
Concept explainers
Check your understanding of the flow of genetic information through a cell by filling in the blanks.
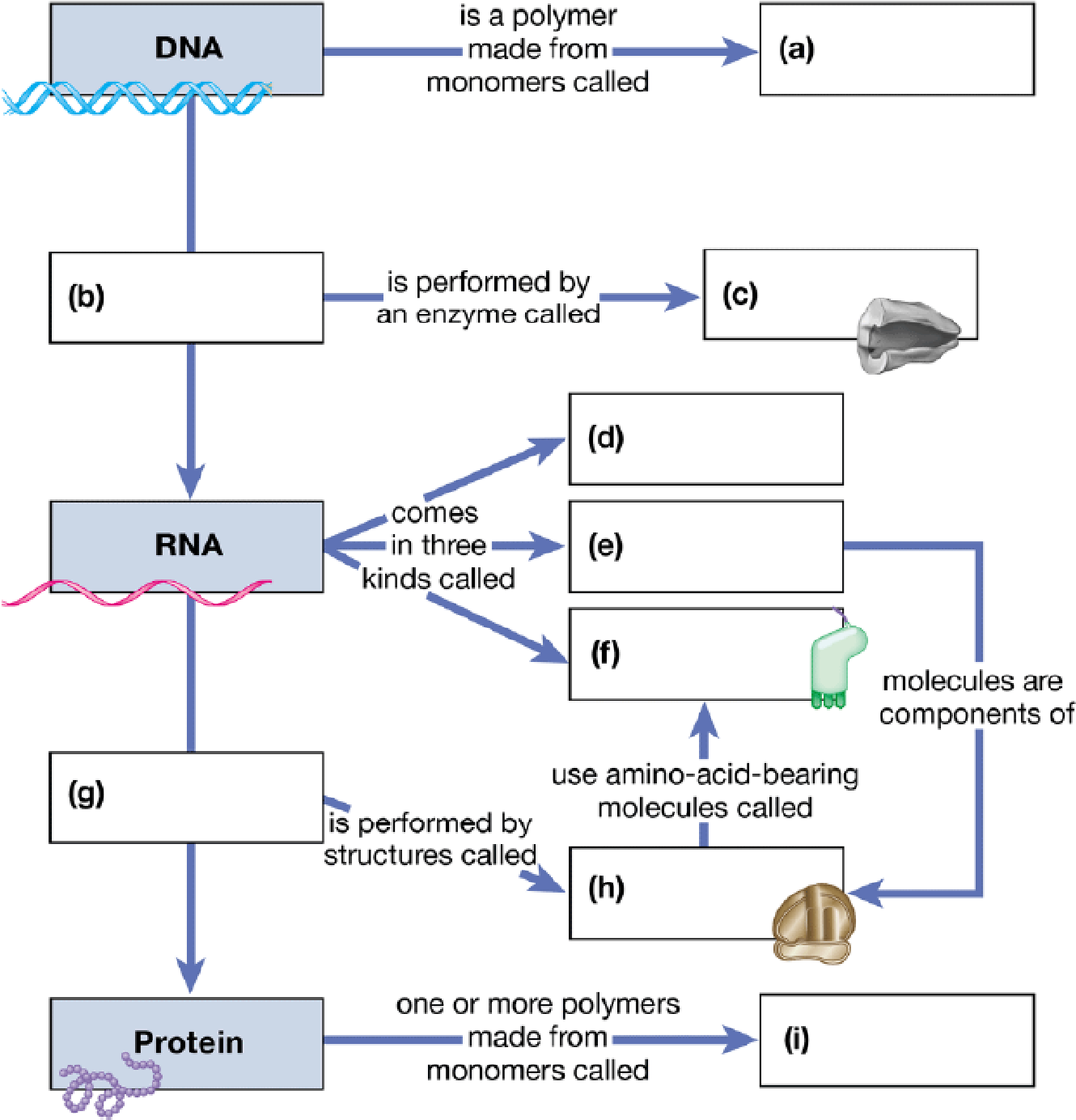
To complete: The given map showing the flow of genetic information through a cell.
Introduction: DNA is the blueprint of life. The genetic information of DNA is based in the nucleotide base sequences. These sequences are transcribed into mRNA triplets. These triplets of nucleotides are known as codons and they form the genetic code. They code for specific amino acids for the synthesis of proteins is known as functional gene products. This is known as gene expression.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 shows the completed map of flow of genetic information through a cell.
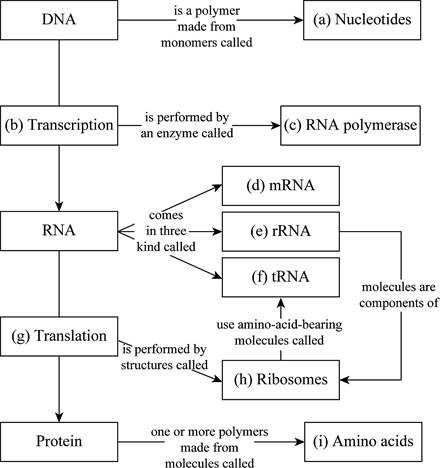
Fig.1 Flow of genetic information through a cell
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Nucleotides.
Explanation: The nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). DNA is a polymer made up of nucleotide monomers (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) and also known as polynucleotide. Hence, the correct answer is nucleotides.
(b)
Correct answer: Transcription.
Explanation: DNA consists of genetic instructions in the form of nucleotide sequences. It acts as a template and directs the messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis in the cell. The process of formation of mRNA is known as transcription. Hence, the correct answer is transcription.
(c)
Correct answer: RNA polymerase.
Explanation: RNA polymerase enzymes are of three types out of which, RNA pol II transcribes mRNA. RNA pol II enzyme first binds to the transcription factors and then forms a complex with promoter at start codon for the beginning of transcription process. Hence, the correct answer is RNA polymerase.
(d)
Correct answer: mRNA.
Explanation: Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes consist of three types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. mRNA forms 5% of the total RNA in a cell. mRNA consists of the genetic code in the form of triplets of nucleotides known as codons. Hence, the correct answer is mRNA.
(e)
Correct answer: rRNA
Explanation: rRNA forms 80% of the total RNA and is found in ribosomes. rRNAs along with proteins form ribosomes, which act as a site for protein synthesis. Hence, the correct answer is rRNA.
(f)
Correct answer: tRNA
Explanation: tRNAs are smallest among the three types of RNA. The mRNA sequence is read by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) to form polypeptide or a chain of amino acids in a process known as translation. The tRNA molecule with an attached amino acid binds to its specific mRNA codon. This mRNA codon codes for that specific amino acid. Hence, the correct answer is tRNA.
(g)
Correct answer: Translation.
Explanation: The mRNA acts as a template for the synthesis of polypeptide chain. Each letter in the gene sequence is copied which codes for a particular amino acid. The polypeptide chain is synthesized on the basis of amino acid sequences in the reading frame. This process is known as translation. Hence, the correct answer is translation.
(h)
Correct answer: Ribosomes.
Explanation: rRNAs along with proteins form ribosomes. Ribosomes act as a site of protein synthesis, that is, translation. Hence, the correct answer is ribosomes.
(i)
Correct answer: Amino acids.
Explanation: Amino acids are the monomer units of proteins. Amino acids are linked through peptide bonds to form a long polypeptide chain. Hence, the correct answer is amino acids.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- 12. Calculate the area of a circle which has a radius of 1200 μm. Give your answer in mm² in scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forwardDescribe the image quality of the B.megaterium at 1000X before adding oil? What does adding oil do to the quality of the image?arrow_forwardWhich of the follwowing cells from this lab do you expect to have a nucleus and why or why not? Ceratium, Bacillus megaterium and Cheek epithelial cells?arrow_forward
- 14. If you determine there to be debris on your ocular lens, explain what is the best way to clean it off without damaging the lens?arrow_forward11. Write a simple formula for converting mm to μm when the number of mm's is known. Use the variable X to represent the number of mm's in your formula.arrow_forward13. When a smear containing cells is dried, the cells shrink due to the loss of water. What technique could you use to visualize and measure living cells without heat-fixing them? Hint: you did this technique in part I.arrow_forward
- 10. Write a simple formula for converting μm to mm when the number of μm's are known. Use the variable X to represent the number of um's in your formula.arrow_forward8. How many μm² is in one cm²; express the result in scientific notation. Show your calculations. 1 cm = 10 mm; 1 mm = 1000 μmarrow_forwardFind the dental formula and enter it in the following format: I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format) Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).arrow_forward
- Answer iarrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forwardcalculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





