
Grand Canyon Manufacturing Inc. produces and sells a product with a price of $100 per unit. The following cost data have been prepared for its estimated upper and lower limits of activity:


Selling and administrative expenses:

Required:
- 1. Classify each cost element as either variable, fixed, or semi-variable. (Hint: Recall that variable expenses must go up in direct proportion to changes in the volume of activity.)
- 2. Calculate the break-even point in units and dollars. (Hint: First use the high-low method illustrated in Chapter 4 to separate costs into their fixed and variable components.)
- 3. Prepare a break-even chart.
- 4. Prepare a contribution income statement, similar in format to the statement appearing on page 540, assuming sales of 5,000 units.
- 5. Recompute the break-even point in units, assuming that variable costs increase by 20% and fixed costs are reduced by $50,000.
1.
Classify the each cost element as either variable, fixed or semi-variable.
Explanation of Solution
Classify the each cost element as either variable, fixed or semi-variable as follows:
- Variable costs vary with the number of units produced or for the services provided. For example, the labor costs increase if the number of labor hours is increased, and the labor costs decrease if the number of labor hours is decreased. Direct material, direct labor and indirect material are considered as the variable costs.
- Fixed Cost is a cost which is constant in the short run, it is not related to any change in the production of goods or service, it will be fixed disregarding of increase or decrease in output. Fixed cost is generally incurred on fixed assets in long run. Depreciation, office salary and advertising are considered as the fixed cost.
- Semi variable costs are the cost that changes based on the changes in the production, but it is not proportionately. Indirect labor, sales salaries and other expense are considered as semi-variable cost.
2.
Calcualte the break even point in units and dollars.
Explanation of Solution
Calcualte the break even point in units and dollars as follows:
Working note (1):
Calcualte the vairable cost per unit:
Working note (2):
Calculate the variable cost for 4,000 units.
Working note (3):
Calcualte the fixed cost:
3.
Prepare a break-even chart.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a break-even chart as follows:
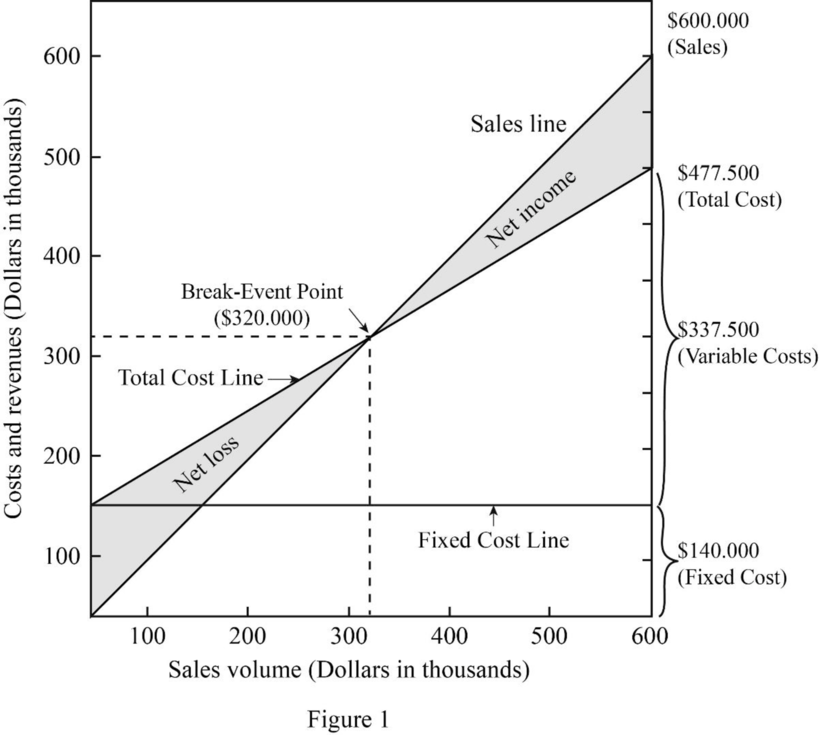
4.
Prepare a contribution income statement of company G.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a contribution income statement of company G as follows:
| Company G | |
| Income statement | |
| For the year ended --- | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Sales | $ 500,000 |
| Less: Variable cost | $281,250 |
| Contribution margin | $218,250 |
| Less: Fixed costs (3) | $140,000 |
| Net operating income | $ 78,750 |
Table (1)
5.
Calculate the break-even point in units, assume that the variable costs is increased by 20% and fixed cost is decreased by $50,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the break-even point in units, assume that the variable costs is increased by 20% and fixed cost is decreased by $50,000 as follows:
Working note (4):
Calcualte the decrase in fixed cost:
Working note (5):
Calcualte the increase in variable cost:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
PRINCIPLES OF COST ACCOUNTING
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF CORPORATE FINANCE
Management (14th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
PRIN.OF CORPORATE FINANCE
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
- Aihua Manufacturing Inc. has two divisions. Division A has a profit of $225,000 on sales of $4,500,000. Division B is only able to make $78,000 on sales of $650,000. Based on the profit margins (returns on sales), which division is superior?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this financial accounting question using valid financial accounting techniques?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forward
- Gibson Inc. has provided the following data for the month of December. The balance in the Finished Goods inventory account at the beginning of the month was $94,200 and at the end of the month was $89,750. The cost of goods manufactured for the month was $412,800. The actual manufacturing overhead cost incurred was $142,300 and the manufacturing overhead cost applied to jobs was $148,500. The adjusted cost of goods sold that would appear on the income statement for December is __. Provide answerarrow_forwardMichael Jones's capital statement reveals that his drawings during the year were $55,000. He made an additional capital investment of $35,000, and his share of the net income for the year was $28,000. His ending capital balance was $240,000. What was Michael Jones's beginning capital balance? a. $232,000 b. $202,000 c. $162,000 d. $202,000arrow_forwardWhat will net income be?arrow_forward
- Eric Industries' break-even point in units is 2,500. The sales price per unit is $35, and the variable cost per unit is $25. If the company sells 6,800 units, what will net income be?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forwardLumo Co had the following transactions in 2020arrow_forward
- Nordica Chemicals produces joint products M and N from Compound Z in a single operation. 800 liters of Compound Z, costing $2,400, produce 500 liters of Product M, selling for $3.50 per liter, and 300 liters of Product N, selling for $6.00 per liter. The portion of the $2,400 cost that should be allocated to Product M using the value basis of allocation is____.arrow_forwardI need help solving this financial accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forward5 PTSarrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning

