
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977268
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.1, Problem 10.24P
Solve Prob. 10.23, assuming that the 800-N force is replaced by a 24-N·m clockwise couple applied at D.
10.23 Rod AB is attached to a block at A that can slide freely in the vertical slot shown. Neglecting the effect of friction and the weights of the rods, determine the value of θ corresponding to equilibrium.
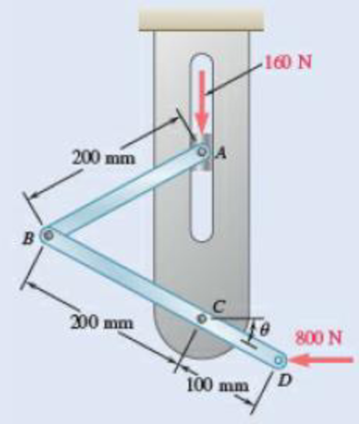
Fig. P10.23
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve Prob. 10.32 assuming that the 900-N vertical force is applied at C instead of E.Reference to Problem 10.32:Two bars AD and DG are connected by a pin at D and by a spring AG . Knowing that the spring is 300 mm long when unstretched and that the constant of the spring is 5 kN/m, determine the value of x corresponding to equilibrium when a 900-N load is applied at E as shown.
Collars A and B are connected by a 25-in.-long wire and can slide freely on frictionless rods. Determine the distances x and z for which the equilibrium of the system is maintained when P=120 lb and Q=60 lb.
9. A man is trying to pull the sled by applying a force of 500 N, as shown. The weight of the stone and the sled
is 800 N while the sled is about to slide (i.e., it is still in equilibrium).
Determine the magnitude of the reaction force R.
a.
b.
W = 800 N
650 N
700 N
0
R
P = 500 N
30⁰
Cc.
d.
750 N
800 N
Chapter 10 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Ch. 10.1 - Determine the vertical force P that must be...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the horizontal force P that must be...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10.1 - 10.3 and 10.4 Determine the couple M that must be...Ch. 10.1 - A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and...Ch. 10.1 - A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and...Ch. 10.1 - The two-bar linkage shown is supported by a pin...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the weight W that balances the 10-lb...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.9PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.10P
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.11PCh. 10.1 - Knowing that the line of action of the force Q...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.12 assuming that the force P...Ch. 10.1 - The mechanism shown is acted upon by the force P....Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.15PCh. 10.1 - 10.15 and 10.16 Derive an expression for the...Ch. 10.1 - A uniform rod AB with length l and weight W is...Ch. 10.1 - The pin at C is attached to member BCD and can...Ch. 10.1 - For the linkage shown, determine the couple M...Ch. 10.1 - For the linkage shown, determine the force...Ch. 10.1 - A 4-kN force P is applied as shown to the piston...Ch. 10.1 - A couple M with a magnitude of 100 Nm isapplied as...Ch. 10.1 - Rod AB is attached to a block at A that can...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.23, assuming that the 800-N force...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10.1 - Determine the value of corresponding to...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.27PCh. 10.1 - Determine the value of corresponding to...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.29PCh. 10.1 - Two rods AC and CE are connected by a pin at Cand...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.30 assuming that force P is movedto...Ch. 10.1 - Two bars AD and DG are connected by a pin at Dand...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.32 assuming that the 900-N...Ch. 10.1 - Two 5-kg bars AB and BC are connected by a pin atB...Ch. 10.1 - A vertical force P with a magnitude of 150 N...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.36PCh. 10.1 - 10.37 and 10.38 Knowing that the constant of...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.38PCh. 10.1 - The lever AB is attached to the horizontal shaft...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.39, assuming that P = 350 N, l =250...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.41PCh. 10.1 - The position of boom ABC is controlled by...Ch. 10.1 - The position of member ABC is controlled by the...Ch. 10.1 - The position of member ABC is controlled by...Ch. 10.1 - The telescoping arm ABC is used to provide...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.45, assuming that the workers...Ch. 10.1 - Denoting the coefficient of static friction...Ch. 10.1 - Knowing that the coefficient of static...Ch. 10.1 - A block with weight W is pulled up a plane forming...Ch. 10.1 - Derive an expression for the mechanical...Ch. 10.1 - Denoting the coefficient of static friction...Ch. 10.1 - Knowing that the coefficient of static...Ch. 10.1 - Using the method of virtual work,...Ch. 10.1 - Using the method of virtual work, determine...Ch. 10.1 - Referring to Prob. 10.43 and using the value...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.56PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.57PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.29....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.30....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.31....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.32....Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.34....Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.64PCh. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.37....Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.66PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10.2 - Show that equilibrium is neutral in Prob. 10.7....Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods, each with a mass m, areattached...Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods, AB and CD, are attached to gears...Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods AB and CD, of the same length...Ch. 10.2 - Two uniform rods, each of mass m and length l, are...Ch. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob....Ch. 10.2 - In Prob. 10.40, determine whether each of...Ch. 10.2 - A load W of magnitude 144 lb is applied to...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.76PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.77PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.78PCh. 10.2 - A slender rod AB with a weight W is attached to...Ch. 10.2 - A slender rod AB with a weight W is attached totwo...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.81PCh. 10.2 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to two...Ch. 10.2 - A slender rod AB is attached to two collars A and...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.2 - 10.85 and 10.86 Cart B, which weighs 75 kN, rolls...Ch. 10.2 - 10.85 and 10.86 Cart B, which weighs 75 kN, rolls...Ch. 10.2 - 10.87 and 10.88 Collar A can slide freely on the...Ch. 10.2 - 10.87 and 10.88 Collar A can slide freely on the...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.89PCh. 10.2 - A vertical bar AD is attached to two springs...Ch. 10.2 - Rod AB is attached to a hinge at A and to two...Ch. 10.2 - Rod AB is attached to a hinge at A and to...Ch. 10.2 - Two bars are attached to a single spring of...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.94PCh. 10.2 - The horizontal bar BEH is connected to three...Ch. 10.2 - The horizontal bar BEH is connected to three...Ch. 10.2 - Bars AB and BC, each with a length l and of...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.98PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.99PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.100PCh. 10 - Determine the vertical force P that must be...Ch. 10 - Determine the couple M that must be applied...Ch. 10 - Determine the force P required to maintain...Ch. 10 - Derive an expression for the magnitude of the...Ch. 10 - Derive an expression for the magnitude of the...Ch. 10 - A vertical load W is applied to the linkage at B....Ch. 10 - A force P with a magnitude of 240 N is applied to...Ch. 10 - Two identical rods ABC and DBE are connected bya...Ch. 10 - Solve Prob. 10.108 assuming that the 24-lb load...Ch. 10 - Two uniform rods each with a mass m and length...Ch. 10 - A homogeneous hemisphere with a radius r isplaced...Ch. 10 - A homogeneous hemisphere with a radius r isplaced...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve Prob. 10.12 assuming that the force P applied at point A acts horizontally to the left.Reference to Problem 10.12:Knowing that the line of action of the force Q passes through point C , derive an expression for the magnitude of Q required to maintain equilibrium.arrow_forwardDetermine the value of θ corresponding to the equilibrium position of the rod of Prob. 10.12 when P = 80 N, and Q= 100 N.Reference to Problem 10.12:Knowing that the line of action of the force Q passes through point C , derive an expression for the magnitude of Q required to maintain equilibrium.arrow_forwardCollar A is connected as shown to a 50-lb load and can slide on a frictionless horizontal rod. Determine the magnitude of the force P required to maintain the equilibrium of the collar when (a) x = 4.5 in., (b) x =15 in. B C 20 in. 50 lb P Aarrow_forward
- Collars A and B are connected by a 25-in.-long wire and can slide freely on frictionless rods. Determine the distances x and z for which the equilibrium of the system is maintained when P= 120 lb and O= 60 lb. %3D 20 in.arrow_forwardMp Fig. P8.126 8.127 Solve Prob. 8.126 assuming that u = 75°. B 8.128 The 10-lb bar AE is suspended by a cable that passes over a 5-in.- radius drum. Vertical motion of end E of the bar is prevented by the two stops shown. Knowing that m, = 0.30 between the cable and the drum, determine (a) the largest counterclockwise couple M, that can be applied to the drum if slipping is not to occur, (b) the corresponding force exerted on end E of the bar. A E 10 lb 5 in. 5 in. 3 in. Fig. P8.128arrow_forwardA homogeneous hemisphere with a radius r is placed on an incline as shown. Assuming that friction is sufficient to prevent slipping between the hemisphere and the incline, determine (a) the largest angle β for which a position of equilibrium exists, (b) the angle 0 corresponding to equilibrium when the angle β is equal to half the value found in part a.arrow_forward
- The 10-lb bar AE is suspended by a cable that passes over a 5-in.-radius drum. Vertical motion of end E of the bar is prevented by the two stops shown. Knowing that μs= 0.30 between the cable and the drum, determine (a) the largest counterclockwise couple M0 that can be applied to the drum if slipping is not to occur, (b) the corresponding force exerted on end E of the bar.arrow_forwardCollar A is connected as shown to a 50-lb load and can slide on a frictionless horizontal rod. Determine the distance x for which the collar is in equilibrium when P = 48 Ib. C 20 in. 50 Ibarrow_forwardThe uniform 10 kg rod AB is supported by a ball and socket joint at A and by the cord CG that is attached to the midpoint G of the rod. Knowing that the rod leans against a frictionless vertical wall at B and that the tension in the cord CG, TCG=52.1 N, determine the following a.) Which of the following best shows the equivalent force-couple set at point A of the tension at cord CG, TCG? Choices: a F= -36.8 N i + 24.5 N j - 27.6 N k M = -7.36 Nm i - 11.03 Nm j b F= -36.8 N i + 24.5 N j - 27.6 N k M = -7.36 Nm i - 29.4 Nm k c F= 36.8 N i - 24.5 N j + 27.6 N k M = 7.36 Nm i + 11.03 Nm j d F= 36.8 N i - 24.5 N j + 27.6 N k M = 7.36 Nm i + 29.4 Nm k b.) Which of the following moments is equal to zero? Choices: The moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about point OThe moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about point AThe moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about point BThe moment of the tension in cord CG, TCG about axis ABarrow_forward
- Q.4. Determine the force F required to hold the system in equilibrium if a torque M of 240 N-m is applied at point D in the counter-clockwise direction. Assume the weights of all members are negligible and that collar B freely moves along the horizontal rod with negligible friction. 160 mm 90 mm 180 mm B M 320 mm D 125 mm 300 mmarrow_forwardIn the planetary gear system shown, the radius of the central gear A is a= 18 mm, the radius of each planetary gear is b , and the radius of the outer gear E is (a + 2b). A clockwise couple with a magnitude of MA = 10 N.m is applied to the central gear A and a counterclockwise couple with a magnitude of MS= 50 N.m is applied to the spider BCD . If the system is to be in equilibrium, determine (a) the required radius b of the planetary gears, (b) the magnitude ME of the couple that must be applied to the outer gear E.arrow_forwardA freight wagon is at rest on a track at an angle of 25o to the vertical. The gross weight of the wagon and its load is 36kN and acts at a point 750 mm from the track, in the middle between the two axles. The wagon is held by a cable 600 mm from the track. Determine the traction on the cable and the reaction on each pair of wheels.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License