
Concept explainers
The following transactions were completed by Yang Restaurant Equipment during January, the first month of this fiscal year. Terms of sale are 2/10, n/30. The balances of the accounts as of January 1 have been recorded in the general ledger in your Working Papers or in CengageNow. Yang Restaurant Equipment does not track cash sales by customer.
Jan. 2 Issued Ck. No. 6981 to Tri-County Management Company for monthly rent, $850.
2 L. Yang, the owner, invested an additional $4,500 in the business.
4 Bought merchandise on account from Valentine and Company, invoice no. A694, $2,830; terms 2/10, n/30; dated January 2.
4 Received check from Velez Appliance for $980 in payment of invoice for $1,000 less discount.
4 Sold merchandise on account to L. Parrish, invoice no. 6483, $755.
6 Received check from Peck, Inc., $637, in payment of $650 invoice less discount.
7 Issued Ck. No. 6982, $588, to Frost and Son, in payment of invoice no. C127 for $600 less discount.
7 Bought supplies on account from Dudley Office Supply, invoice no. 190B, $93.54; terms net 30 days.
7 Sold merchandise on account to Ewing and Charles, invoice no. 6484, $1,115.
9 Issued credit memo no. 43 to L. Parrish, $47, for merchandise returned.
11 Cash sales for January 1 through January 10, $4,454.87.
11 Issued Ck. No. 6983, $2,773.40, to Valentine and Company, in payment of $2,830 invoice less discount.
14 Sold merchandise on account to Velez Appliance, invoice no. 6485, $2,100.
14 Received check from L. Parrish, $693.84, in payment of $755 invoice, less return of $47 and less discount.
Jan. 19 Bought merchandise on account from Crawford Products, invoice no. 7281, $3,700; terms 2/10, n/60; dated January 16; FOB shipping point, freight prepaid and added to invoice, $142 (total $3,842).
21 Issued Ck. No. 6984, $245, to A. Bautista for miscellaneous expenses not recorded previously.
21 Cash sales for January 11 through January 20, $3,689.
23 Received credit memo no. 163, $87, from Crawford Products for merchandise returned.
29 Sold merchandise on account to Bradford Supply, invoice no. 6486, $1,697.20.
29 Issued Ck. No. 6985 to Western Freight, $64, for freight charges on merchandise purchased January 4.
31 Cash sales for January 21 through January 31, $3,862.
31 Issued Ck. No. 6986, $65, to M. Pineda for miscellaneous expenses not recorded previously.
31 Recorded payroll entry from the payroll register: total salaries, $5,899.95; employees’ federal income tax withheld, $795; FICA Social Security tax withheld, $365.80, FICA Medicare tax withheld, $85.50.
31 Recorded the payroll taxes: FICA Social Security tax, $365.80; FICA Medicare tax, $85.50; state
31 Issued Ck. No. 6987, $4,653.65, for salaries for the month.
31 L. Yang, the owner, withdrew $1,000 for personal use, Ck. No. 6988.
Required
- 1. Record the transactions for January using a sales journal, page 91; a purchases journal, page 74; a cash receipts journal, page 56; a cash payments journal, page 63; and a general journal, page 119. Assume the periodic inventory method is used.
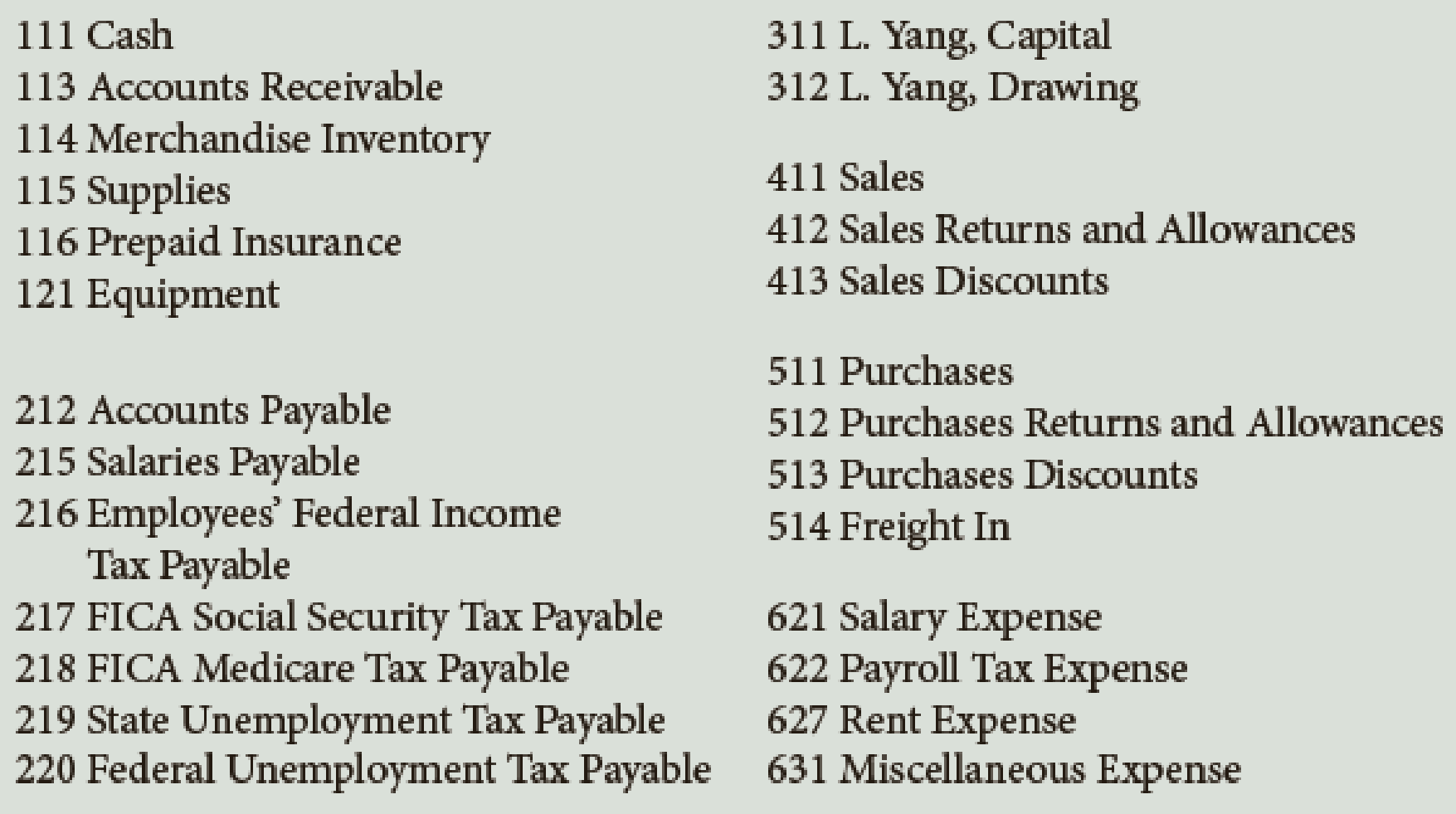
- 2.
Post daily all entries involving customer accounts to theaccounts receivable ledger. - 3. Post daily all entries involving creditor accounts to the accounts payable ledger.
- 4. Post daily those entries involving the Other Accounts columns and the general journal to the general ledger. Write the owner’s name in the Capital and Drawing accounts.
- 5. Add the columns of the special journals and prove the equality of the debit and credit totals.
- 6. Post the appropriate totals of the special journals to the general ledger.
- 7. Prepare a
trial balance . - 8. Prepare a schedule of accounts receivable and a schedule of accounts payable. Do the totals equal the balances of the related controlling accounts?
1.
Journalize the transactions using types of journals.
Explanation of Solution
Sales Journal: Sales journal is one form of special journal book, which records all the sales transactions that are sold to customers on credit. In a single column sales journal, debit aspect of accounts receivable and credit aspect of inventory are recorded, and then posted to individual subsidiary customer account.
Purchase Journal: Purchase journal records all the merchandise purchase on credit. In a single column purchase journal, debit aspect of inventory and credit aspect of accounts payable are recorded, and then posted to individual subsidiary supplier account.
Cash Receipts Journal: It is a special book where only cash receipts transactions that are received from customers, merchandise sales and service made in cash and collection of accounts receivable are recorded.
Cash payments journal: Cash payments journal refers to the journal that is used to record the all transaction which is involve the cash payments. For example, the business paid cash to employees (salary paid to employees). Cash payments journal is used to record merchandise purchases made in cash and payments of accounts payable. It also records all other cash payments to various purposes. To include all these transactions, companies use multi-column cash payments journal.
General journal is a record of financial transaction. The transactions are recorded in the journal prior to posting them to the accounts in the general ledger.
Journalize the transactions using the types of journals.
- Sales Journal
| Sales Journal | Page no: 91 | ||||
| Date | Invoice No. | Customer Name | Post Ref. | Accounts Receivable Dr. | |
| Sales Cr.($) | |||||
| 20__ | |||||
| Jan. | 4 | 6483 | Mr. P | ✓ | 755 |
| 7 | 6484 | Mr. E&C | ✓ | 1,115 | |
| 14 | 6485 | Mr. V | ✓ | 2,100 | |
| 29 | 6486 | Mr. B | ✓ | 1,697 | |
| 31 | Total | $5,667 | |||
| (113) (411) | |||||
Table (1)
- Purchase Journal
| Purchase Journal | Page no:74 | ||||||||
| Date | Customer name | Invoice no. | Invoice date | Terms. | Post Ref. | Accounts Payable | Freight in | Purchases | |
| Credit ($) | Debit ($) | Debit ($) | |||||||
| 20__ | |||||||||
| Jan. | 4 | V Company | A691 | 2-Jan | 2/10,n/30 | ✓ | 2,830 | 2,830 | |
| 18 | C Company | 7281D | 16-Jan | 2/10,n/60 | ✓ | 3,842 | 142 | 3,700 | |
| 31 | Totals | 6,672 | 142 | 6,530 | |||||
| (212) | (514) | (511) | |||||||
Table (2)
- Cash receipts journal
| Cash Receipts Journal | Page:56 | |||||||
| Date | Accounts Credited | Post ref. | Cash | Sales Discount | Accounts Receivable | Sales | Other Accounts | |
| debit($) | debit($) | credit($) | credit($) | Credit($) | ||||
| 20__ | ||||||||
| Jan | 2 | Mr. Y, Capital | 311 | 4,500 | 4,500 | |||
| 4 | V company | 980 | 20 | 1,000 | ||||
| 6 | P company | 637 | 13 | 650 | ||||
| 11 | 4,455 | 4,455 | ||||||
| 14 | Mr. P | 693 | 14.16 | 708 | ||||
| 21 | 3,689 | 3,689 | ||||||
| 31 | 3,862 | 3,862 | ||||||
| 31 | Totals | 18,816.71 | 47.16 | 2,358 | 12,005.87 | 4,500 | ||
| (111) | (413) | (113) | (411) | (X) | ||||
Table (3)
- Cash payment journal
| Cash payments journal | Page:63 | |||||||
| Date | CK no | Account Debited | Post ref. | Other accounts | Accounts payable | Purchases discounts | Cash | |
| debit($) | debit($) | credit($) | credit($) | |||||
| 20__ | ||||||||
| Jan | 2 | 6981 | Rent expense | 627 | 850 | 850 | ||
| 7 | 6982 | F company | ✓ | 600 | 12 | 588 | ||
| 11 | 6983 | V Company | ✓ | 2,830 | 57 | 2,773.4 | ||
| 21 | 6984 | Miscellaneous expense | 631 | 245 | 245 | |||
| 29 | 6985 | Freight in | 514 | 64 | 64 | |||
| 31 | 6986 | Miscellaneous expense | 631 | 65 | 65 | |||
| 31 | 6987 | Salaries payable | 215 | 4,653 | 4,653.65 | |||
| 31 | 6988 | Mr. Y drawing | 312 | 1,000 | 1,000 | |||
| 31 | Totals | 6,887.65 | 3,430 | 68.6 | 10,239.05 | |||
| (X) | (212) | (513) | (111) | |||||
Table (4)
- General journal
| General journal | Page:100 | ||||
| Date | Description | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |
| 20___ | |||||
| Jan. | 7 | Supplies | 115 | 93.54 | |
| Accounts payable, D company | 212/ | 93.54 | |||
| (Record purchase of supplies from D company | |||||
| invoice no. 1906B, terms net 30) | |||||
| 9 | Sales returns and allowances | 412 | 47 | ||
| Accounts receivable, Mr. L | 113/ | 47 | |||
| (Record issued credit memo no.43) | |||||
| 23 | Accounts payable, C company | 212/ | 87 | ||
| Purchase returns and allowances | 512 | 87 | |||
| (Received credit memo for return of | |||||
| merchandise memo no:163) | |||||
| 31 | Salaries expense | 621 | 5,899.95 | ||
| Employee's federal income tax payable | 216 | 795 | |||
| FICA social security tax payable | 217 | 365 | |||
| FCIA Medicare tax payable | 218 | 85 | |||
| Salaries payable | 215 | 4,653.65 | |||
| (Record salaries paid for the month) | |||||
| 31 | Payroll tax expense | 622 | 805.3 | ||
| FICA social security tax payable | 217 | 365.8 | |||
| Medicare tax payable | 218 | 85.5 | |||
| State unemployment tax payable | 219 | 318.6 | |||
| Federal unemployment tax payable | 220 | 35.4 | |||
| ( Record employer's share of FCIA taxes and | |||||
| employer's state and federal unemployment | |||||
| taxes for the month) | |||||
Table (5)
2.
Record the entries from customer accounts to the accounts receivable ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Account receivable: The amount of money to be received by a company for the sale of goods and services to the customers is referred to as account receivable.
| Accounts Receivable Ledger | ||||||
| Name: B company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 29 | S91 | 1,697 | 1,697.2 | ||
| Name: E and C company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 7 | S91 | 1,115 | 1,115 | ||
| Name: Mr. P | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 4 | S91 | 755 | 755 | ||
| 9 | J119 | 47 | 708 | |||
| 14 | CR56 | 708 | ||||
| Name: P company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 650 | ||
| 6 | CR38 | 650 | 0 | |||
| Name: V company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,000 | ||
| 4 | CR56 | 1,000 | 0 | |||
| 14 | S91 | 2,100 | 2,100 | |||
Table (6)
3.
Record the entries from creditor accounts to the accounts payable ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Account payable: The amount of money to be paid by a company for the purchase of goods and services from the seller is referred to as account payable.
Record the entries from creditor accounts to the accounts payable ledger.
| Accounts payable ledger | ||||||
| Name: C company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 19 | P74 | 3,842 | 3,842 | ||
| 23 | J119 | 87 | 3,755 | |||
| Name: D company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 7 | J119 | 93.54 | 93.54 | ||
| Name: F and sons | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 600 | |||
| 7 | CP63 | 600 | 0 | |||
| Name: V company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 4 | P74 | 2,830 | 2,830 | ||
| 11 | CP63 | 2,830 | 0 | |||
Table (7)
4.
Post the prepared journals and other accounts column to general ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Posting of transaction: The process of transferring the journalized transactions into the accounts of the ledger is known as posting of transaction.
Post the prepared journals to the general ledger:
| General ledger | |||||||
| Account: Cash | Account No:111 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 8,740 | |||
| 31 | CR56 | 18,816.71 | 27,556.71 | ||||
| 31 | CP63 | 10,239.05 | 17,317.66 | ||||
| Account: Accounts receivable | Account No:113 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,650 | |||
| 9 | J119 | 47 | 1,603 | ||||
| 31 | S91 | 5,667.20 | 7,270.2 | ||||
| 31 | CR56 | 2,358.00 | 4,912 | ||||
| Account: Merchandise inventory | Account No:114 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 20,584 | |||
| Account: Supplies | Account No:115 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 592 | |||
| 7 | J119 | 93.54 | 685.54 | ||||
| Account: Prepaid insurance | Account No:116 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 390 | |||
| Account: Equipment | Account No:121 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,644 | |||
| Account: Accounts payable | Account No:212 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | Balance | ✓ | 600 | |||
| 7 | J119 | 93.54 | 693.54 | ||||
| 23 | J119 | 87 | 606.54 | ||||
| 31 | P74 | 6,672 | 7,278.54 | ||||
| 31 | CP63 | 3,430 | 3,848.54 | ||||
| Account: Salaries payable | Account No:215 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 4,653.65 | 4,653.65 | |||
| 31 | CP63 | 4,653.65 | |||||
| Account: Employees federal income tax payable | Account No:216 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 795 | 795 | |||
| Account: FICA social security tax payable | Account No:217 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 365.8 | 365.8 | |||
| 31 | J119 | 365.8 | 731.6 | ||||
| Account: FICA Medicare payable | Account No:218 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 85.5 | 85.5 | |||
| 31 | J119 | 85.5 | 171 | ||||
| Account: State Unemployment tax payable | Account No:219 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 318.6 | 318.6 | |||
| Account: Federal unemployment tax payable | Account No:220 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 35.4 | 35.4 | |||
| Account: Mr. Y Capital | Account No:311 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 35,000 | |||
| 2 | CR56 | 4,500 | 39,500 | ||||
| Account: Mr. Y Drawing | Account No:312 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | CP63 | 1,000 | 1,000 | |||
| Account: Sales | Account No:411 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | S91 | 5,667 | 5,667.2 | |||
| 31 | CR56 | 12,005.9 | 17,673.07 | ||||
| Account: Sales return and allowance | Account No:412 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 9 | J119 | 47 | 47 | |||
| Account: Sales discounts | Account No:413 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | CR56 | 47 | 47 | |||
| Account: Purchases | Account No:511 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | P74 | 6,530 | 6,530 | |||
| Account: Purchases returns and allowances | Account No:512 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 23 | J119 | 87 | 87 | |||
| Account: Purchase discounts | Account No:513 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | CP63 | 68.6 | 68.6 | |||
| Account: Freight in | Account No:514 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 29 | CP63 | 64 | 64 | |||
| 31 | P74 | 142 | 206 | ||||
| Account: Salary expense | Account No:621 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 5,899.95 | 5,899.95 | |||
| Account: Payroll tax expense | Account No:622 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 31 | J119 | 805.3 | 805.3 | |||
| Account: Rent expense | Account No:627 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 2 | CP63 | 850 | 850 | |||
| Account: Miscellaneous expense | Account No:631 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||
| Jan | 21 | CP63 | 245 | 245 | |||
| 31 | CP63 | 65 | 310 | ||||
Table (8)
5.
Report the equality of debit and credit totals in special journal column.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Equality of debit and credit column in purchase journal:
| EQUALITY OF DEBITS AND CREDITS | |||
| DEBITS ($) | CREDITS ($) | ||
| 142 | 6,672 | ||
| 6,530 | |||
| 6,672 | 6,672 | ||
Table (9)
Equality of debit and credit column in Cash receipt journal:
| EQUALITY OF DEBITS AND CREDITS | |||
| DEBITS ($) | CREDITS ($) | ||
| 47.16 | 4,500 | ||
| 18,816.71 | 2,358 | ||
| 12,005.87 | |||
| 18,816.87 | 18,863.87 | ||
Table (10)
Equality of debit and credit column in Cash payment journal:
| EQUALITY OF DEBITS AND CREDITS | |||
| DEBITS ($) | CREDITS ($) | ||
| 6,877.65 | 68.6 | ||
| 3,430.00 | 10,239.05 | ||
| 10,307.65 | 10,307.65 | ||
Table (11)
2, 3, 4, and 6.
Post the appropriate special journal to the general ledger.
Explanation of Solution
General ledger: General ledger is a record of all accounts of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity, necessary to prepare financial statements.
7.
Prepare a trail balance of Y Company.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a trail balance of Y Company.
| Y company | ||
| Trail balance | ||
| January 31, 20__ | ||
| Account Name | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| Cash | 17,317.66 | |
| Accounts receivable | 4,912.2 | |
| Merchandise inventory | 20,584 | |
| Supplies | 685.54 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 390 | |
| Equipment | 3,644 | |
| Accounts payable | 3,848.54 | |
| Employee's federal income tax payable | 795 | |
| FICA social security tax payable | 731.6 | |
| FICA Medicare tax payable | 171 | |
| State unemployment tax payable | 318.6 | |
| Federal unemployment tax payable | 35.4 | |
| Mr. Y Capital | 39,500 | |
| Mr. Y Drawings | 1,000 | |
| Sales | 17,673.07 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | 47 | |
| Sales discounts | 47.16 | |
| Purchases | 6,530 | |
| Purchases returns and allowances | 87 | |
| Purchases discounts | 68.6 | |
| Freight in | 206 | |
| Salary expense | 5,899.95 | |
| Payroll tax expense | 805.3 | |
| Rent expense | 850 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 310 | |
| 63,228.81 | 63,228.81 | |
Table (12)
8.
Prepare a schedule for accounts receivable and accounts payable.
Explanation of Solution
Schedule for the accounts receivable:
| Y company | |
| Schedule of accounts receivable | |
| January 31, 20__ | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| B company | 1,697.2 |
| E and C company | 1,115 |
| V company | 2,100 |
| Total accounts receivable | 4912.2 |
Table (13)
| H company | |
| Schedule of accounts payable | |
| January 31, 20__ | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| C company | 3,755 |
| D company | 93.54 |
| Total accounts payable | 3848.54 |
Table (14)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub


