
Concept explainers
Self-Construction Olson Machine Company manufactures small and large milling machines. Selling prices of these machines range from $35,000 to $200,000. During the 5-month period from August 1, 2019, through December 31, 2019, Olson manufactured a milling machine for its own use. This machine was built as part of the regular production activities. The project required a large amount of time front planning and supervisory personnel, as well as that of some of the company’s officers, because it was a more sophisticated type of machine than the regular production models.
Throughout the 5-month period, Olson charged all costs directly associated with the construction of the machine to a special account entitled “Asset Construction Account.” An analysis of the charges to this account as of December 31, 2019, follows:
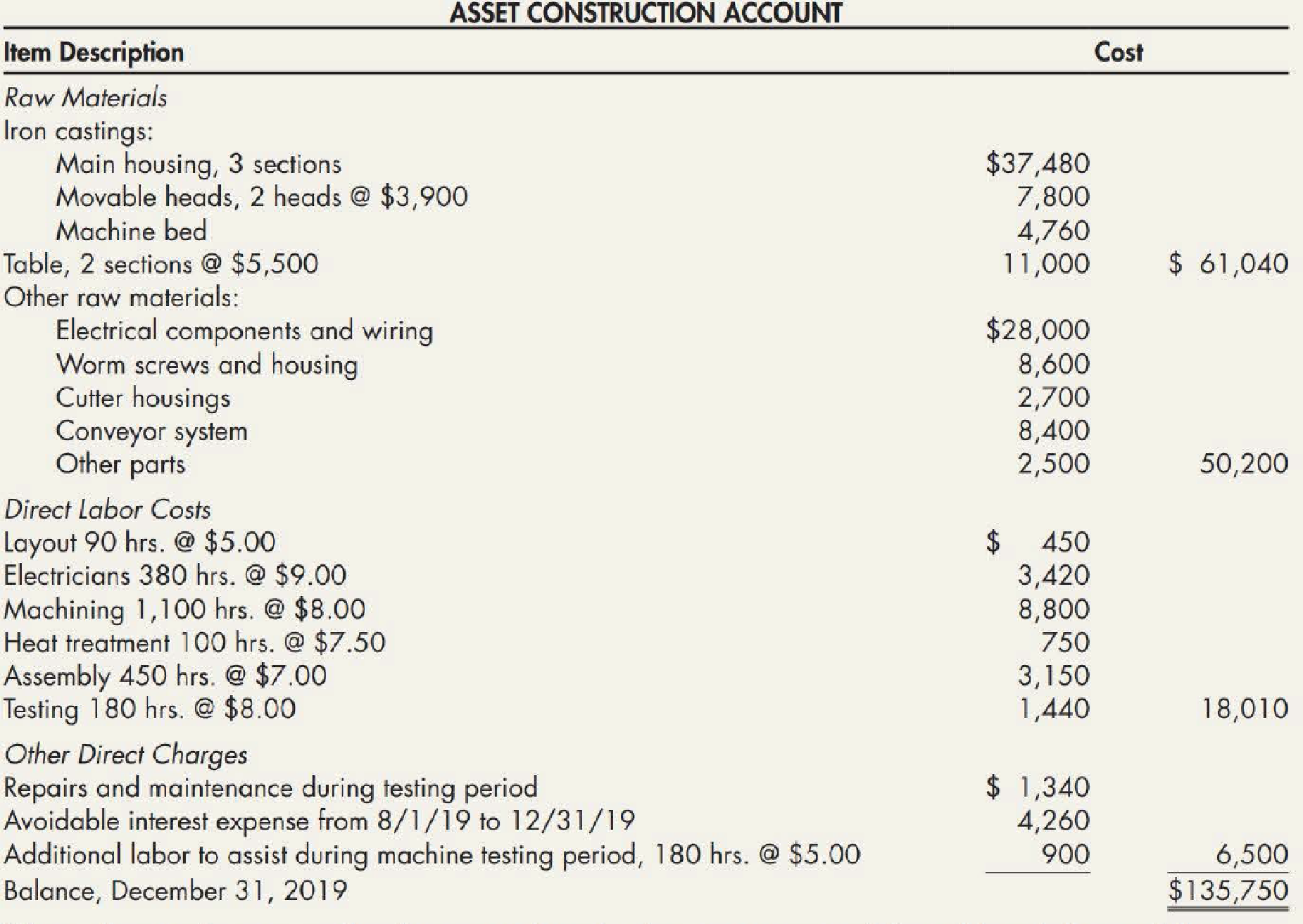
Olson allocates factory

Olson uses a flat rate of 40% of direct labor dollars to allocate general and administrative overhead.
During the machine testing period, a cutter head malfunctioned and did extensive damage to the machine table and one cutter housing. This damage was not anticipated and was the result of an error in the assembly operation. Although no additional raw materials were needed to make the machine operational after the accident, the following labor for rework was required:

Olson has included all these labor charges in the asset construction account. In addition, it included in the account the repairs and maintenance charges of $1,340 that it incurred as a result of the malfunction.
Required:
- 1. Compute, consistent with GAAP and common practice, the amount that Olson should capitalize for the milling machine as of December 31, 2019, when it declares the machine operational.
- 2. Next Level Identify the costs you included in Requirement 1 for which there are acceptable alternative procedures. Describe the alternative procedure(s) in each case.
1.
Calculate the amount that Company O must capitalize for the milling machine as of December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of self-constructed assets:
Company sometimes constructs an item of “property, plant and equipment” which is used in the business operations and these are known as self-constructed assets. The cost of self-constructed assets comprises of expenses that are required to build an asset and put it in operating condition.
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Raw materials: | ||
| Iron castings | 61,040 | |
| Other raw materials. | 50,200 | $111,240 |
| Direct labor: | ||
| Layout (1) | $450 | |
| Electricians (2) | 2,700 | |
| Machinery (3) | 7,200 | |
| Heat treatment (4) | 750 | |
| Assembly (5) | 2,450 | |
| Testing (6) | 1,280 | |
| Additional testing labor (7) | 800 | 15,630 |
| Factory overhead: | ||
| Layout and electricians (8) | $2,205 | |
| Machining, heat treatment, assembly, testing (9) | ||
| 12,480 | 14,685 | |
| Interest paid | 4,260 | |
| Total amount to be capitalized | 145,815 |
Table (1)
Working notes:
(1)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for layout:
(2)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for electricians:
(3)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for machinery:
(4)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for Heat treatment:
(5)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for assembly:

(6)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for testing:

(7)Calculate the amount of direct labor costs for additional testing labor:
(8)Calculate the factory overhead for layout and electricians:
(9)Calculate the factory overhead for machinery, heat treatment, assembly and testing:
2.
Ascertain the costs included in requirement 1 for which there are acceptable alternative procedures and explain the alternative procedures for each case.
Explanation of Solution
“Alternate procedures are probable for two costs— factory overhead and rework costs (affects direct labor, repairs and maintenance, and factory overhead)”
- Rework costs must be taken as cost for the period in which they are nonstandard. Rework costs rising from errors that must not have incurred should be considered as losses of the period. Seemingly, this was the case in this condition since the impairment resulted from a type of error that is not expected. Accordingly, related repairs, maintenance expenses and rework costs are not capitalized in requirement 1.
- Two alternative ways are there to allocate overhead costs to self-constructed assets. The method followed in “requirement 1” is to allot a portion of all overhead costs to the self-constructed asset. The reason which justifies this particular treatment is that all productive output must absorb its proportionate share of all factory overhead costs. Additionally, this method result in a cost of the constructed asset that approximates the cost of the equivalent asset acquired.
- Capitalizing the incremental overhead, that is traceable fixed and variable overhead is the second method that increases as a result of construction. Additional costs occurred in production of the fixed asset (part of the assets’ cost) are included in this method. Traceable fixed overhead and variable overhead are occurred to build the asset and it will be advantageous in the upcoming periods therefore, these costs must be capitalized.
- If there is no relationship between the self-constructed asset and fixed overhead costs, non-traceable fixed overhead costs will be incurred so, these costs must not be capitalized.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
- helparrow_forwardWhat is the stock price??arrow_forwardAlleyway Corp. manufactures two styles of a leather bowling bag, the Strike and Turkey. Budgeted production levels for October follow: Strike Turkey Production 2,500 bags 3,500 bags Two departments, Cutting and Sewing, produce the bowling bags. Direct labor hours needed for each style are as follows: Cutting Sewing Strike 0.100 hour per bag 0.300 hour per bag Turkey 0.200 hour per bag 0.450 hour per bag Hourly direct labor rates are $13 for the Cutting Department and $14 for Sewing. Determine Alleyway's budgeted direct labor cost for October.arrow_forward
- An asset's book value is $28,000 on December 31, Year 5. The asset has been depreciated at an annual rate of $12,000 on the straight-line method. Assuming the asset is sold on December 31, Year 5 for $24,000, the company should record: please provide answerarrow_forwardSelected costs associated with a product are as follows: Total standard hours for units produced Total actual direct labor cost Actual per hour labor rate 5,000 $ 1,11,625.00 $ 23.50 $ 24.00 Standard per hour labor rate What amount is the total direct labor price variance? a. $2,375 unfavorable. b. $2,375 favorable. c. $2,500 unfavorable. d. $2,500 favorable.arrow_forwardCompute the variable and fixed cost elementsarrow_forward
- The formula AH * (SR-AR) is the: a. direct labor spending variance. b. direct labor volume variance. c. direct labor rate variance. d. direct labor efficiency variance.arrow_forwardStrait Company manufactures office furniture. During the most productive month of the year, 4,400 desks were manufactured at a total cost of $61,000. In the month of lowest production, the company made 2,335 desks at a cost of $43,000. Using the high-low method of cost estimation, total fixed costs are____. Options: a. $24,800 b. $29,400 c. $40,000 d. $22,632.arrow_forwardOn December 31, Strike Company decided to sell one of its batting cages. The initial cost of the equipment was $308,000 with accumulated depreciation of $199,000. Depreciation has been taken up to the end of the year. The company found a company that is willing to buy the equipment for $35,000. What is the amount of the gain or loss on this transaction? Answer this questionarrow_forward
- Ayayai Itzek manufactures and sells homemade wine, and he wants to develop a standard cost per gallon. The following are required for the production of a 50-gallon batch. - 2,910 ounces of grape concentrate at $0.08 per ounce. - 54 pounds of granulated sugar at $0.40 per pound. 60 lemons at $0.70 each. 250 yeast tablets at $0.29 each. - 200 nutrient tablets at $0.12 each. - 2,800 ounces of water at $0.005 per ounce. Ayayai estimates that 3% of the grape concentrate is wasted, 10% of the sugar is lost, and 25% of the lemons cannot be used. Compute the standard cost of the ingredients for one gallon of wine.arrow_forwardOn December 31, Strike Company decided to sell one of its batting cages. The initial cost of the equipment was $308,000 with accumulated depreciation of $199,000. Depreciation has been taken up to the end of the year. The company found a company that is willing to buy the equipment for $35,000. What is the amount of the gain or loss on this transaction?arrow_forwardFinancial accounting questionarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

