
Concept explainers
Answers to all problems are at the end of this book. Detailed solutions are available in the Student Solutions Manual, Study Guide, and Problems Book.
The Structure and Ionization Properties of
Interpretation: The principal ionic species of
Concept introduction: A nucleotide refers to a basic DNA building block and structural unit. It contains a five-sided sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotides join together to form a chain of DNA. The nucleotides of DNA and RNA are linked covalently by bridges of the phosphate group. A phosphodiester linkage joins the
Answer to Problem 1P
The principal ionic species of
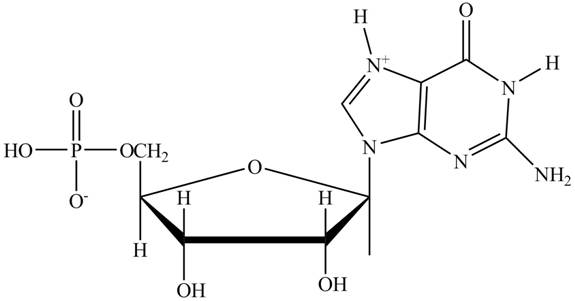
Explanation of Solution
In the polar backbone of DNA and RNA, the phosphate groups are completely ionizable and negatively charged at
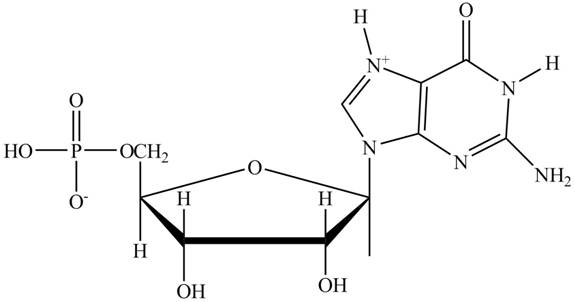
Figure 1
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK BIOCHEMISTRY
- Show the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose.arrow_forwardImagine that aldolase can react with the seven carbon molecule Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (below). Use the mechanism to predict the two products generated.arrow_forwardShow the mechanisms of PGK and PFK-1. How are they different?arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP.arrow_forwardSodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a potent inhibitor of aldolase. It is known to ONLY inhibit theenzyme when it is complexed with substrate. Treatment of the enzyme alone has no effect.What is the mechanism for this inhibition?arrow_forwardA non-hydrolysable ATP (AMPPNP - below) is ingested by a graduate student on a dare. Whateffects would you anticipate on his metabolism?arrow_forward
- Show the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of an [α-1,6] glycosidic linkagebetween two molecules of α-D-glucopyranose. Please sketch the structure and use arrows showing electron flow!arrow_forwardI am a Biochemistry student and I am confused on how to analyze FRAP Analysis using Excel Spread Sheets. The following spread sheet has my 0 minute data listed at top and the 4 minute data listed on the bottom. Sheet: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EXjrCizWiXRPmpittqZA12IB8EkB5eE8iaRqj_iun-IAtg?rtime=Wo9zPHFY3Ug The formula for FRAP Analysis is: FRAP value = A (4 min sample) - A (0 min sample) over A (4 min 30 uM ascorbic acid) - A (0 min 30 uM ascorbic acid) multiplied by 30 uM and the dilution factor of 1/10arrow_forwardHO Fill in the missing boxes. ON 800 NO NO Glucose ATP NADH Hexokinase 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate Mg2+ ADP NAD+, Pi Phosphoglucose Isomerase Glucose-6-Phosphate ON 沁 Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate HO حلمة ADP ADP Phospho Mg2+ glycerate Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate ATP kinase ATP Phosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate Mutase H₁₂O Fructose-6-Phosphate ATP Mg2+ ADP Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate 2-phosphoglycerate H₂O Phosphoenolpyruvate ADP Mg2+ ATP Pyruvatearrow_forward
- In a diffraction experiment of a native crystal, intensity of reflection (-1 0 6) is equivalent to the intensity of reflection (1 0 -6). true or false?arrow_forwardin an x-ray diffraction experiment, moving the detector farther away from the crystal will allow collection of reflection of reflections with high Miller indices. true or false?arrow_forwardShow the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of an [α-1,6] glycosidic linkagebetween two molecules of α-D-glucopyranose.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
