
A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and F of the linkage shown. Neglecting the weight of the spring and linkage, determine the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical downward 120-N force is applied (a) at point E, (b) at points E and F.
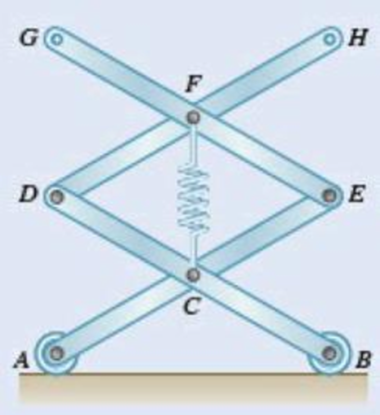
Fig. P10.5 and P10.6
(a)
Find the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical load of
Answer to Problem 10.6P
The force in the spring is
The vertical motion of point G is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The spring constant is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the spring assembly as in Figure 1.
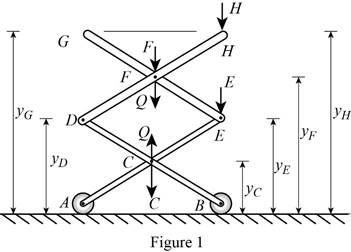
Write the relation of the deflections at point G, H, F, E, D with C as follows;
The deflection
Assume the spring force Q is in tension.
Find the force in the spring Q using the relation.
Here, the spring constant is k.
Substitute
Use the virtual work principle:
Here,
Substitute 0 for C,
The spring force Q is in compression. The assumption is incorrect.
Therefore, the force in the spring is
Substitute –120 N for Q in Equation (1).
Find the vertical motion
Substitute –4 mm for
Therefore, the vertical motion of point G is
(b)
Find the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical load of 120-N force is applied at point E and F.
Answer to Problem 10.6P
The force in the spring is
The vertical motion of point G is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The spring constant is
Calculation:
Use the virtual work principle:
Here,
Substitute 0 for C,
The spring force Q is in compression. The assumption is incorrect.
Therefore, the force in the spring is
Substitute –300 N for Q in Equation (1).
Find the vertical motion
Substitute –10 mm for
Therefore, the vertical motion of point G is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Please draw the front top and side view for the following objectarrow_forwardDraw the top viewarrow_forwardSuppose that a steel of eutectoid composition is cooled to 675°C (1250°F) from 760°C (1400°F) in less than 0.5 s and held at this temperature. (a) How long will it take for the austenite-topearlite reaction to go to 50% completion? To 100% completion? (b) Estimate the hardness of the alloy that has completely transformed to pearlite.arrow_forward
- Problem 2: Determine the components of the reaction at point B (Please use paper sheet + FBD ,don't use chatgpt) MECHANICAL ENGGarrow_forwardARL040_AE_Kn_2of3... Dor Question 4. A two-throw crankshaft has masses distributed as shown: RAH 90 rpm A TRAV B Re Rev M₁ = 15kg; M₂ = 12kg L = 950mm; 1, 350mm; 1₁ = 600mm; 0₁ = 90°; 02=0°; r₁ = 300mm; r250mm The crankshaft is to be balanced by attaching masses at radii of 300 mm and rotating in planes 150 mm outside the planes of number one and number two cranks. Determine the magnitude and angular position of the balance masses. Answer 4.arrow_forwardFEAarrow_forward
- Finite Element Analysisarrow_forwardan experimental research station is constructed on a concrete slab floor. The heat loss from the floor slab is significant, given the cold environment, and is measured to be 5 kW. The edges of the floor slab are insulated with a 60 mm thickness of cellular glass insulation. The width of this insulation at the floor slab is 0.9 m. To avoid excessive fuel consumption, the station air temperature is maintained at a slightly cool temperature of 18ºC. The station is constructed in a square shape, to keep the surface area to volume ratio low; the horizontal dimensions of the floor of the station are 20 m by 20 m. The number of occupants in the research station varies between 5 and 20, depending on the research workload.a) Determine the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station.b) If the floor dimensions of the station are changed to 15 m by 25 m, would the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station from part (a) change? If so,…arrow_forwardFinite element analysisarrow_forward
- a station is constructed on a concrete slab floor. The heat loss from the floor slab is significant, given the cold environment, and is measured to be 5 kW. The edges of the floor slab are insulated with a 60 mm thickness of cellular glass insulation. The width of this insulation at the floor slab is 0.9 m. To avoid excessive fuel consumption, the station air temperature is maintained at a slightly cool temperature of 18ºC. The station is constructed in a square shape, to keep the surface area to volume ratio low; the horizontal dimensions of the floor of the station are 20 m by 20 m. The number of occupants in the research station varies between 5 and 20, depending on the research workload.a) Determine the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station.b) If the floor dimensions of the station are changed to 15 m by 25 m, would the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station from part (a) change? If so, what would it be?…arrow_forwardFinite Element Analysisarrow_forwardFinite Element Analysisarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





