
Concept explainers
A projectile of mass m moves to the right with a speed vi (Fig. P10.81a). The projectile strikes and sticks to the end of a stationary rod of mass M, length d, pivoted about a frictionless axle perpendicular to the page through O (Fig. P10.81b). We wish to find the fractional change of kinetic energy in the system due to the collision. (a) What is the appropriate analysis model to describe the projectile and the rod? (b) What is the
Figure P10.81
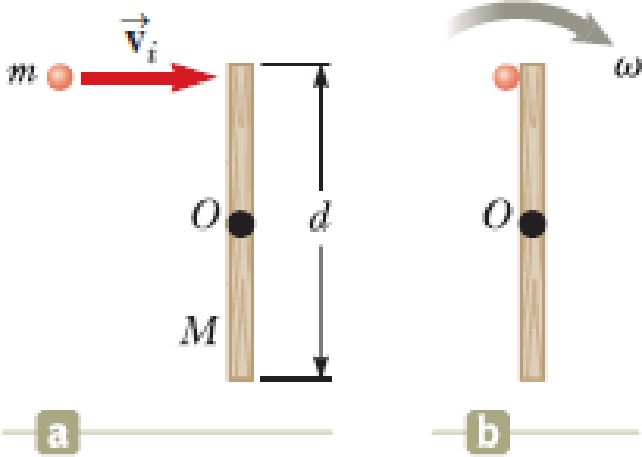
(a)
The appropriate model to analyze the system.
Answer to Problem 81P
The appropriate model to analyze the system is by considering it as an
Explanation of Solution
The striking and sticking of the given projectile on the stationary rod can be considered as a collision. The collision occurring between two object is an isolated system for which the total momentum is conserved. The momentum of both objects before and after collision will be same. This is because the system is free from any external force which changes the momentum.
Since the rod and projectile is not experiencing any external force and torque the total momentum of the system will be conserved, and the system can be considered as isolated. Thus, the best suited analysis model is by treating the system as isolated.
Conclusion
Therefore, the appropriate model to analyze the system is by considering it as an
(b)
The angular momentum of the system before collision about an axis passing through
Answer to Problem 81P
The angular momentum of the system before collision about an axis passing through
Explanation of Solution
The total angular momentum is the sum of the angular momentum of projectile and the rod. Since the rod is initially at rest its angular momentum before collision will be zero.
Write the expression for the total angular momentum.
Here,
Write the expression for the angular momentum of the projectile at
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the angular momentum of the system before collision about an axis passing through
(c)
The moment of inertia of the rod after collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The moment of inertia of the rod after collision is
Explanation of Solution
The total moment of inertia is the sum of the moment of inertia of rod and the projectile.
Write the expression for the total moment of inertia.
Here,
Let
Here,
Write the expression for the moment of inertia of the projectile about an axis passing through
Conclusion:
Substitute, equation (IV) and (V) in (III).
Therefore, the moment of inertia of the rod after collision is
(d)
The angular momentum of the system after collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The angular momentum of the system after collision is
Explanation of Solution
After the collision there is only a single angular momentum since the projectile stick to the rod after striking.
Write the expression for the final angular momentum.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the angular momentum of the system after collision is
(e)
The angular speed after the collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The angular speed after the collision is
Explanation of Solution
According to principle of conservation of angular momentum the momentum after and before collision will be same.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the angular speed after the collision is
(f)
The kinetic energy of the system before collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The kinetic energy of the system before collision is
Explanation of Solution
Since the rod is at rest the kinetic energy is only for the projectile. The projectile has mass
Hence the kinetic energy of the projectile is.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the system before collision is
(g)
The kinetic energy of the system after collision
Answer to Problem 81P
The kinetic energy of the system after collision is
Explanation of Solution
The kinetic energy after the collision is the rotational kinetic energy of the system.
Write the expression for the rotational kinetic energy.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the system after collision is
(h)
The fractional change in kinetic energy due o collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The fractional change in kinetic energy due to collision is
Explanation of Solution
The change in energy is obtained by taking the difference of energy before, and after collision.
Write the expression for change in kinetic energy.
Substitute,
Write the expression for the fractional change in kinetic energy.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the fractional change in kinetic energy due to collision is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card)
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Alreadyarrow_forwardTwo objects get pushed by the same magnitude of force. One object is 10x more massive. How does the rate of change of momentum for the more massive object compare with the less massive one? Please be able to explain why in terms of a quantitative statement found in the chapter.arrow_forwardA box is dropped on a level conveyor belt that is moving at 4.5 m/s in the +x direction in a shipping facility. The box/belt friction coefficient is 0.15. For what duration will the box slide on the belt? In which direction does the friction force act on the box? How far will the box have moved horizontally by the time it stops sliding along the belt?arrow_forward
- Plz solution should be complete No chatgpt pls will upvote .arrow_forwardA box with friction coefficient of 0.2 rests on a 12 foot long plank of wood. How high (in feet) must one side of the plank be lifted in order for the box to begin to slide?arrow_forwardWhat is a good general rule to follow in order to find the best choice of coordinate system to solve a dynamics problem?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





