
Introductory Circuit Analysis; Laboratory Manual For Introductory Circuit Analysis Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780134297446
Author: Boylestad, Robert L.
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 41P
For the system in Fig. 10.109. using a DMM with a 10 M
a. Determine the voltmeter reading one time constant after the switch is closed.
b. Find the current ic two time constants after the switch is closed.
c. Calculate the time that must pass after the closing of the switch for the voltage UC to be 50V.
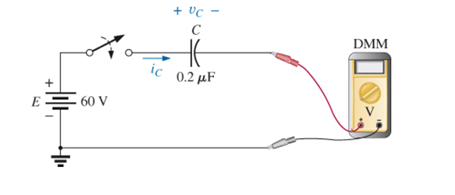
Fig. 10.109
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A left-sided signal x(t)=-ebt u(-t):
A right-sided signal x(t)=e¯at u(t)
Find Laplace transform of x(t)=u(t)
Find Laplace transform of x(t) = −e¯btu(−t) + e¯atu(t)
Find Laplace transform of x(t) = u(t)
Expert only, don't use artificial intelligence ,or screenshot of an AI solving steps
Chapter 10 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis; Laboratory Manual For Introductory Circuit Analysis Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
Ch. 10 - a. Find the electric field strength at a point 1 m...Ch. 10 - The electric field strength is 72 newtons/coulomb...Ch. 10 - Find the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor...Ch. 10 - How much charge is deposited on the plates of a...Ch. 10 - a. Find the electric field strength between the...Ch. 10 - A 6.8 pF parallel plate capacitor has 160 C of...Ch. 10 - Find the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 7 if the dielectric is...Ch. 10 - Find the distance in mils between the plates of a...Ch. 10 - The capacitance of a capacitor with a dielectric...
Ch. 10 - The plates of a parallel plate capacitor with a...Ch. 10 - A parallel plate air capacitor has a capacitance...Ch. 10 - Find the maximum voltage that can be applied...Ch. 10 - Find the distance in micrometers between the...Ch. 10 - A 22 pF capacitor has -200 ppm/C at room...Ch. 10 - What is the capacitance of a small teardrop...Ch. 10 - A large, flat, mica capacitor is labeled 471F....Ch. 10 - A small, flat, disc ceramic capacitor is labeled...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.94, composed of...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 19 for R=100k, and compare the...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.95, composed of...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.96, composed of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 23PCh. 10 - The voltage across a 10 F capacitor in a series...Ch. 10 - For the R-C circuit in Fig. 10.97. composed of...Ch. 10 - For the network in Fig. 10.98. composed of...Ch. 10 - For the network in Fig.10.99.composed of standard...Ch. 10 - The 1000 F capacitor in Fig.10.100 is charged to...Ch. 10 - The capacitor in Fig. 10.101 is initially charged...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 29 if the initial charge is -40V.Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 29 if the initial charge is +40V.Ch. 10 - The capacitor in Fig. 10.102 is initially charged...Ch. 10 - The capacitor in Fig. 10.103 is initially charged...Ch. 10 - The capacitor in Fig. 10.104 is initially charged...Ch. 10 - The capacitors of Fig. 10.105 are initially...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 35 if a 10 k resistor is placed in...Ch. 10 - Given the expression vc=140mV(1-e-t/2ms) a....Ch. 10 - For the automobile circuit of Fig. 10.106. VL must...Ch. 10 - Design the network in Fig.10.107 such that the...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.108: a. Find the time...Ch. 10 - For the system in Fig. 10.109. using a DMM with a...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.110: a. Find the...Ch. 10 - The capacitor in Fig. 10.111 is initially charged...Ch. 10 - The capacitors in Fig. 10.112 are initially...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.113: a. Find the...Ch. 10 - The capacitor in Fig. 10.114 is initially charged...Ch. 10 - For the system in Fig. 10.115, using a DMM with a...Ch. 10 - Find the waveform for the average current if the...Ch. 10 - Find the waveform for the average current if the...Ch. 10 - Given the waveform in Fig.10.118 for the current...Ch. 10 - Find the total capacitance CT for the network in...Ch. 10 - Find the total capacitance CT for the network in...Ch. 10 - Find the steady-state voltage across and the...Ch. 10 - Find the steady-state voltage across and the...Ch. 10 - For the configuration in Fig. 10.123, determine...Ch. 10 - For the configuration in Fig.10.124, determine the...Ch. 10 - Find the energy stored by a 120 pF capacitor with...Ch. 10 - If the energy stored by a 6 F capacitor is 1200 J,...Ch. 10 - For the network in Fig. 10.125, determine the...Ch. 10 - An electronic flashgun has a 1000 F capacitor that...Ch. 10 - Using PSpice or Multisim, verify the results in...Ch. 10 - Using the initial condition operator, verify the...Ch. 10 - Using PSpice or Multisim, verify the results for...Ch. 10 - Using PSpice or Multisim, verify the results in...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- find inverse LT for the following functions 1- [0.2s+1.4] s2+1.96. 2. L-1 5s+1 Ls2-25. 4s+32 3. L- L(s2-16).arrow_forwardQ Figurel shows the creation of the Frequency Reuse Pattern Using the Cluster Size K (A) illustrates how i and j can be used to locate a co-channel cell. Juster Cluster CB Cluster 2 X=7(i=2,j=1)arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Q2. For the transformer shown in Fig. 1. A. Plot the winding connection for the transformer and justify your answer. (4M) B. If the transformer is adopted in 12 pulse diode rectifier, where two-series connected bridge rectifiers are used to supply a highly inductive load with 100 A. (i) Select a suitable turns ratio for the transformer (ii) Plot the line current of each winding ( secondary + primary) showing the current magnitude at each interval (iii) Use Fourier Page 1 of 3 analysis to obtain the Fourier series of all line currents then calculate the THD of the input current. (8=0° (16M) (Y) = 30° Fig. 1 P. I v Iarrow_forwardQ2. For the transformer shown in Fig.1, A. Find the phase shift between the primary and star-connected secondary. B. If the transformer is adopted in a 12-pulse diode rectifier, where a two-series connected bridge rectifier is connected in series and supplies a highly inductive load (i) Select a suitable turns ratio for the transformer (ii) Plot the line current of each winding (secondary + primary). (iii)Using Fourier analysis to obtain the Fourier series of all line currents, then calculate the THD of the input current. (iv) Draw the output voltage of the first and second rectifiers and give the relation of the total output voltage. N2 B C Fig. 1 N3 aarrow_forwardQ2.A. It is planned to use the transformer shown in Fig. 1, a 12-pulse rectifier. Each secondary is connected to three phase controlled bridge rectifier. The two rectifiers are connected in series to supply a highly inductive load. 1. Based on the phasor relationship between different windings. If suitable turns ratio is selected, is it possible to use this transformer to produce 12 pulse output voltage? Show the reason behind your answer. 2. Assuming this arrangement is possible to be used in 12-pulse rectifier, draw the output voltage of the 1st and 2nd rectifier and give the relation of the total output voltage. 3. Use the Fourier analysis to show the harmonics in all line currents of the transformer. A B in C Fig. 1 b la a 2 b.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY