
Concept explainers
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method.
Explanation of Solution
Absorption costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering all fixed as well as the variable or direct costs. The
Variable costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering only the variable or direct costs or the cost that happened to occurred due to the product only. It also called as marginal costing as it takes marginal costs while calculating the product cost.
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method as follows:
Comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month:
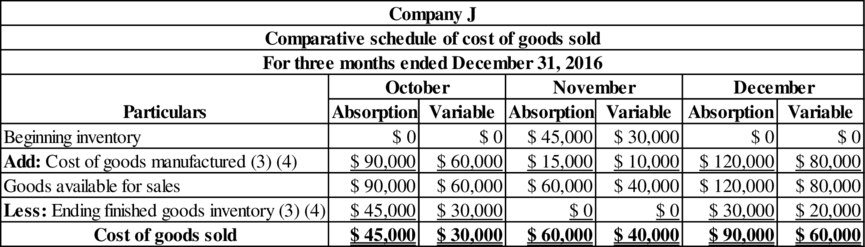
Table (1)
Comparative income statement for each month:
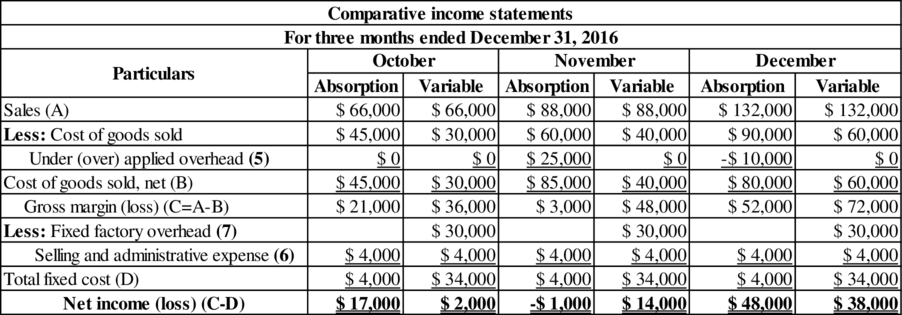
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Calculate the absorption costing per unit.
Working note (2):
Calculate the ending inventory units for each month.
| Particulars | October | November | December |
| Beginning inventory | 0 | 3,000 | 0 |
| Add: Number of units produced | 6,000 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Less: Number of units sold | 3,000 | 4,000 | 6,000 |
| Ending inventory | 3,000 | 0 | 2,000 |
Table (3)
Working note (3):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under absorption costing for each month.
| Particulars | October | November | December |
| Number of units produced (A) | 6,000 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (B) (1) | $ 15 | $ 15 | $ 15 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | $ 90,000 | $ 15,000 | $ 120,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 3000 | 0 | 2000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (D) | $ 15 | $ 15 | $ 15 |
| Ending inventory | $ 45,000 | $ 0 | $ 30,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 3,000 | 0 |
| Absorption cost per unit (F) | $ 15 | $ 15 | $ 15 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 45,000 | $ 0 |
Table (4)
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under variable costing for each month.
| Particulars | October | November | December |
| Number of units produced (A) | 6,000 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Variable cost per unit (B) | $ 10 | $ 10 | $ 10 |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 60,000 | $ 10,000 | $ 80,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 3000 | 0 | 2000 |
| Variable cost per unit (D) | $ 10 | $ 10 | $ 10 |
| Ending inventory | $ 30,000 | $ 0 | $ 20,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 3,000 | 0 |
| Variable cost per unit (F) | $ 10 | $ 10 | $ 10 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 30,000 | $ 0 |
Table (5)
Working note (5):
Calculate the under or over applied fixed
October:
November:
December:
Working note (6):
Calculate the fixed selling and administrative expense per month.
Working note (7):
Calculate the fixed factory overhead per month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
PRINCIPLES OF COST ACCOUNTING
- Please need answer the general accounting question not use aiarrow_forwardGroot Co. (GC) sells $1,200,000 of 6-year, 10% bonds at par plus accrued interest. The bonds are dated January 1, 2026 but due to market conditions are not issued until May 1, 2026. Interest is payable on June 30 and December 31 each year. The market rate of interest at time of issue is the same as the stated rate. Required The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 2026. Assume that GC has adopted a policy of crediting accrued interest payable for the accrued interest on the date of sale. Payment of interest on June 30, 2026. Payment of interest on December 31, 2026.arrow_forward1. Define working capital and explain its importance in financial health and liquidity management. 2. Assess how the matching concept and accrual basis affect the reporting of current assets and liabilities. 3. Using a hypothetical balance sheet (you may create one), identify at least 5 current assets and 5 current liabilities and analyze how changes in these elements affect liquidity ratios. 4. Recommend at least two strategies VinGrenDom Ltd. can implement to optimize working capital.arrow_forward
- Theron Interiors manufactures handcrafted cabinetry and uses a process costing system. During the month of October, the company started Production on 720 units and completed 590 units. The remaining 120 units were 60% complete in terms of materials and 40% complete in terms of labor and overhead. The total cost incurred during the month was $45,000 for materials and $31,200 for labor and overhead. Using the weighted-average method, what is the equivalent unit cost for materials and conversion costs (labor and overhead)?arrow_forwardGeneral Accountingarrow_forwardKamala Khan has to decide between the following two options: Take out a student loan of $70,000 and study accounting full time for the next three years. The interest on the loan is 4% per year payable annually. The principle is to be paid in full after ten years. Study part time and work part time to earn $15,000 per year for the following six years. Once Kamala graduates, she estimates that she will earn $30,000 for the first three years and $40,000 the next four years. Kamala's banker says the market interest for a ten-year horizon is 6%. Required Calculate NPV of the ten-year cash flows of the two options. For simplification assume that all cash flows happen at year-end. Based on the NPV which of the two options is better for Kamala?arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub





