
Explain whether it is possible that the acceptance to graduate school is independent of department at the level of significance of
Answer to Problem 2CS
There is not enough evidence to conclude that the acceptance rate does not differ among departments.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The
Contingency table:
A contingency table is obtained as using two qualitative variables. One of the qualitative variable is row variable that has one category for each row of the table another is column variable has one category for each column of the table.
Step 1:
The hypotheses are:
Null Hypothesis:
That is, the acceptance rate does not differ among departments.
Alternate Hypothesis:
That is, the acceptance rate differs among departments.
Step 2:
Now, it is obtained that,
| Department | A | B | C | D | E | F | Row Total |
| Accept | 601 | 370 | 322 | 269 | 147 | 46 | 1,755 |
| Reject | 332 | 215 | 596 | 523 | 437 | 668 | 2,771 |
| Column Total | 933 | 585 | 918 | 792 | 584 | 714 | 4,526 |
Step 3:
Expected frequencies:
The expected frequencies in case of contingency table is obtained as,
Now, using the formula of expected frequency it is found that the expected frequency for the accepted applicants in department A is obtained as,
Hence, in similar way the expected frequencies are obtained as,
| Department | A | B | C |
| Accept | |||
| Reject |
| Department | D | E | F |
| Accept | |||
| Reject |
Step 4:
Level of significance:
The level of significance is given as 0.01.
Chi-Square statistic:
The chi-square statistic is obtained as
The classification of department can be rewritten as,
| A | 1 |
| B | 2 |
| C | 3 |
| D | 4 |
| E | 5 |
| F | 6 |
Test Statistic:
Software procedure:
Step -by-step software procedure to obtain test statistic using MINITAB software is as follows:
- Select Stat > Table > Cross Tabulation and Chi-Square.
- Check the box of Raw data (categorical variables).
- Under For rows enter Row.
- Under For columns enter Department.
- Check the box of Count under Display.
- Under Chi-Square, click the box of Chi-Square test.
- Select OK.
- Output using MINITAB software is given below:
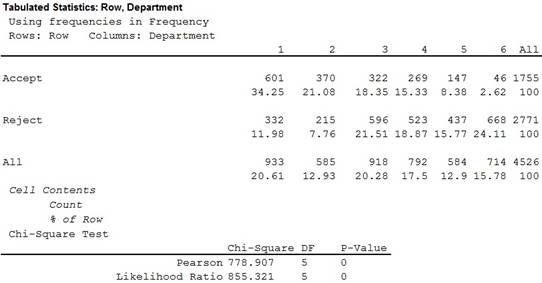
Thus, the value of chi-square statistic is 778.907.
It is known that under the null hypothesis
In the given question there are 2 rows and 6 columns.
Hence, the degrees of freedom is
Thus, the degree of freedom is 5.
It is known that when the null hypothesis
It is found that all the expected frequencies corresponding to all rows and columns of the given contingency table are more than 5.
Hence, the test of independence is appropriate.
Step 5:
Critical value:
In a test of hypotheses the critical value is the point by which one can reject or accept the null hypothesis.
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain critical value using MINITAB software is as follows:
- Select Graph > Probability distribution plot > view probability
- Select Chi -Square under distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 5.
- Choose Probability Value and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.01 under shaded area.
- Select OK.
- Output using MINITAB software is given below:
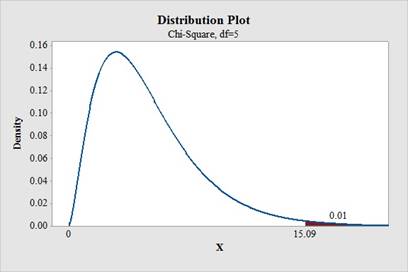
Hence, the critical value at
Rejection rule:
If the
Step 6:
Conclusion:
Here, the
That is,
Thus, the decision is “reject the null hypothesis”.
Thus, there is not enough evidence to conclude that the acceptance rate does not differ among departments.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ESSENT. STAT ACCESS CARD
- Questions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardA population that is uniformly distributed between a=0and b=10 is given in sample sizes 50( ), 100( ), 250( ), and 500( ). Find the sample mean and the sample standard deviations for the given data. Compare your results to the average of means for a sample of size 10, and use the empirical rules to analyze the sampling error. For each sample, also find the standard error of the mean using formula given below. Standard Error of the Mean =sigma/Root Complete the following table with the results from the sampling experiment. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Sample Size Average of 8 Sample Means Standard Deviation of 8 Sample Means Standard Error 50 100 250 500arrow_forwardA survey of 250250 young professionals found that two dash thirdstwo-thirds of them use their cell phones primarily for e-mail. Can you conclude statistically that the population proportion who use cell phones primarily for e-mail is less than 0.720.72? Use a 95% confidence interval. Question content area bottom Part 1 The 95% confidence interval is left bracket nothing comma nothing right bracket0.60820.6082, 0.72510.7251. As 0.720.72 is within the limits of the confidence interval, we cannot conclude that the population proportion is less than 0.720.72. (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardA survey of 250 young professionals found that two-thirds of them use their cell phones primarily for e-mail. Can you conclude statistically that the population proportion who use cell phones primarily for e-mail is less than 0.72? Use a 95% confidence interval. Question content area bottom Part 1 The 95% confidence interval is [ ], [ ] As 0.72 is ▼ above the upper limit within the limits below the lower limit of the confidence interval, we ▼ can cannot conclude that the population proportion is less than 0.72. (Use ascending order. Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardQuestions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forward
- Questions An insurance company's cumulative incurred claims for the last 5 accident years are given in the following table: Development Year Accident Year 0 2018 1 2 3 4 245 267 274 289 292 2019 255 276 288 294 2020 265 283 292 2021 263 278 2022 271 It can be assumed that claims are fully run off after 4 years. The premiums received for each year are: Accident Year Premium 2018 306 2019 312 2020 318 2021 326 2022 330 You do not need to make any allowance for inflation. 1. (a) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the basic chain ladder method. (b) Calculate the reserve at the end of 2022 using the Bornhuetter-Ferguson method. 2. Comment on the differences in the reserves produced by the methods in Part 1.arrow_forwardFrom a sample of 26 graduate students, the mean number of months of work experience prior to entering an MBA program was 34.67. The national standard deviation is known to be18 months. What is a 90% confidence interval for the population mean? Question content area bottom Part 1 A 9090% confidence interval for the population mean is left bracket nothing comma nothing right bracketenter your response here,enter your response here. (Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA test consists of 10 questions made of 5 answers with only one correct answer. To pass the test, a student must answer at least 8 questions correctly. (a) If a student guesses on each question, what is the probability that the student passes the test? (b) Find the mean and standard deviation of the number of correct answers. (c) Is it unusual for a student to pass the test by guessing? Explain.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





