
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Pentane has higher melting point than decane has to be indicated as true or false.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. Decane contains ten carbon atoms and twenty two hydrogen atoms. As the molar mass increases, the London Dispersion forces become stronger and as a result melting and boiling points will also increase. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(b)
Interpretation:
Pentane is a substituted hydrocarbon has to be indicated as true or false.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. The structure of pentane can be given as,

As seen from the above structure, there are no substituents present on the carbon chain. Hence, the given statement is a false one.
(c)
Interpretation:
Pentane is a saturated hydrocarbon has to be indicated as true or false.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. The structure of pentane can be given as,

As there is only single bonds present between the carbon atoms in the entire molecule as shown above, pentane is a saturated hydrocarbon only. The given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
Pentane is nonpolar has to be indicated as true or false.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. The structure of pentane can be given as,

Pentane contains only carbon and hydrogen atom. Therefore, this is a nonpolar molecule only. Given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
Pentane has structural formula of
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. It is a linear
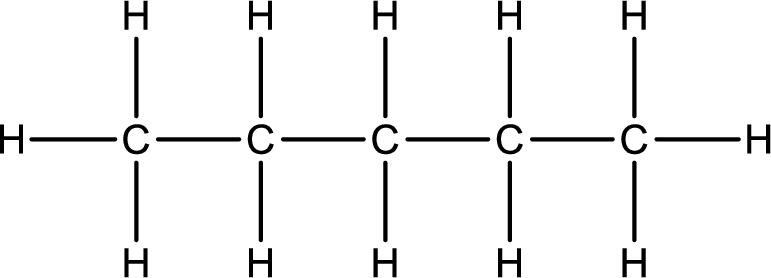
Molecular formula of pentane is only
(f)
Interpretation:
Pentane has weak London Dispersion forces than octane has to be indicated as true or false.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. Octane contains eight carbon atoms and eighteen hydrogen atoms. As the molar mass increases, the London Dispersion forces become stronger. This means pentane will have weaker London dispersion forces than octane. Hence, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
Pentane is a gas at room temperature has to be indicated as true or false.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Alkanes with one to four carbon atoms are gases at room temperature, and alkanes with five to seventeen carbon atoms are colorless liquids at room temperature. Pentane contains five carbon atoms in its skeleton. Hence, pentane is a liquid at room temperature. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(h)
Interpretation:
Pentane has only carbon‑carbon single bonds and carbon‑hydrogen single bonds has to be indicated as true or false.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane contains five carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms. The structure of pentane can be given as,

As there are no multiple bonds present in the above structure, pentane contains only single bonds between carbon and carbon, and carbon and hydrogen. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
Per mol of Pentane requires
(i)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane has a molecular formula as
Balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of pentane can be given as,
As from the above equation it is understood that one mol of pentane requires eight mol of oxygen for complete combustion, the given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
Pentane is a structural isomer of 2-methylpropane has to be indicated as true or false.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane has a molecular formula as
(k)
Interpretation:
Pentane on reaction with
(k)
Explanation of Solution
Pentane is a saturated hydrocarbon. It undergoes only substitution reaction and not addition reactions. Pentane does not undergo reaction with hydrogen bromide to form 1-bromopropane, 2-bromopropane, and 3-bromopropane. Therefore, the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
GENERAL, ORGANIC, BIOCHEM (LL W/ ACCESS)
- Plleeaasseee solllveeee question 3 andd thankss sirr, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee don't use AIarrow_forwardCalculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbonsarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward
- Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseeearrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forward4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forward
- Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardIII O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward
- 2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





