
Safegate Foods, Inc., is redesigning the checkout lanes in its supermarkets throughout the country and is considering two designs. Tests on customer checkout times conducted at two stores where the two new systems have been installed result in the following summary of the data.
| System A | System B |
| n1 = 120 | n2 = 100 |
|
|
|
| σ1 = 2.2 minutes | σ2 = 1.5 minutes |
Test at the .05 level of significance to determine whether the population
Test whether the population mean checkout times of the two systems differ at .05 level of significance or not.
Suggest the preferable system.
Answer to Problem 38SE
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that, there is a difference between the population mean checkout times of the two systems.
The preferable system is system A.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The results of the tests on customer checkout times at system A and system B are as follows:
| System A | System B |
The level of significance is
State the hypothesis:
The test hypotheses are as follows:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no difference between the population mean checkout times of the two systems.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is difference between the population mean checkout times of the two systems.
Test statistic:
The test statistic for hypothesis tests about
Substitute
Thus, the test statistic is 2.79.
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain the mean using MINITAB software is as follows,
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose X Value and Two Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the data value as 2.79.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is as follows:
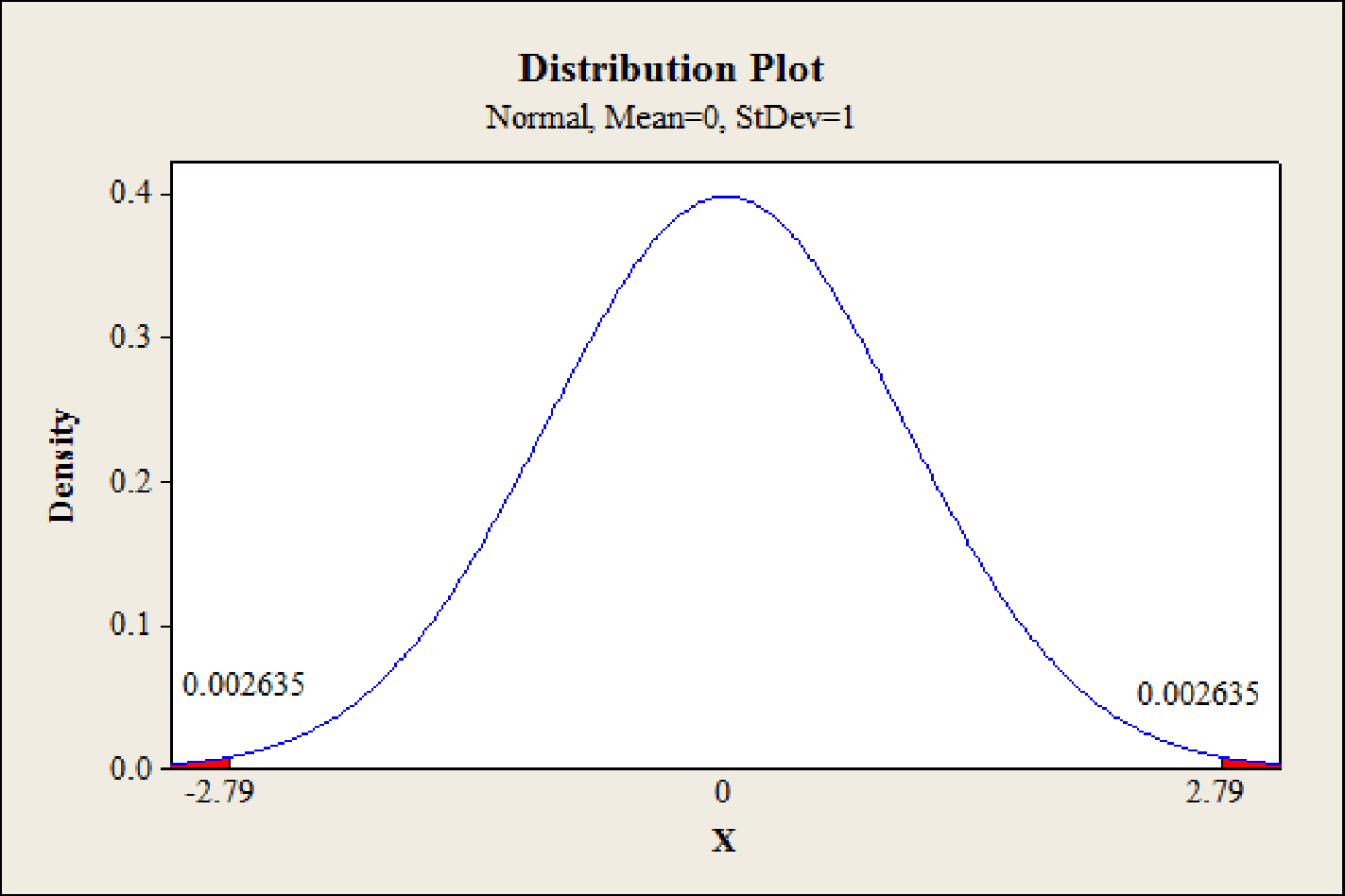
Thus, the p-value is 0.0052
Decision rule based on p-value approach:
If p-value ≤ α, then reject the null hypothesis H0.
If p-value > α, then fail to reject the null hypothesis H0.
Conclusion:
Here, the p-value 0.0052 is less than or equal to the significance level 0.05.
That is,
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Therefore, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that, there is a difference between the population mean checkout times of the two systems.
Thus, there is a difference between the population mean checkout times of the two systems.
Here the mean checkout time of system B is less when compared to the mean checkout time of system A.
Therefore, system A is preferable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK STATISTICS FOR BUSINESS & ECONOMICS
- Negate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forwardQuestion 6: Negate the following compound statements, using De Morgan's laws. A) If Alberta was under water entirely then there should be no fossil of mammals.arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forward
- Characterize (with proof) all connected graphs that contain no even cycles in terms oftheir blocks.arrow_forwardLet G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C3 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C3 free). Prove that G is a complete bipartite grapharrow_forwardProve sufficiency of the condition for a graph to be bipartite that is, prove that if G hasno odd cycles then G is bipartite as follows:Assume that the statement is false and that G is an edge minimal counterexample. That is, Gsatisfies the conditions and is not bipartite but G − e is bipartite for any edge e. (Note thatthis is essentially induction, just using different terminology.) What does minimality say aboutconnectivity of G? Can G − e be disconnected? Explain why if there is an edge between twovertices in the same part of a bipartition of G − e then there is an odd cyclearrow_forward
- Let G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C4 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C4 free). Prove that G has a vertex adjacent to all othersarrow_forwardWe consider a one-period market with the following properties: the current stock priceis S0 = 4. At time T = 1 year, the stock has either moved up to S1 = 8 (with probability0.7) or down towards S1 = 2 (with probability 0.3). We consider a call option on thisstock with maturity T = 1 and strike price K = 5. The interest rate on the money marketis 25% yearly.(a) Find the replicating portfolio (φ, ψ) corresponding to this call option.(b) Find the risk-neutral (no-arbitrage) price of this call option.(c) We now consider a put option with maturity T = 1 and strike price K = 3 onthe same market. Find the risk-neutral price of this put option. Reminder: A putoption gives you the right to sell the stock for the strike price K.1(d) An investor with initial capital X0 = 0 wants to invest on this market. He buysα shares of the stock (or sells them if α is negative) and buys β call options (orsells them is β is negative). He invests the cash balance on the money market (orborrows if the amount is…arrow_forwardDetermine if the two statements are equivalent using a truth tablearrow_forward
- Question 4: Determine if pair of statements A and B are equivalent or not, using truth table. A. (~qp)^~q в. р л~9arrow_forwardDetermine if the two statements are equalivalent using a truth tablearrow_forwardQuestion 3: p and q represent the following simple statements. p: Calgary is the capital of Alberta. A) Determine the value of each simple statement p and q. B) Then, without truth table, determine the va q: Alberta is a province of Canada. for each following compound statement below. pvq р^~q ~рл~q ~q→ p ~P~q Pq b~ (d~ ← b~) d~ (b~ v d) 0 4arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



