
Concept explainers
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method.
Explanation of Solution
Absorption costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering all fixed as well as the variable or direct costs. The
Variable costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering only the variable or direct costs or the cost that happened to occurred due to the product only. It also called as marginal costing as it takes marginal costs while calculating the product cost.
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method as follows:
Comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month:
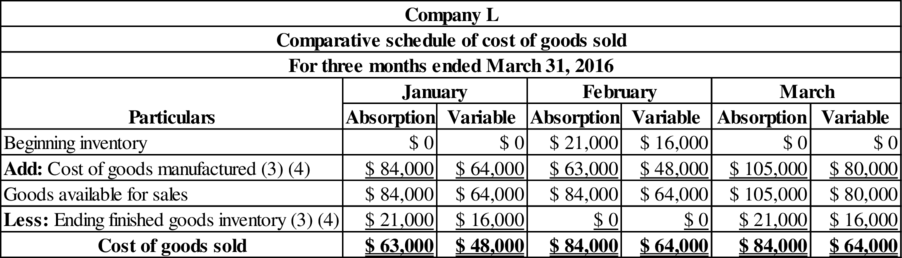
Table (1)
Comparative income statement for each month:
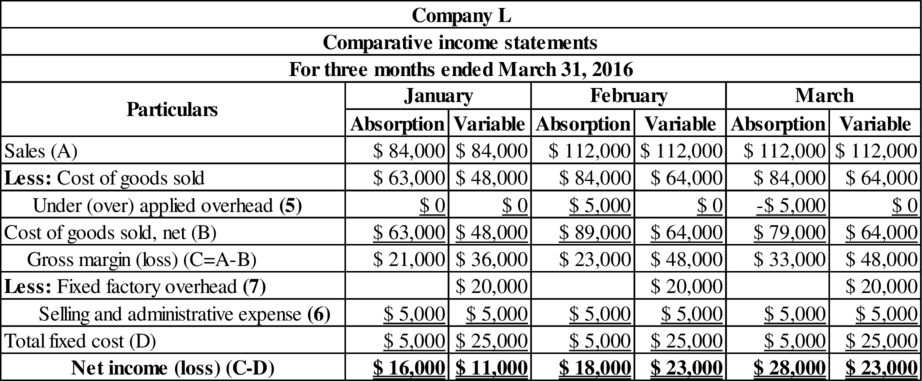
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Calculate the absorption costing per unit.
Working note (2):
Calculate the ending inventory units for each month.
| Particulars | January | February | March |
| Beginning inventory | 0 | 1,000 | 0 |
| Add: Number of units produced | 4,000 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Less: Number of units sold | 3,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 |
| Ending inventory | 1,000 | 0 | 1,000 |
Table (3)
Working note (3):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under absorption costing for each month.
| Particulars | January | February | March |
| Number of units produced (A) | 4,000 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (B) (1) | $ 21 | $ 21 | $ 21 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | $ 84,000 | $ 63,000 | $ 105,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 1,000 | 0 | 1,000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (D) | $ 21 | $ 21 | $ 21 |
| Ending inventory | $ 21,000 | $ 0 | $ 21,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 1,000 | 0 |
| Absorption cost per unit (F) | $ 21 | $ 21 | $ 21 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 21,000 | $ 0 |
Table (4)
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under variable costing for each month.
| Particulars | January | February | March |
| Number of units produced (A) | 4,000 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
| Variable cost per unit (B) | $ 16 | $ 16 | $ 16 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | $ 64,000 | $ 48,000 | $ 80,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 1,000 | 0 | 1,000 |
| Variable cost per unit (D) | $ 16 | $ 16 | $ 16 |
| Ending inventory | $ 16,000 | $ 0 | $ 16,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 1,000 | 0 |
| Variable cost per unit (F) | $ 16 | $ 16 | $ 16 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 16,000 | $ 0 |
Table (5)
Working note (5):
Calculate the under or over applied fixed overhead.
January:
February:
March:
Working note (6):
Calculate the fixed selling and administrative expense per month.
Working note (7):
Calculate the fixed factory overhead per month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
- I need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardCan you solve this financial accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
- Gabrien is a full-time exempt employee at a local electricity co-operative. He earns an annual salary of $55,130 and is paid biweekly. He contributes 3% of his earnings to his 401(k) account and has no other pre-tax deductions. What is his Social Security tax deduction for each pay period?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this financial accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forward
- I need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardThe Great Eastern TableGreat Eastern Table Company produces dining tables in a three-stage process: Sawing, Assembly, and Staining. Costs incurred in the Sawing Department during September are summarized as follows: Working in process inventory sawing. September 1 balance = 0Direct materials = 1,860,000Direct labor = 143,000Manufacturing overhead = 161,500Direct materials (lumber) are added at the beginning of the sawing process, while conversion costs are incurred evenly throughout the process. September activity in the Sawing Department included sawing of 13,000 meters of lumber, which were transferred to the Assembly Department. Also, work began on 2,000 meters of lumber, which on September 30 were 75% of the way through the sawing process.arrow_forwardBlack Oil Company is trying to decide whether to lease or buy a new computer-assisted drilling system for its extraction business. Management has already determined that acquisition of the system has a positive NPV. The system costs $9.4 million and qualifies for a 25% CCA rate. The equipment will have a $975,000 salvage value in five years. Black Oil’s tax rate is 36%, and the firm can borrow at 9%. Cape Town Company has offered to lease the drilling equipment to Black Oil for payments of $2.15 million per year. Cape Town’s policy is to require its lessees to make payments at the start of the year. Suppose it is estimated that the equipment will have no savage value at the end of the lease. What is the maximum lease payment acceptable to Black Oil now?arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





