
Concept explainers
To label: The parts of the clavicle in Figure 10.2 (a).
Introduction: Pectoral girdles are otherwise called shoulder girdle and they are the set of bones. An upper limb is attached to the axial skeleton by each pectoral girdle. Each shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is composed of a clavicle and a scapula.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
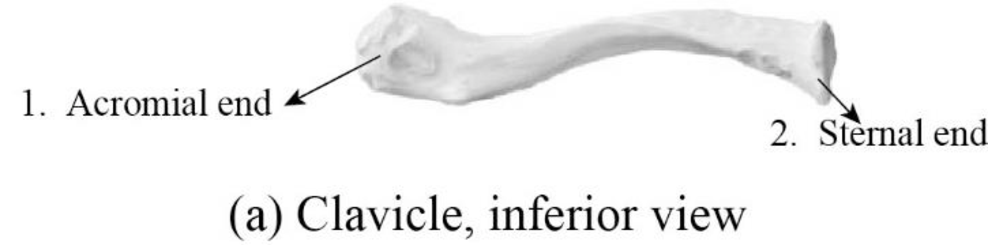
Fig1: The parts of the clavicle
Explanation of Solution
1. Acromial end: The acromial end is the flattened lateral end. It is anchored to the coracoid process by trapezoid ligaments and conoid. It articulates with the acromion.
2. Sternal end: The sternal end is the enlarged medial end. It articulates with manubrium sterni.
To label: The parts of scapula in Figure 10.2 (b).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
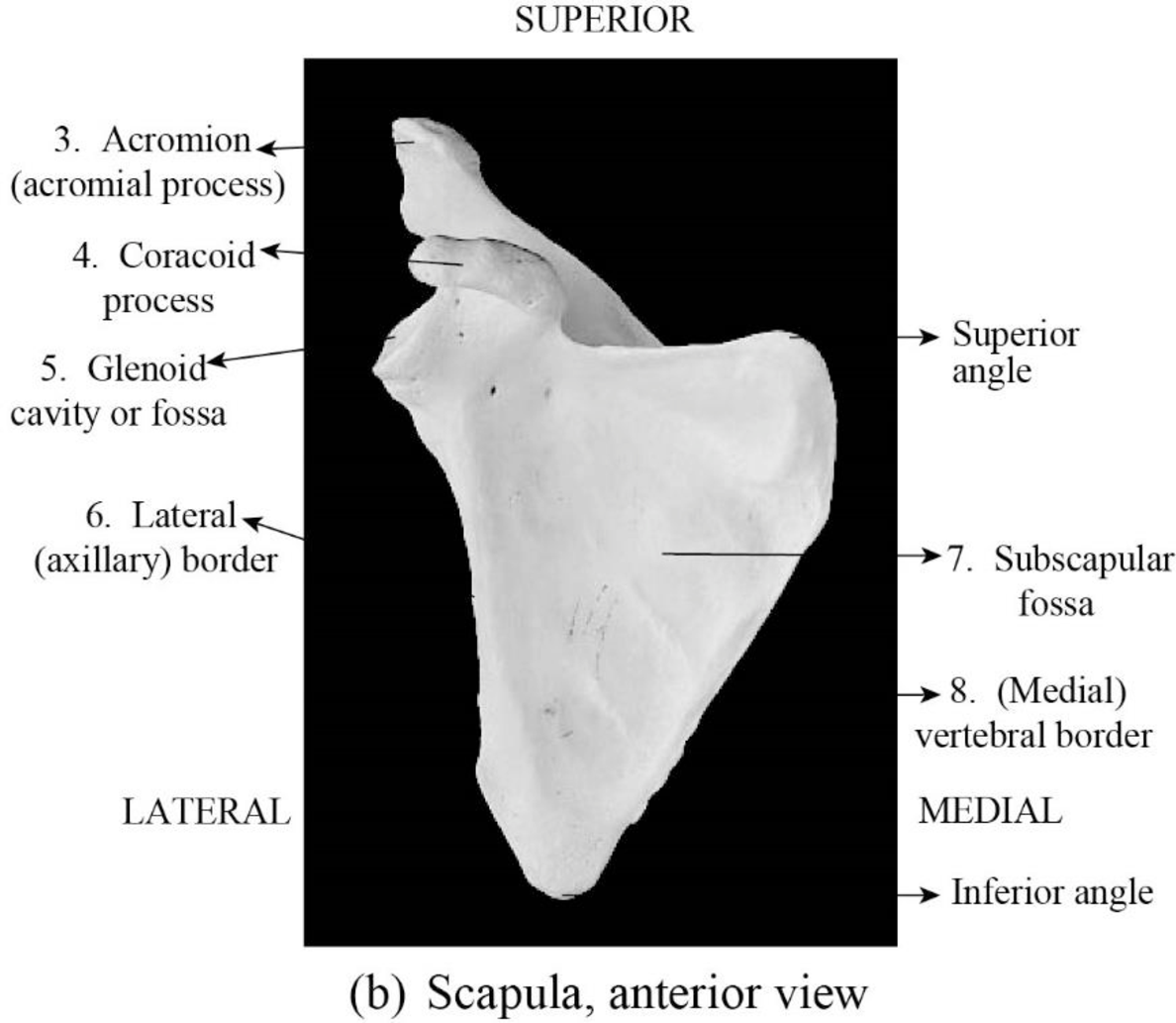
Fig 2: The parts of the scapula anterior view
Explanation of Solution
3. Acromion (acromial process): Acromion is a portion of the scapula and it is found at the shoulder peak. The shape of the acromion is a triangle and it protrudes laterally. The acromion is otherwise referred as acromion process, which articulates with the collar bone or clavicle to form the acromioclavicular joint.
4. Coracoid process: The coracoid process is a thick, long curved projection attached by a broad base to the upper portion of the neck of the scapula.
5. Glenoid cavity or fossa: Glenoid cavity is a portion of the shoulder. It is depression inferior to acromion. The glenoid cavity is otherwise called a glenoid fossa of the scapula.
6. Lateral (axillary) border: The lateral border is a structural feature on the bone of scapula or border near the axilla. The lateral border of the scapula is also called an axillary border.
7. Subscapular fossa: Subscapular fossa is the concave depression on the anterior surface of the scapula. It provides origin to the subscapularis muscle. The subscapular fossa is otherwise called the shoulder bone.
8. (medial) vertebral border: The vertebral border is the edge or margin of scapula near the vertebral column. It extends to the inferior angle from a superior angle.
To label: The parts of the clavicle in Figure 10.2 (c).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
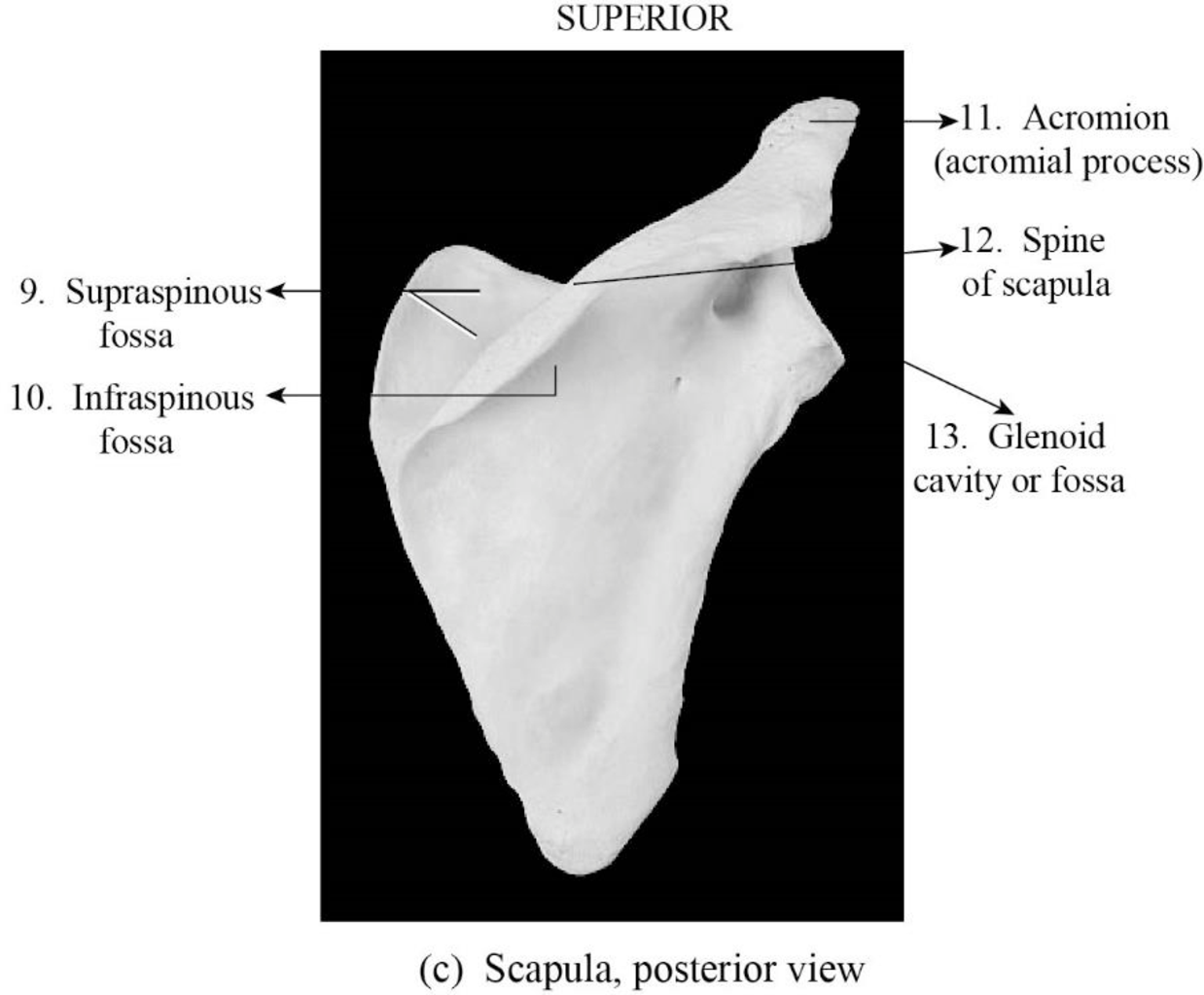
Fig1: The parts of the scapula posterior view
Explanation of Solution
9. Supraspinous fossa: Supraspinous fossa is a depression superior to the spine. It provides origin to the supraspinatus muscle.
10. Infraspinous fossa: Infraspinous fossa is the depression or hollow on the dorsal aspect inferior to the spine. It mainly provides attachment to the infraspinatus muscle.
11. Acromion (acromial process): Acromion is the portion of the scapula and it is found at the shoulder peak. The acromion is otherwise referred as acromion process, which articulates with the collar bone or clavicle to form the acromioclavicular joint.
12. Spine of the scapula: The spine of the scapula is otherwise called a scapular spine. It is a sharp ridge present on the posterior side.
13. Glenoid cavity or fossa: Glenoid cavity is otherwise called a glenoid fossa of the scapula. The glenoid cavity is a portion of the shoulder. It is a depression inferior to acromion.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion with WileyPLUS Blackboard Card Set
- Amino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forwardWhat is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forward
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





