
(a)
The level of significance, null and alternative hypothesis & determine whether we should use a left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed test.
(a)
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution: The level of significance is
Explanation of Solution
The level of significance is defined as the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, it is denoted by
Null hypothesis
Alternative hypothesis
Since
(b)
To find: The sampling distribution that should be used along with assumptions and compute the value of the sample test statistic.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution: The sampling distribution of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
| A | B | |||
| 21 | 24 | -3 | 0.5625 | |
| 25 | 23 | 2 | 18.0625 | |
| 20 | 25 | -5 | 7.5625 | |
| 14 | 18 | -4 | 3.0625 | |
| -4 | 6 | -10 | 60.0625 | |
| 19 | 4 | 15 | 297.5625 | |
| 15 | 21 | -6 | 14.0625 | |
| 30 | 37 | -7 | 22.5625 | |
| Sum | 140 | 158 | -18 | 423.5 |
| Average | 17.5 | 19.75 | -2.25 | 52.9375 |
The d distribution is mound shaped and symmetrical and we have a random sample of
Using
(c)
To find: The critical value of the test statistic and sketch the sampling distribution showing the critical region.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution: The critical value of the test statisticis
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The level of significance is
95% of the t-distribution curve lies between -
Using table 4 from Appendix we get
Critical region is
Graph:
To draw the required graphs using the Minitab, follow the below instructions:
Step 1: Go to the Minitab software.
Step 2: Go to Graph > Probability distribution plot > View probability.
Step 3: Select ‘t’ and d.f = 7.
Step 4: Click on the Shaded area > Probability.
Step 5: Select ‘Both tail’ and enter Probability as 0.05.
Step 6: Click on OK.
The obtained distribution graph is:
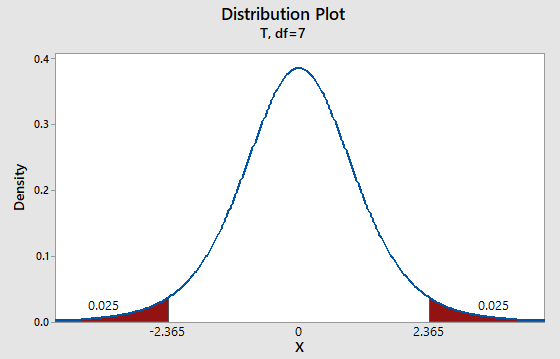
Interpretation:
If the value of the sample test statistics lies in the critical region then we have to reject the null hypothesis.
(d)
Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and whether the data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.05.
(d)
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution: The t-value (- 0.82) does not lie in the critical region. The data is not statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.05
Explanation of Solution
The critical regionis
The t-value (- 0.82)does not lie in the critical region. Therefore we don’t have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis
(e)
The interpretation for the conclusion.
(e)
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution: There is not enough evidence to conclude that the populations mean percentage increase in corporate revenue is different from the population mean percentage increase in CEO salary.
Explanation of Solution
The t-value (- 0.82) does not lie in the critical region. Therefore we don’t have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis
(f)
The comparison for our conclusion with the conclusion obtained from the P-value method.
(f)
Answer to Problem 19P
Solution: Both the conclusions are same.
Explanation of Solution
The conclusion from the P-value method is:
The P-value of 0.4392 is greater than the level of significance (
Since we are using the same significance level of 0.05, hence both the conclusions will be same.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Understanding Basic Statistics, Loose-leaf Version, 8th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Single-Term
- Please help me with the following question on statisticsFor question (e), the drop down options are: (From this data/The census/From this population of data), one can infer that the mean/average octane rating is (less than/equal to/greater than) __. (use one decimal in your answer).arrow_forwardHelp me on the following question on statisticsarrow_forward3. [15] The joint PDF of RVS X and Y is given by fx.x(x,y) = { x) = { c(x + { c(x+y³), 0, 0≤x≤ 1,0≤ y ≤1 otherwise where c is a constant. (a) Find the value of c. (b) Find P(0 ≤ X ≤,arrow_forwardNeed help pleasearrow_forward7. [10] Suppose that Xi, i = 1,..., 5, are independent normal random variables, where X1, X2 and X3 have the same distribution N(1, 2) and X4 and X5 have the same distribution N(-1, 1). Let (a) Find V(X5 - X3). 1 = √(x1 + x2) — — (Xx3 + x4 + X5). (b) Find the distribution of Y. (c) Find Cov(X2 - X1, Y). -arrow_forward1. [10] Suppose that X ~N(-2, 4). Let Y = 3X-1. (a) Find the distribution of Y. Show your work. (b) Find P(-8< Y < 15) by using the CDF, (2), of the standard normal distribu- tion. (c) Find the 0.05th right-tail percentage point (i.e., the 0.95th quantile) of the distri- bution of Y.arrow_forward6. [10] Let X, Y and Z be random variables. Suppose that E(X) = E(Y) = 1, E(Z) = 2, V(X) = 1, V(Y) = V(Z) = 4, Cov(X,Y) = -1, Cov(X, Z) = 0.5, and Cov(Y, Z) = -2. 2 (a) Find V(XY+2Z). (b) Find Cov(-x+2Y+Z, -Y-2Z).arrow_forward1. [10] Suppose that X ~N(-2, 4). Let Y = 3X-1. (a) Find the distribution of Y. Show your work. (b) Find P(-8< Y < 15) by using the CDF, (2), of the standard normal distribu- tion. (c) Find the 0.05th right-tail percentage point (i.e., the 0.95th quantile) of the distri- bution of Y.arrow_forward== 4. [10] Let X be a RV. Suppose that E[X(X-1)] = 3 and E(X) = 2. (a) Find E[(4-2X)²]. (b) Find V(-3x+1).arrow_forward2. [15] Let X and Y be two discrete RVs whose joint PMF is given by the following table: y Px,y(x, y) -1 1 3 0 0.1 0.04 0.02 I 2 0.08 0.2 0.06 4 0.06 0.14 0.30 (a) Find P(X ≥ 2, Y < 1). (b) Find P(X ≤Y - 1). (c) Find the marginal PMFs of X and Y. (d) Are X and Y independent? Explain (e) Find E(XY) and Cov(X, Y).arrow_forward32. Consider a normally distributed population with mean μ = 80 and standard deviation σ = 14. a. Construct the centerline and the upper and lower control limits for the chart if samples of size 5 are used. b. Repeat the analysis with samples of size 10. 2080 101 c. Discuss the effect of the sample size on the control limits.arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothesis test. The following results are for two independent samples taken from the two populations. Sample 1 Sample 2 n 1 = 80 n 2 = 70 x 1 = 104 x 2 = 106 σ 1 = 8.4 σ 2 = 7.6 What is the value of the test statistic? If required enter negative values as negative numbers (to 2 decimals). What is the p-value (to 4 decimals)? Use z-table. With = .05, what is your hypothesis testing conclusion?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


