
Organic Chemistry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781260119107
Author: Janice Gorzynski Smith
Publisher: McGraw Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 42P
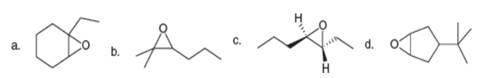
Now that you have learned how to name
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
When talking about the acidity of carboxylic acids, is it the same thing to say higher or stronger acidity?
Using the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$
Indicate characteristics of oxodec acid.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (6th Edition)
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 10.2 - Problem 10.2 How many degrees of unsaturation are...Ch. 10.3 - Give the IUPAC name for each alkene. abcdeCh. 10.3 - Give the IUPAC name for each polyfunctional...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 9PCh. 10.6 - Linolenic acidTable 10.2 and stearidonic acid are...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 12PCh. 10.9 - Problem 10.13 What product is formed when each...Ch. 10.9 - Prob. 14PCh. 10.10 - Problem 10.15 Draw the products formed when each...
Ch. 10.10 - Prob. 16PCh. 10.10 - Prob. 17PCh. 10.10 - Addition of HBr to which of the following alkenes...Ch. 10.11 - Problem 10.19 Draw the products, including...Ch. 10.11 - Prob. 20PCh. 10.12 - Problem 10.21 What two alkenes give rise to each...Ch. 10.12 - Prob. 22PCh. 10.13 - Problem 10.23 Draw the products of each reaction,...Ch. 10.14 - Problem 10.24 Draw all stereoisomers formed in...Ch. 10.15 - Prob. 25PCh. 10.16 - Problem 10.26 What alkylborane is formed from...Ch. 10.16 - Draw the products formed when each alkene is...Ch. 10.16 - What alkene can be used to prepare each alcohol as...Ch. 10.16 - Prob. 29PCh. 10.17 - Draw the products of each reaction using the two...Ch. 10.18 - Problem 10.31 Devise a synthesis of each compound...Ch. 10 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a.b.Ch. 10 - a Label the carbon-carbon double bond in A as E or...Ch. 10 - Prob. 34PCh. 10 - 10.35 Calculate the number of degrees of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 36PCh. 10 - Label the alkene in each drug as E or Z....Ch. 10 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a. c. e. b....Ch. 10 - Prob. 39PCh. 10 - 10.40 (a) Draw all possible stereoisomers of, and...Ch. 10 - Prob. 41PCh. 10 - 10.42 Now that you have learned how to name...Ch. 10 - Prob. 43PCh. 10 - Prob. 44PCh. 10 - Prob. 45PCh. 10 - Draw the products formed when (CH3)2C=CH2 is...Ch. 10 - What alkene can be used to prepare each alkyl...Ch. 10 - Prob. 48PCh. 10 - Draw the constitutional isomer formed in each...Ch. 10 - Prob. 50PCh. 10 - Draw all stereoisomers formed in each reaction. a....Ch. 10 - Draw the products of each reaction, including...Ch. 10 - Prob. 53PCh. 10 - Draw a stepwise mechanism that shows how all three...Ch. 10 - Less stable alkenes can be isomerized to more...Ch. 10 - Prob. 60PCh. 10 - Prob. 61PCh. 10 - Bromoetherification, the addition of the elements...Ch. 10 - Devise a synthesis of each product from the given...Ch. 10 - 10.65 Draw a synthesis of each compound from...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
2. A gene is a segment of DNA that has the information to produce a functional product. The functional product ...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles
Why are mutants used as test organisms in the Ames test?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
An electric motor has an effective resistance of 32.0 and an inductive reactance of 45.0 when working under l...
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
11. In the early 1800s, French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck suggested that the best explanation for the rel...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #24; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j04zMFwDeDU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY