
(a)
Interpretation:
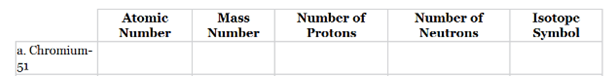
The given table of isotope should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 21P
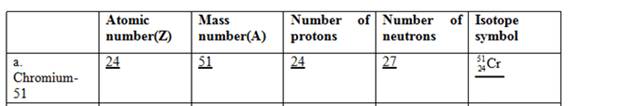
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The atomic number for chromium is 24 and mass number is 51.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the number of protons in chromium is 24 and the number of neutrons in chromium can be calculated by simply subtracting number of protons from mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Chromium is
(b)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotopes should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 21P
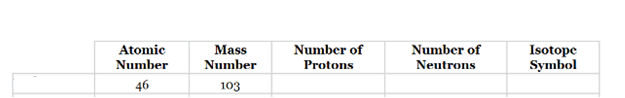
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Palladium-103 | 46 | 103 | 46 | 57 |
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons.
The atomic number for the element listed in b option is given which is equal to 46 and the mass number is 103. So, the element is Palladium (Pd).
Since atomic number = number of protons.
Thus, the number of protons in palladium is 46 and the number of neutrons in palladium can be calculated by simply subtracting number of protons from the mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Palladium is
(c)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotopes should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 21P
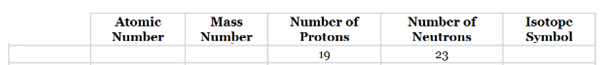
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Potassium-19 | 19 | 42 | 19 | 23 |
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The number of protons in element listed in option c is 19 and the number of neutrons is 23.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the atomic number of this element is 19 and the element will be Potassium (K) and the mass number will be calculated as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Palladium is
(d)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotopes should be completed.

Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 21P
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Xenon-133 | 54 | 133 | 54 | 79 |
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The number of protons for element listed in d option are 54 and mass number is 133.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, atomic number for this element will be 54 and the element is Xenon (Xe) and the number of neutrons in xenon can be calculated by simply subtracting number of protons from mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Xenon is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





