
In the diagram below, label the parts of the respiratory system and the structures that enclose some of its parts
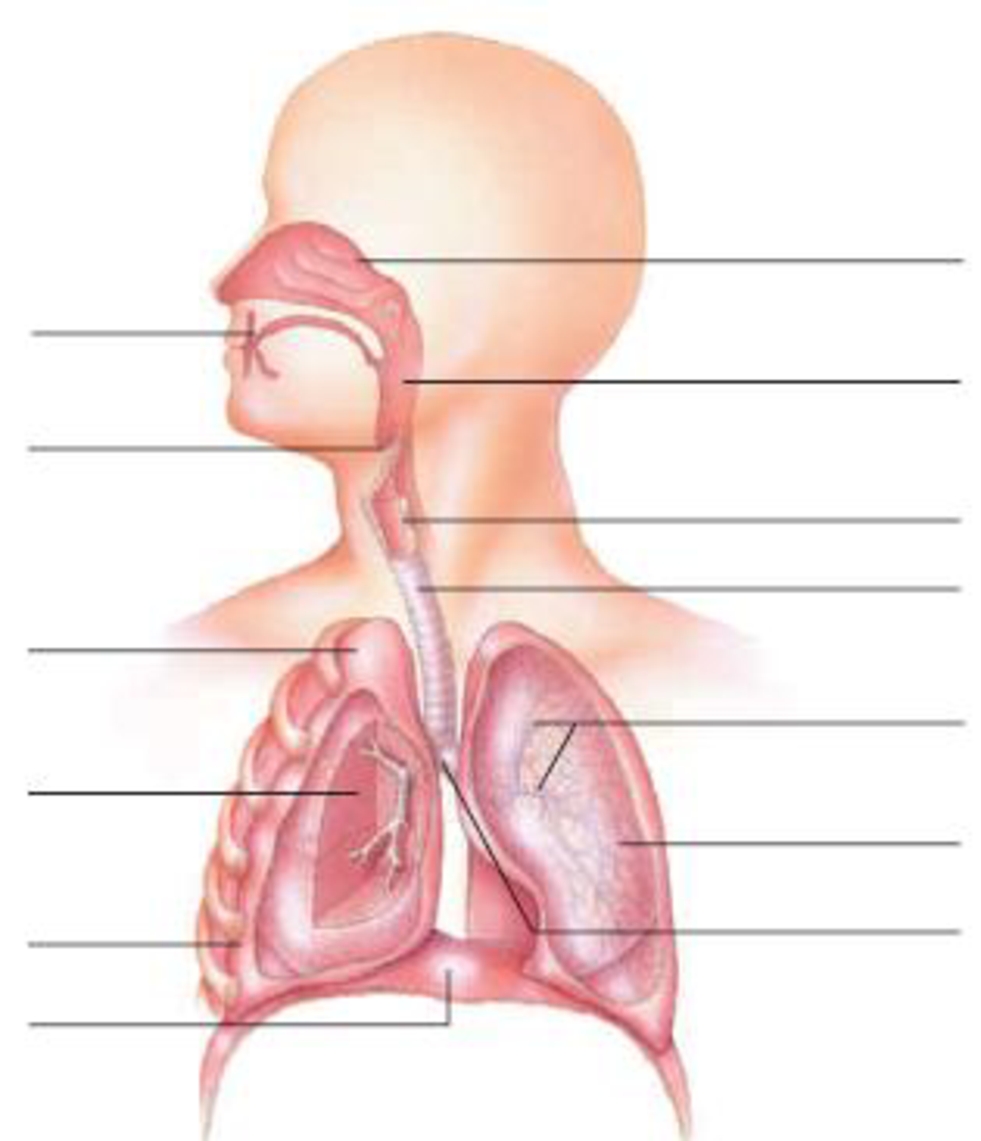
To label: The parts of the respiratory system and the structure that surrounds the parts of respiratory system.
Introduction: The process of gas exchange that occurs between an organism and its environment is known as respiration. For cellular respiration, most of the animal cells need a continuous oxygen supply. During respiration, oxygen is inhaled from the environment and transported to individual cells of the body. Carbon dioxide produced during the cellular respiration is exhaled from the body to the environment.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the parts of the respiratory system and the structure that encloses some of its parts.
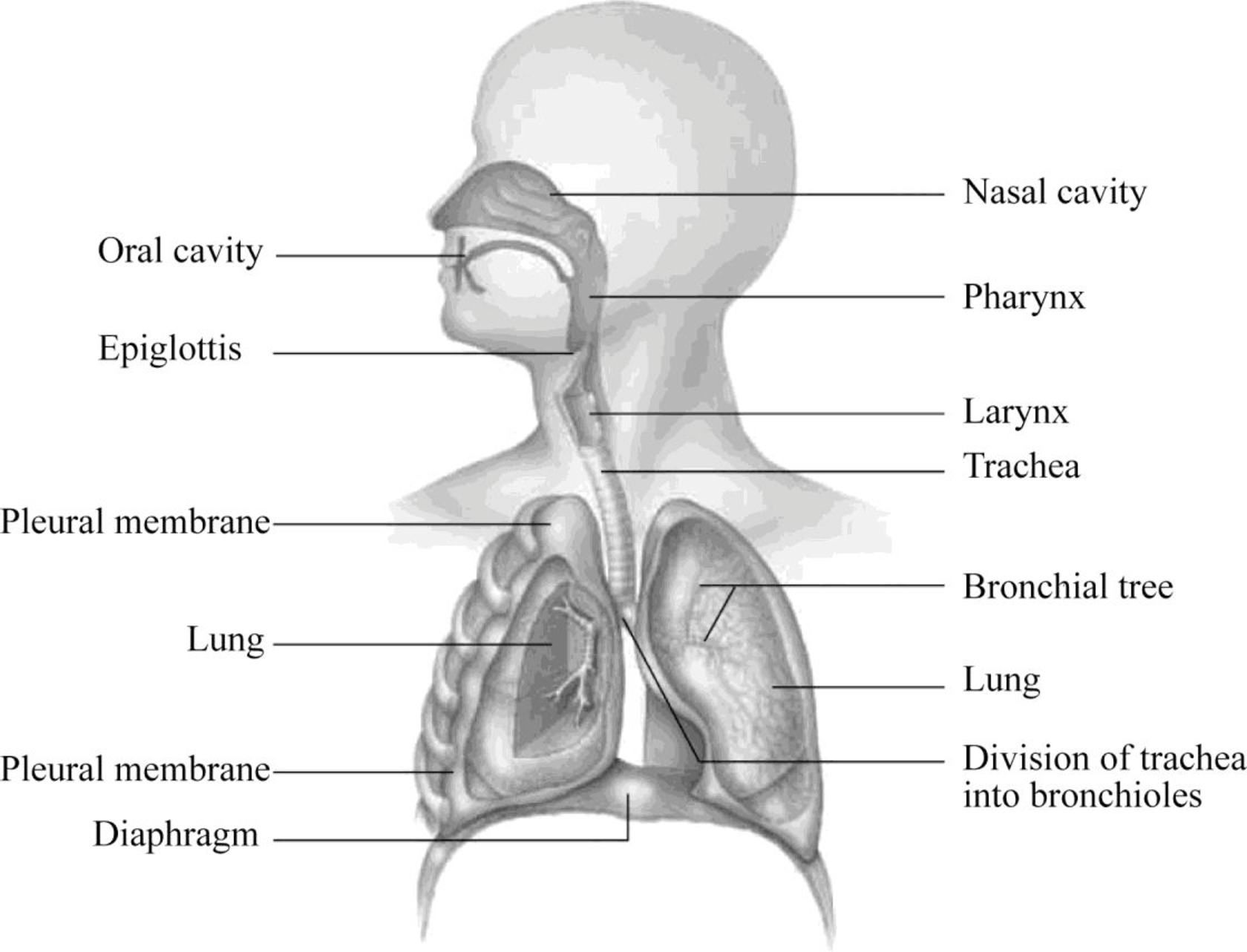
Fig.1: Parts of the respiratory system and the structure that encloses some of its parts
Explanation of Solution
Oral cavity: It is the additional airway when breathing through nasal cavity is ceased.
Nasal cavity: The nasal cavity is oblong-shaped and extends from the nostril to the posterior nasal apertures. The posterior nasal apertures lead into the pharynx.
Pharynx: Pharynx is commonly known as the throat. It is a funnel-shaped pathway of about 13 centimeters in length. It is the common passageway for food and air.
Epiglottis: A flap like structure present in the throat which keeps the food from entering the windpipe and the lungs is called epiglottis.
Larynx: Larynx is also known as the voice box. It is a cylindrical structure of about 4 centimeters in length. It is continuous inferiorly with trachea and superiorly with laryngopharynx.
Trachea: The trachea is a slightly rigid, flexible, and tubular organ that referred to as windpipe. It is an open tube that attaches to the larynx and to two main bronchi.
Pleural membrane: It is double layered membrane that fills with fluid. It keeps the lungs airtight and mostly helps them to stick to the chest wall during breathing.
Bronchial tree: The highly branched system of the respiratory pathway is known as bronchial tree. The bronchial tree originates at the main bronchi and gradually branches into the narrower tubes of the respiratory pathway.
Lungs: Lungs are an important part of the respiratory system. It is the lobed elastic organ that processes the exchange of gaseous which consists of the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the blood stream and the elimination of carbon dioxide from the blood stream to the lungs.
Diaphragm: It is the muscular sheet present between the plural cavity and abdominal cavity. It has an important role in breathing process, in inhalation it contracts and flattens and in exhale, it relaxes.
Division of trachea into bronchioles: Bronchioles represent the ending portion of the conducting pathway of the respiratory system. These bronchioles lead into the initial segments of the respiratory zone (respiratory bronchioles)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781337794909Author:Des Jardins, Terry.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning





