
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
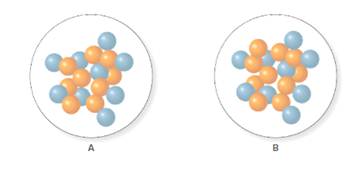
Concept Introduction:
Atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in it. Atomic number is represented by Z.
Answer to Problem 19P
The atomic number for isotope of fluorine A and B is 9.
Explanation of Solution
In the molecular model of fluorine, orange balls represent neutrons, whereas blue balls represent protons. Since the number of protons from given molecular models A and B is 9, the atomic number becomes 9 for A and B both, as the atomic number is equal to the number of protons in that atom.
(b)
Interpretation:
Mass number for each isotope of fluorine given below should be predicted.
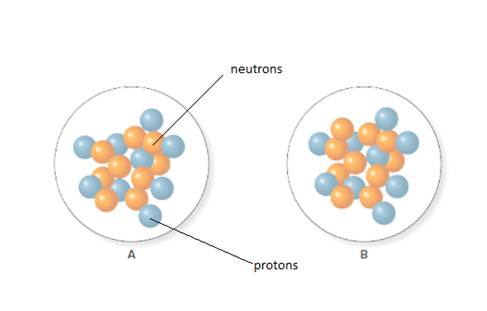
Concept Introduction:
The mass number is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Answer to Problem 19P
The atomic number for isotope of fluorine A and B is 18 and 19 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
From the molecular model of an isotope of fluorine, the number of neutrons can be counted. Thus, the number of neutrons in A and B is 9 and 10 respectively.
As
For A and B, the mass number will be calculated as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
Number of protons for each isotope of fluorine given below should be predicted.
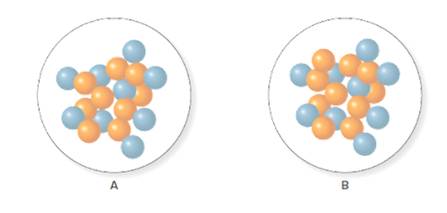
Concept Introduction:
The number of protons is equal to the atomic number of that atom.
Answer to Problem 19P
The number of protons in isotope of fluorine A and B is 9.
Explanation of Solution
In the molecular model of fluorine, protons are represented by blue balls. Thus, the number of protons in A and B will be calculated by counting the number of blue balls in A and B in the given figure as follows:
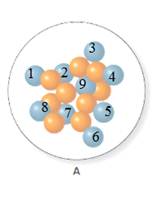
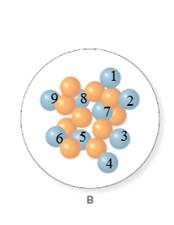
Thus, the number of protons in A and B is 9.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of neutrons for each isotope of fluorine given below should be predicted.
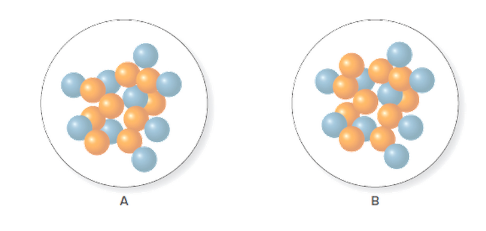
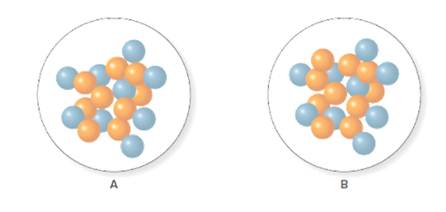
Concept Introduction:
The mass number is the sum of all the protons and neutrons present in an atom. Thus, the number of neutrons can be calculated simply by subtracting the number of protons from the mass number of that atom.
Answer to Problem 19P
The number of neutrons in A and B is 9 and 10 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
For A, the mass number and number of protons are 18 and 9 respectively. Thus, the number of neutrons in A will be calculated as follows:
For B the mass number and number of protons are 19 and 9 respectively. Thus, the number of neutrons in B will be calculated as follows:
(e)
Interpretation:
The isotope symbol for each isotope of fluorine given below should be predicted.
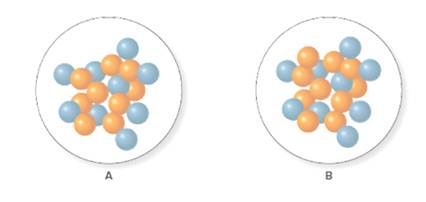
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different
To write an isotope symbol atomic number (Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 19P
The isotope symbol for A and B is
Explanation of Solution
For A, the mass number and atomic numbers are 18 and 9 respectively. Thus, the isotope symbol for A will be represented as follows:
For B, the mass number and atomic numbers are 19 and 9 respectively. Thus, the isotope symbol for B will be represented as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Draw the complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of this alkene. esc 田 Explanation Check 1 888 Q A slock Add/Remove step Q F4 F5 F6 A བྲA F7 $ % 5 @ 4 2 3 & 6 87 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce W E R T Y U S D LL G H IK DD 요 F8 F9 F10 F1 * ( 8 9 0 O P J K L Z X C V B N M H He commandarrow_forwardExplanation Check F1 H₂O H₂ Pd 1) MCPBA 2) H3O+ 1) Hg(OAc)2, H₂O 2) NaBH4 OH CI OH OH OH hydration halohydrin formation addition halogenation hydrogenation inhalation hydrogenation hydration ☐ halohydrin formation addition halogenation formation chelation hydrogenation halohydrin formation substitution hydration halogenation addition Ohalohydrin formation subtraction halogenation addition hydrogenation hydration F2 80 F3 σ F4 F5 F6 1 ! 2 # 3 $ 4 % 05 Q W & Å © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. F7 F8 ( 6 7 8 9 LU E R T Y U A F9arrow_forwardShow the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forward
- Soap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the mechanism for this transformation: *see imagearrow_forwardAssign all the signals individually (please assign the red, green and blue)arrow_forwardThe two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHERChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHERChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781285199030Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





