
a)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
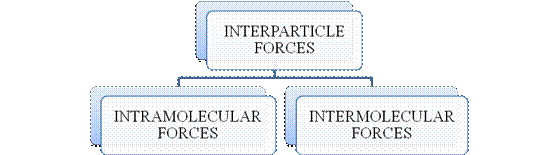
Figure 1
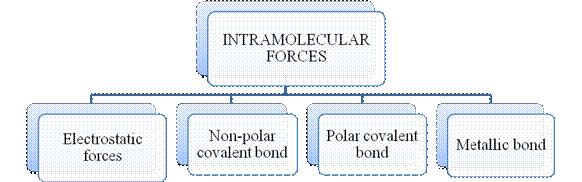
Figure 2
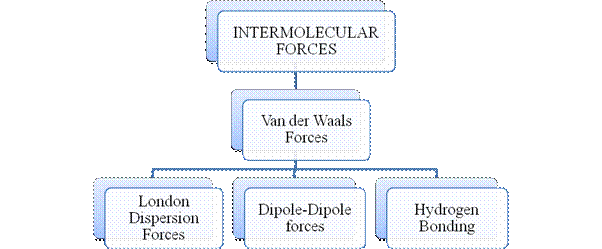
Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
b)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
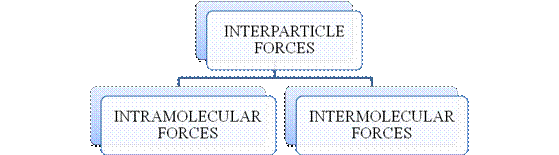
Figure 1
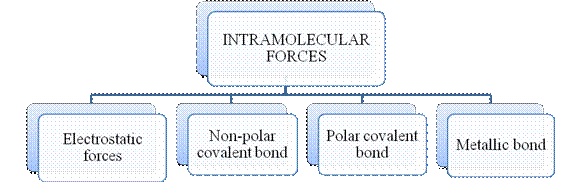
Figure 2
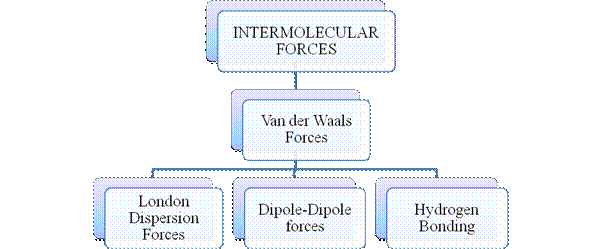
Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
c)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
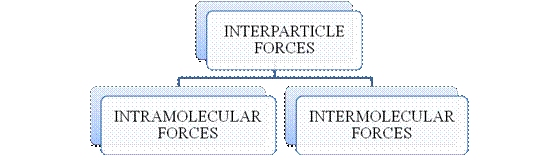
Figure 1

Figure 2
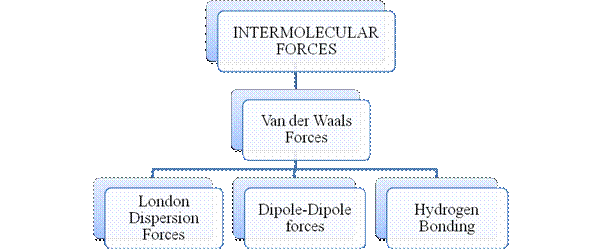
Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
d)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
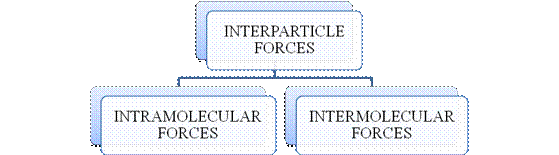
Figure 1

Figure 2

Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + Enhanced Webassign Printed Access Card For Chemistry, Multi-term Courses
- Using wedge-and-dash bonds, modify the bonds on the chiral carbon in the molecule below so the molecule has R stereochemical configuration. NH H Br X टेarrow_forwardProvide photos of models of the following molecules. (Include a key for identification of the atoms) 1,2-dichloropropane 2,3,3-trimethylhexane 2-bromo-3-methybutanearrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forward
- Given a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forwardTRANSMITTANCE เบบ Please identify the one structure below that is consistent with the 'H NMR and IR spectra shown and draw its complete structure in the box below with the protons alphabetically labeled as shown in the NMR spectrum and label the IR bands, including sp³C-H and sp2C-H stretch, indicated by the arrows. D 4000 OH LOH H₂C CH3 OH H₂C OCH3 CH3 OH 3000 2000 1500 HAVENUMBERI-11 1000 LOCH3 Draw your structure below and label its equivalent protons according to the peak labeling that is used in the NMR spectrum in order to assign the peaks. Integrals indicate number of equivalent protons. Splitting patterns are: s=singlet, d=doublet, m-multiplet 8 3Hb s m 1Hd s 3Hf m 2Hcd 2Had 1He 鄙视 m 7 7 6 5 4 3 22 500 T 1 0arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





