
Concept explainers
Carbon–carbon bond dissociation enthalpies have been measured for many
Without referring to Table
has the lower carbon–carbon bond-dissociation enthalpy, and explain the reason for your
choice.
Ethane or propane
Propane or
Cyclobutane or cyclopentane
Interpretation:
In each of the given pairs, the alkane having lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy is to be identified and the reason for this is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Species that contain unpaired electrons are called free radicals.
Alkyl radicals are described by the presence of carbon with three bonds. The alkyl radicals are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary on the basis of the number of carbon atoms directly attached to the carbon atom bearing unpaired electron.
Similar to carbocation’s, free radicals are stabilized by alkyl substituents. The stability order of alkyl radicals is
In a hemolytic cleavage, each atom of the bond keeps one of the electrons in the bond.
The bond dissociation energy represents the stability of radical formed.
Answer to Problem 16P
Solution:
a) Propane has the lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy because it produces more stable free radicals.
b)
c)
d) Cyclopentane has the lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy because it produces more stable free radicals.
Explanation of Solution
a) The given alkanes are ethane and propane.
The cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in propane produces one methyl radical and one ethyl radical.
The ethyl radical is a primary radical and is more stable than the methyl radical. Hence propane produces more stable radicals than ethane upon homolytic cleavage. Lower energy is required to generate free radicals in propane. Thus, propane has a lower bond dissociation enthalpy than ethane.
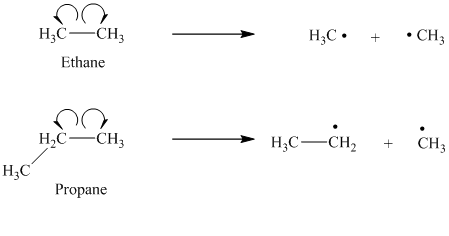
b) The given alkanes are propane and
The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in propane produces one methyl radical and one ethyl radical. The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in
The isopropyl radical is a secondary radical and is more stable than the ethyl radical, which is a primary radical. Hence
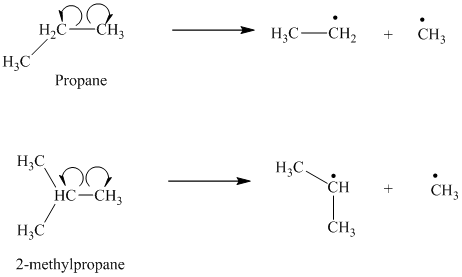
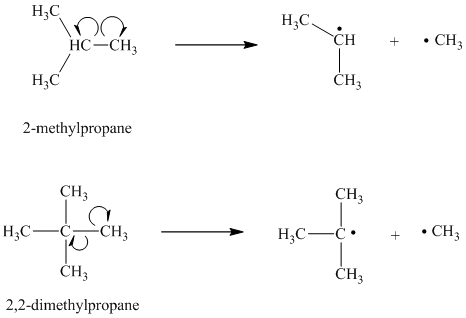
c) The given alkanes are
The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in
The tertiary butyl radical is a tertiary radical and is more stable than the isopropyl radical, which is a secondary radical. Hence
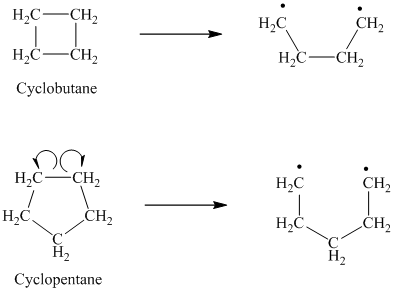
d) The given alkanes are cyclobutane and cyclopentane.
The homolytic cleavage of cyclobutane produces two radicals, which are attached to each other. Both the unpaired electrons are present on primary carbon atoms.
The homolytic cleavage of cyclopentane also produces two radicals, which are attached to each other. Both the unpaired electrons are present on primary carbon atoms.
In the radicals produced by cyclopentane, there is one alkyl substituent more as compared to the radicals in cyclobutane. The more the alkyl substituents, the more stable is the radical. Hence, in cyclopentane, the radicals are slightly more stable as compared to cyclobutane. Hence, cyclopentane has a lower bond dissociation enthalpy than cyclobutane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- What is the molarisuty of a 0.396 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 /mol.arrow_forwardProvide the proper IUPAC or common name for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be used correctly. Br ......Im OHarrow_forwardCan you please help me solve this problems. The top one is just drawing out the skeletal correct and then the bottom one is just very confusing to me and its quite small in the images. Can you enlarge it and explain it to me please. Thank You much (ME EX1) Prblm #33arrow_forward
- I'm trying to memorize VESPR Shapes to solve problems like those. I need help making circles like the second image in blue or using an x- and y-axis plane to memorize these and solve those types of problems, especially the ones given in the top/first image (180, 120, 109.5). Can you help me with this? or is their any other efficient method do soarrow_forwardCan you please explain this problems to me? I'm very confused about it. Please provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation for me! (ME EX1) Prblm 27arrow_forwardQuestion 6 of 7 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 1 of 1 = 1 ✓2 ✓ 3 ✓ 4 ✓ 5 6 ✓ 7 This organic molecule is dissolved in a basic aqueous solution: Jen ✓ ? A short time later sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C-OH stretch absorption. That is, must now be a new molecule present with at least one C- OH bond. there 18 In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule Ar © + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Add/Remove step Click and drawing Save For Later Submit Assignmentarrow_forward
- Can you please explain this problem to me? I'm very confused about it. Please provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation for me! (ME EX1) Prblm 22arrow_forwardCan you please explain this problems to me? I'm very confused about it. Please provide a detailed, step-by-step explanation for me! (ME EX1) Prblm 30arrow_forwardThis organic molecule is dissolved in a basic aqueous solution: O ? olo RET A short time later sensitive infrared spectroscopy reveals the presence of a new C-OH stretch absorption. That is, there Ar must now be a new molecule present with at least one C - OH bond. In the drawing area below, show the detailed mechanism that could convert the molecule above into the new molecule. $ Add/Remove steparrow_forward
- So the thing is im trying to memorize VESPR Shapes in order to be able to solve problems like so, and I need help with making circles like the second image that's in blue or using an x and y axis plane in order to memorize these and be able to solve those type of problems. Especially like the ones given in the top / first image. (180 , 120 , 109.5) Can you help me with this.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward2. (15 points) Draw an appropriate mechanism for the following reaction. H N. H* + H₂Oarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





