of AC =7.211 unit
Length of AB =3.6055 unit
Length of BC =7.057 unit
Calculation:
Area of
Perimeter of
Conclusion:
Therefore, we are able to calculate area and perimeter of
Chapter 10 Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Write an equation for the function shown. You may assume all intercepts and asymptotes are on integers. The blue dashed lines are the asymptotes. 10 9- 8- 7 6 5 4- 3- 2 4 5 15-14-13-12-11-10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 1 1 2 3 -1 -2 -3 -4 1 -5 -6- -7 -8- -9 -10+ 60 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15arrow_forwardUse the graph of the polynomial function of degree 5 to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. -6 3 6+ 5 4 3 2 1 2 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 3 4 6 Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicityarrow_forwardUse the graph to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. 6 5 4 -6-5-4-3-2 3 21 2 1 2 4 5 ૪ 345 Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity པ་arrow_forward
- Use the graph to write the formula for a polynomial function of least degree. -5 + 4 3 ♡ 2 12 1 f(x) -1 -1 f(x) 2 3. + -3 12 -5+ + xarrow_forwardUse the graph to identify zeros and multiplicity. Order your zeros from least to greatest. 6 -6-5-4-3-2-1 -1 -2 3 -4 4 5 6 a Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicity Zero at with multiplicityarrow_forwardUse the graph to write the formula for a polynomial function of least degree. 5 4 3 -5 -x 1 f(x) -5 -4 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 f(x) =arrow_forward
- Write the equation for the graphed function. -8 ง -6-5 + 5 4 3 2 1 -3 -2 -1 -1 -2 4 5 6 6 -8- f(x) 7 8arrow_forwardWrite the equation for the graphed function. 8+ 7 -8 ง A -6-5 + 6 5 4 3 -2 -1 2 1 -1 3 2 3 + -2 -3 -4 -5 16 -7 -8+ f(x) = ST 0 7 8arrow_forwardThe following is the graph of the function f. 48- 44 40 36 32 28 24 20 16 12 8 4 -4 -3 -1 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 -40 -44 -48+ Estimate the intervals where f is increasing or decreasing. Increasing: Decreasing: Estimate the point at which the graph of ƒ has a local maximum or a local minimum. Local maximum: Local minimum:arrow_forward
- For the following exercise, find the domain and range of the function below using interval notation. 10+ 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 -1 -2 Domain: Range: -4 -5 -6 -7- 67% 9 -8 -9 -10-arrow_forward1. Given that h(t) = -5t + 3 t². A tangent line H to the function h(t) passes through the point (-7, B). a. Determine the value of ẞ. b. Derive an expression to represent the gradient of the tangent line H that is passing through the point (-7. B). c. Hence, derive the straight-line equation of the tangent line H 2. The function p(q) has factors of (q − 3) (2q + 5) (q) for the interval -3≤ q≤ 4. a. Derive an expression for the function p(q). b. Determine the stationary point(s) of the function p(q) c. Classify the stationary point(s) from part b. above. d. Identify the local maximum of the function p(q). e. Identify the global minimum for the function p(q). 3. Given that m(q) = -3e-24-169 +9 (-39-7)(-In (30-755 a. State all the possible rules that should be used to differentiate the function m(q). Next to the rule that has been stated, write the expression(s) of the function m(q) for which that rule will be applied. b. Determine the derivative of m(q)arrow_forwardSafari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





