
Concept explainers
To describe:
The proportion of offspring being heterozygous for all the genes.
Concept introduction:
Mating between two ferns, one having genotype
Explanation of Solution
Tabular representation:
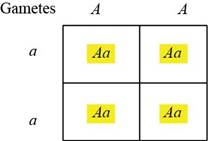
Table.1: The progeny obtained by crossing AA and aa.
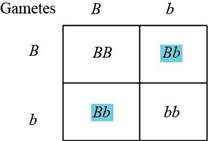
Table.2: The progeny obtained by crossing Bb and Bb.
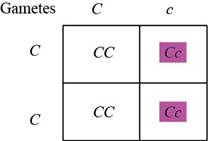
Table.3: The progeny obtained by crossing Cc and CC.
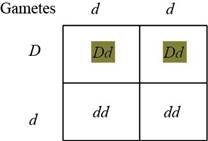
Table.4: The progeny obtained by crossing dd and Dd.
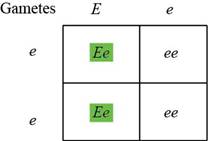
Table.5: The progeny obtained by crossing Ee and ee.
Explanation:
The genotypes for the first traits are AA and aa. The gametes formed by these will be as follows:
The offspring obtained from crossing can be observed in the Punnett square in Table.1: “The progeny obtained by crossing AA and aa”. All the offspring would be heterozygous. The probability of having heterozygous offspring from first trait is
The genotypes for the second traits are Bb and Bb. The gametes formed by these will be as follows:
The probability of offspring produced from crossing can be observed in the Punnett square in Table.2: “The progeny obtained by crossing Bb and Bb”. There will be
The genotypes for the third traits are Cc and CC. The gametes formed by these will be as follows:
The offspring obtained from crossing can be observed in the Punnett square in Table.3: “The progeny obtained by crossing Cc and CC”. There will be
The genotypes for the fourth traits are dd and Dd. The gametes formed by these will be as follows.
The offspring obtained from crossing can be observed in the Punnett square in Table.4: “The progeny obtained by crossing dd and Dd”. There will be
The genotypes for the fifth traits are Ee and ee. The gametes formed by these will be as follows.
The offspring obtained from crossing can be observed in the Punnett square in Table.5: “The progeny obtained by crossing Ee and ee”. There will be
The probability of offspring heterozygous for all the traits can be calculated using the product rule that is by multiplying individual probabilities of heterozygotes for each trait. The probability of offspring heterozygous for all genes can be calculated as follows:
The probability of offspring heterozygous for all the genes is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
- A sample of blood was taken from the above individual and prepared for haemoglobin analysis. However, when water was added the cells did not lyse and looked normal in size and shape. The technician suspected that they had may have made an error in the protocol – what is the most likely explanation? The cell membranes are more resistant than normal. An isotonic solution had been added instead of water. A solution of 0.1 M NaCl had been added instead of water. Not enough water had been added to the red blood cell pellet. The man had sickle-cell anaemia.arrow_forwardA sample of blood was taken from the above individual and prepared for haemoglobin analysis. However, when water was added the cells did not lyse and looked normal in size and shape. The technician suspected that they had may have made an error in the protocol – what is the most likely explanation? The cell membranes are more resistant than normal. An isotonic solution had been added instead of water. A solution of 0.1 M NaCl had been added instead of water. Not enough water had been added to the red blood cell pellet. The man had sickle-cell anaemia.arrow_forwardWith reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forward
- With reference to their absorption spectra of the oxy haemoglobin intact line) and deoxyhemoglobin (broken line) shown in Figure 2 below, how would you best explain the reason why there are differences in the major peaks of the spectra? Figure 2. SPECTRA OF OXYGENATED AND DEOXYGENATED HAEMOGLOBIN OBTAINED WITH THE RECORDING SPECTROPHOTOMETER 1.4 Abs < 0.8 06 0.4 400 420 440 460 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 nm 1. The difference in the spectra is due to a pH change in the deoxy-haemoglobin due to uptake of CO2- 2. There is more oxygen-carrying plasma in the oxy-haemoglobin sample. 3. The change in Mr due to oxygen binding causes the oxy haemoglobin to have a higher absorbance peak. 4. Oxy-haemoglobin is contaminated by carbaminohemoglobin, and therefore has a higher absorbance peak 5. Oxy-haemoglobin absorbs more light of blue wavelengths and less of red wavelengths than deoxy-haemoglobinarrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forwardWhich ONE of the following is FALSE regarding haemoglobin? It has two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The subunits are joined by disulphide bonds. Each subunit covalently binds a haem group. Conformational change in one subunit can be transmitted to another. There are many variant ("mutant") forms of haemoglobin that are not harmful.arrow_forward
- During a routine medical check up of a healthy man it was found that his haematocrit value was highly unusual – value of 60%. What one of the options below is the most likely reason? He will have a diet high in iron. He is likely to be suffering from anaemia. He lives at high altitude. He has recently recovered from an accident where he lost a lot of blood. He has a very large body size.arrow_forwardExplain what age of culture is most likely to produce an endospore?arrow_forwardExplain why hot temperatures greater than 45 degrees celsius would not initiate the sporulation process in endospores?arrow_forward
- Endospore stain: Consider tube 2 of the 7-day bacillus culture. After is was heated, it was incubated for 24 hours then refrigerated. Do you think the cloudiness in this tube is due mostly to vegetative cells or to endospores? Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardReactunts C6H12O6 (Glucose) + 2NAD+ + 2ADP 2 Pyruvic acid + 2NADH + 2ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? GHz 06 (glucose) d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? NAD e. Which of the products have been reduced? NADH f. Which of the products have been oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 3arrow_forwardThere is ________ the concept of global warming. Very strong evidence to support Some strong evidence to support Evidence both supporting and against Evidence againstarrow_forward

 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





