
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977244
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.1, Problem 10.46P
Solve Prob. 10.45, assuming that the workers are lowered to a point near the ground so that θ = −20°.
10.45 The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. The workers and the platform together weigh 500 lb, and their combined center of gravity is located directly above C. For the position when θ = 20°, determine the force exerted on pin B by the single hydraulic cylinder BD.
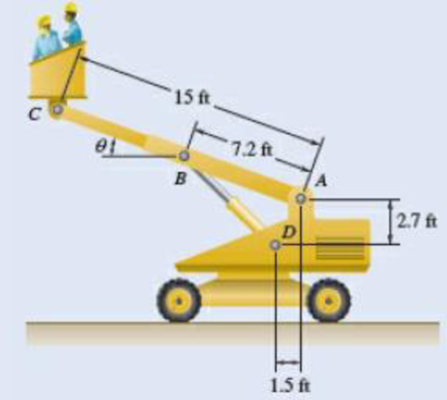
Fig. P10.45
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. The workers and the platform together have a mass of 200 kg and have a combined center of gravity located directly above C. For the position when θ=20°, determine (a) the force exerted at B by the single hydraulic cylinder BD, (b) the force exerted on the supporting carriage at A.
Referring to Prob. 10.45 and using the value found for the force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder BD , determine the change in the length of BD required to raise the platform attached at C by 2.5 in.Reference to Problem 10.45:The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. The workers and the platform together weigh 500 lb, and their combined center of gravity is located directly above C. For the position when 0= 20°, determine the force exerted on pin B by the single hydraulic cylinder BD.
The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. The workers and the platform together have a mass of 200 kg and have a combined center of gravity located directly above C . For the position when 0= 20°, determine (a) the force exerted at B by the single hydraulic cylinder BD, (b) the force exerted on the supporting carriage at A.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Ch. 10.1 - Determine the vertical force P that must be...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the horizontal force P that must be...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10.1 - 10.3 and 10.4 Determine the couple M that must be...Ch. 10.1 - A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and...Ch. 10.1 - A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and...Ch. 10.1 - The two-bar linkage shown is supported by a pin...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the weight W that balances the 10-lb...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.9PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.10P
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.11PCh. 10.1 - Knowing that the line of action of the force Q...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.12 assuming that the force P...Ch. 10.1 - The mechanism shown is acted upon by the force P....Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.15PCh. 10.1 - 10.15 and 10.16 Derive an expression for the...Ch. 10.1 - A uniform rod AB with length l and weight W is...Ch. 10.1 - The pin at C is attached to member BCD and can...Ch. 10.1 - For the linkage shown, determine the couple M...Ch. 10.1 - For the linkage shown, determine the force...Ch. 10.1 - A 4-kN force P is applied as shown to the piston...Ch. 10.1 - A couple M with a magnitude of 100 Nm isapplied as...Ch. 10.1 - Rod AB is attached to a block at A that can...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.23, assuming that the 800-N force...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10.1 - Determine the value of corresponding to...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.27PCh. 10.1 - Determine the value of corresponding to...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.29PCh. 10.1 - Two rods AC and CE are connected by a pin at Cand...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.30 assuming that force P is movedto...Ch. 10.1 - Two bars AD and DG are connected by a pin at Dand...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.32 assuming that the 900-N...Ch. 10.1 - Two 5-kg bars AB and BC are connected by a pin atB...Ch. 10.1 - A vertical force P with a magnitude of 150 N...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.36PCh. 10.1 - 10.37 and 10.38 Knowing that the constant of...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.38PCh. 10.1 - The lever AB is attached to the horizontal shaft...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.39, assuming that P = 350 N, l =250...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.41PCh. 10.1 - The position of boom ABC is controlled by...Ch. 10.1 - The position of member ABC is controlled by the...Ch. 10.1 - The position of member ABC is controlled by...Ch. 10.1 - The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.45, assuming that the workers...Ch. 10.1 - Denoting the coefficient of static friction...Ch. 10.1 - Knowing that the coefficient of static...Ch. 10.1 - A block with weight W is pulled up a plane forming...Ch. 10.1 - Derive an expression for the mechanical...Ch. 10.1 - Denoting the coefficient of static friction...Ch. 10.1 - Knowing that the coefficient of static...Ch. 10.1 - Using the method of virtual work,...Ch. 10.1 - Using the method of virtual work, determine...Ch. 10.1 - Referring to Prob. 10.43 and using the value...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.56PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.57PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.29....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.30....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.31....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.32....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.34....Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.64PCh. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.37....Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.66PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10.2 - Show that equilibrium is neutral in Prob. 10.7....Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods, each with a mass m, areattached...Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods, AB and CD, are attached to gears...Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods AB and CD, of the same length...Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods, each of mass m and length l, are...Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob....Ch. 10.2 - In Prob. 10.40, determine whether each of...Ch. 10.2 - A load W of magnitude 144 lb is applied to...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.76PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.77PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.78PCh. 10.2 - A slender rod AB with a weight W is attached to...Ch. 10.2 - A slender rod AB with a weight W is attached totwo...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.81PCh. 10.2 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to two...Ch. 10.2 - A slender rod AB is attached to two collars A and...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.2 - 10.85 and 10.86 Cart B, which weighs 75 kN, rolls...Ch. 10.2 - 10.85 and 10.86 Cart B, which weighs 75 kN, rolls...Ch. 10.2 - 10.87 and 10.88 Collar A can slide freely on the...Ch. 10.2 - 10.87 and 10.88 Collar A can slide freely on the...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.89PCh. 10.2 - A vertical bar AD is attached to two springs...Ch. 10.2 - Rod AB is attached to a hinge at A and to two...Ch. 10.2 - Rod AB is attached to a hinge at A and to...Ch. 10.2 - Two bars are attached to a single spring of...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.94PCh. 10.2 - The horizontal bar BEH is connected to three...Ch. 10.2 - The horizontal bar BEH is connected to three...Ch. 10.2 - Bars AB and BC, each with a length l and of...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.98PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.99PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.100PCh. 10 - Determine the vertical force P that must be...Ch. 10 - Determine the couple M that must be applied...Ch. 10 - Determine the force P required to maintain...Ch. 10 - Derive an expression for the magnitude of the...Ch. 10 - Derive an expression for the magnitude of the...Ch. 10 - A vertical load W is applied to the linkage at B....Ch. 10 - A force P with a magnitude of 240 N is applied to...Ch. 10 - Two identical rods ABC and DBE are connected bya...Ch. 10 - Solve Prob. 10.108 assuming that the 24-lb load...Ch. 10 - Two uniform rods each with a mass m and length...Ch. 10 - A homogeneous hemisphere with a radius r isplaced...Ch. 10 - A homogeneous hemisphere with a radius r isplaced...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1arrow_forwardQ.3) A luggage transport truck is used to raise and lower luggage from an aircraft. A piece of luggage weighing 450 lbs. is supported in the position shown with a center of gravity at point G. The raising and lowering mechanism are connected to the truck bed by a pin support at F and a roller support at H, and to the luggage platform by a pin support at C and a roller support at D. The hydraulic strut AB is pinned at either end and used to raise and lower the mechanism. Assume the weight of all members within the mechanism are negligible, that point C is vertically aligned with F, point D is vertically aligned with H, and that the strut AB is vertically 20maint oriented. (a) Determine the support reactions at F and H in the stationary position shown. (b) Determine the force in the hydraulic strut AB and state whether it is in tension or compression. 80000000 C 2.5 ft 0.5 ft 3 ft A B F G E H D 4 ft 4 ftarrow_forward(a) Show that the beam of Prob. 8.41 cannot be moved if the top surface of the dolly is slightly lower than the platform. (b) Show that the beam can be moved if two 175-lb workers stand on the beam at B , and determine how far to the left the beam can be moved.(Reference to Problem 8.41):A 10-ft beam, weighing 1200 lb, is to be moved to the left onto the platform as shown. A horizontal force P is applied to the dolly, which is mounted on frictionless wheels. The coefficients of friction between all surfaces are μs= 0.30 and μk = 0.25, and initially, x= 2 ft. Knowing that the top surface of the dolly is slightly higher than the platform, determine the force P required to start moving the beam. (Hint: The beam is supported at A and D.)arrow_forward
- 3. The window washers A and B support themselves and the horizontal, uniform platform CD (i.e. the weight of the platform acts at its centre) by pulling down on the two ropes. The pulling force on the rope by the washer B is 567 N. The mass of washer A is 77 kg. Determine the tension in the rope connected at C, the mass of the washer B and the force that each man exerts on the platform. 13.5 kg 3 m 77 kg A bont '0.6 m' B 1.2 m- Darrow_forwardThe L-shaped member ACB is supported by a pin and bracket at C and by an inextensible cord attached at A and B and passing over a frictionless pulley at D. The tension may be assumed to be the same in portions AD and BD of the cord. If the magnitudes of the forces applied at A and B are, respectively, P = 25 lb and Q = 0, determine (a) the tension in the cord, (b) the reaction at Carrow_forwardQuestion 4 The space (noncoplanar) structure presented is supported by ball-and-socket joints at O and D, and by a slider bearing at C. The two rigid members, OABC and AD, connected by a ball-and-socket joint at A, each have a mass of 75 kg/m. Determine the magnitude of the reaction force components at O and C. 0.9 m D 0.9 m X B A Z 0.9 m 0.9 m с 0.6 m y Answers: Ox = 1.820 kN Oy = 2.72 kN O₂ = -0.77 kN Cx = -1.820 kN Cz = 0.33 kNarrow_forward
- 9. A man is trying to pull the sled by applying a force of 500 N, as shown. The weight of the stone and the sled is 800 N while the sled is about to slide (i.e., it is still in equilibrium). Determine the magnitude of the reaction force R. a. b. W = 800 N 650 N 700 N 0 R P = 500 N 30⁰ Cc. d. 750 N 800 Narrow_forwardDetermine all forces acting on member BCD of the linkage shown in Fig. 40 lb 30° D 1.5 ft 2.0 ft 60° B 2.0 ftarrow_forwardThe telescoping arm ABC of Prob. 6.93 can be lowered until end C is close to the ground, so that workers can easily board the platform.For the position when θ = -220°, determine (a) the force exerted at B by the single hydraulic cylinder BD, (b) the force exerted on the supporting carriage at A.arrow_forward
- Question 4: (a) (i) State the Principle of Moment (Varignon's Theorem). (ii) Prove that the moment of a couple is the same about any axis perpendicular to the plane of action of the couple. (b) A uniform rod Whose centre of gravity G divides it into the ratio AG : GB = a :b is in limiting equilibrium at an angle a with the horizontal with its upper end B resting against a smooth peg and its lower end A attached to a light cord, which is fastened to a point C on the same level as B. Prove that the angle B at which the cord is inclined to the horizontal is given by the equation a+b b tanß = tana cot a a a Question 5: (a) From Lesotho Bank tower an object was observed on the ground at a depression o below the horizon. A gun was fired at an elevation a, but the shot missing the object, stuck the ground at a point whose depression was y. Prove that the correct elevation 0 of the gun is given by sin(20 +0) + sin(o) sin(2a+0) + sin(o) sin y (1+ cos(20)) sin o (1+cos(2y))arrow_forwardPractice Problem 4.4.14: Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder EF that would maintain the parallelogram mechanism in the position 0.6 ft shown. | 200 lb OB 3.75 ft 30 0.75 ft 0.75 ft 2 ftarrow_forwardA hydraulic-lift table is used to raise a 1000-kg crate. The table consists of a platform and two identical linkages on which hydraulic cylindersexert equal forces. (Only one linkage and one cylinder are shown.) Members EDB and CG are each of length 2a, and member AD is pinned to the midpoint of EDB. If the crate is placed on the table so that half of its weight is supported by the system shown, determine the force exerted by each cylinderin raising the crate for θ = 60°, a = 0.70 m, and L=3.20 m.Show that the result is independent of the distance d.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License