
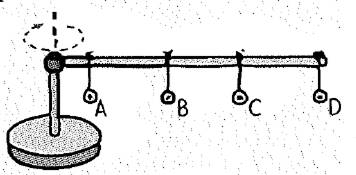
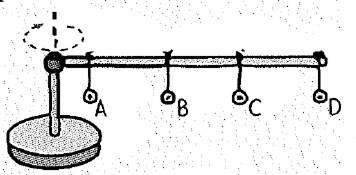
A meterstick is mounted horizontally above a turntable as shown. Identical metal washers are hung at the positions shown. The turntable and meterstick are then spun. Rank from greatest to least, the following quantities for the washers.
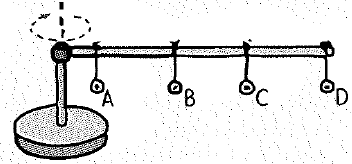
a. rotational speed
b. linear speed
c. angle the string makes with the vertical
d. inward force on each
e. outward force on each
(a)
To rank: The washer on the basis of rotational speed from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
The rank of the rotational speed from greatest to least is
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Rotational speed is the number of rotations per unit time and is also known as angular velocity. It is represented as
The given figure is shown below.
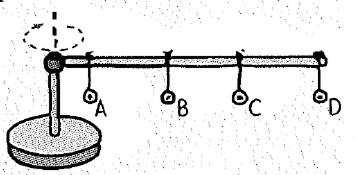
Identical metal washers are hung at the positions on a meterstick is mounted horizontally above a turntable.
The rotation of turn table rotates the metal washers in the meterstick at the same speed. Hence, the rotational speeds of the metal washers are same.
Conclusion:
Thus, the rank of the rotational speed from greatest to least is
(b)
To rank: The washer on the basis of the linear speed from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
The rank of the linear speed from greatest to least is
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The expression for the linear or tangential speed is,
Here,
Tangential speed is dependent on the distance from the axis of rotation and rotational speed.
The given figure is shown below.
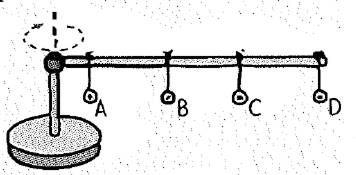
The linear speed and the radius of its circular path’ radius are directly proportional to each other.
The radius of the metal washer D is more when compared to the other washers.
The radius of the metal washer A is less when compared to the other washers.
So, the metal washer D’s linear speed is greater than the linear speed of the other washers.
Conclusion:
Thus, the rank of the linear speed from greatest to least is
(c)
To rank: The washer on the basis of angle that string makes with the vertical from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
The rank of the angle the string makes with the vertical from greatest to least is
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The force exerted on the system is directly proportional to the square of the tangential speed.
Linear speed varies with the distance from the axis of rotation.
The expression for the linear or tangential speed is,
Here,
The given figure is shown below.
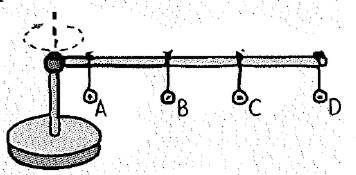
The linear speed is directly proportional to the radius of its circular path.
From part (b), the rank of the linear speed from greatest to least is
The radius of the metal washer D is more when compared to the other washers.
The radius of the metal washer A is less when compared to the other washers.
By comparing the values of the angle the string makes with the vertical is
Conclusion:
Thus, the rank of the angle the string makes with the vertical from greatest to least is
(d)
To rank: The washer on the basis of the inward force on each from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
The rank of the inward force on each from greatest to least is
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The expression for the centripetal force is,
Here,
The expression for the linear or tangential speed is,
Here,
The given figure is shown below.
 From part (b), the rank of the linear speed from greatest to least is
From part (b), the rank of the linear speed from greatest to least is
The centripetal force or inward force is directly proportional to the square of the linear speed.
By comparing the values of the linear speed, the centripetal force is
Conclusion:
Thus, the rank of the inward force on each from greatest to least is
(e)
To rank: The washers on the basis of outward force from greatest to least.
Answer to Problem 20A
The outward force is not there for the system.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The expression for the centripetal force is,
Here,
The expression for the linear or tangential speed is,
Here,
The given figure is shown below.
The centripetal force is the inward force and it is directly proportional to the square of the linear speed.
In the meterstick and turntable, there is only the centripetal or inward force act on the system.
So there is outward force doesn’t act on the system.
Conclusion:
Thus, outward force is not there for the system.
Chapter 10 Solutions
EP CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS-ONLINE ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- PROBLEM 4 What is the resultant of the force system acting on the connection shown? 25 F₁ = 80 lbs IK 65° F2 = 60 lbsarrow_forwardThree point-like charges in the attached image are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 38.0 cm, and the point (C) is located half way between q1 and q3 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (C). Let q1 = −2.80 µC, q2 = −3.40 µC, and q3 = −4.50 µC. Thank you.arrow_forwardSTRUCTURES I Homework #1: Force Systems Name: TA: PROBLEM 1 Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force in the cable shown. PROBLEM 2 The horizontal component of force F is 30 lb. What is the magnitude of force F? 6 10 4 4 F = 600lbs F = ?arrow_forward
- The determined Wile E. Coyote is out once more to try to capture the elusive Road Runner of Loony Tunes fame. The coyote is strapped to a rocket, which provide a constant horizontal acceleration of 15.0 m/s2. The coyote starts off at rest 79.2 m from the edge of a cliff at the instant the roadrunner zips by in the direction of the cliff. If the roadrunner moves with constant speed, find the minimum velocity the roadrunner must have to reach the cliff before the coyote. (proper sig fig)arrow_forwardHello, I need some help with calculations for a lab, it is Kinematics: Finding Acceleration Due to Gravity. Equations: s=s0+v0t+1/2at2 and a=gsinθ. The hypotenuse,r, is 100cm (given) and a height, y, is 3.5 cm (given). How do I find the Angle θ1? And, for distance traveled, s, would all be 100cm? For my first observations I recorded four trials in seconds: 1 - 2.13s, 2 - 2.60s, 3 - 2.08s, & 4 - 1.95s. This would all go in the coloumn for time right? How do I solve for the experimental approximation of the acceleration? Help with trial 1 would be great so I can use that as a model for the other trials. Thanks!arrow_forwardAfter the countdown at the beginning of a Mario Kart race, Bowser slams on the gas, taking off from rest. Bowser get up to a full speed of 25.5 m/s due to an acceleration of 10.4 m/s2. A)How much time does it take to reach full speed? B) How far does Bowser travel while accelerating?arrow_forward
- The drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Side 1 has an area of 1.90 m^2, Side 2 has an area of 3.90 m^2, the electric field in magnitude is around 215 N/C. Please find the electric flux magnitude through side 1 and 2 combined if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with side 2 is 30.0 degrees. I believe side 1 is 60 degrees but could be wrong. Thank you.arrow_forwardAfter the countdown at the beginning of a Mario Kart race, Bowser slams on the gas, taking off from rest. Bowser get up to a full speed of 25.5 m/s due to an acceleration of 10.4 m/s2.arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Side 1 has an area of 1.90 m^2, Side 2 has an area of 3.90 m^2, the electric field in magnitude is around 215 N/C. Please find the electric flux magnitude through side 1 and 2 combined if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with side 2 is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forward
- The drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m^2, while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m^2. The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Please find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (with both 1 and 2 combined) if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m^2, while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m^2. The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Please find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (with both 1 and 2 combined) if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardAccording to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





