
Bonds:
Bonds are a kind of the security which an investor invests in an entity for a specific period at a fixed interest rate. These bonds are issued at that time when entity needs huge amount of fund.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Issue of bonds at discount on January 30, 2017
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 30 | Cash | 184,556 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 4,556 | |||
| Bonds payable | 180,000 | |||
| (To record the issue bonds at premium) |
Table (1)
- Cash account is the assets account. Since the cash is received, the value of assets is increased. So, debit the credit the cash account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increase the liabilities of the company. So, credit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Bonds has been sold, which increases the liabilities of the company. So, credit the bonds payable account.
2.
Net expense of interest on bond.
2.
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | Amounts($) |
| Amount repaid: | |
| Interest payment | 59,400 |
| Add: Maturity value | 180,000 |
| Repaid amount | 239,400 |
| Less: Borrowed amount | (184,556) |
| Net expense of interest on bond | 54,834 |
Table (2)
Hence, net expense interest on bond is $54,834.
Working notes:
Given,
Rate of interest is 11%.
Time period is 0.5.
Calculation of amount of the interest paid at semiannual period,
Calculation of amount of interest repaid,
3.
Effective interest amortization method
3.
Explanation of Solution
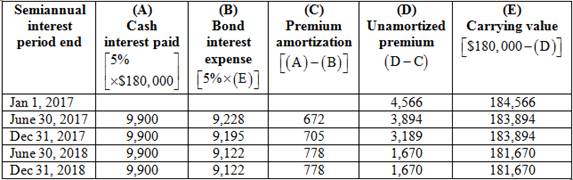
Table (3)
4.
To prepare: Journal entry.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Payment of interest on June 30, 2017
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| June 30 | Bonds interest expense | 9,228 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 672 | |||
| Cash | 9,900 | |||
| (To record the paid semiannual interest and record premium amortization) |
Table (4)
- Bonds interest account is an expense account. Interest has been paid by the company which increases the liabilities of the company. So, debit the bonds interest expense account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increases the liabilities of company. Now premium on bonds payable has been paid which decrease the liability. So, debit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Cash is an asset account. Since the cash is paid, the value of assets is decreased. So, credit the cash account.
Payment of interest on December 31, 2017
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Dec 31 | Bonds interest expense | 9,228 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 672 | |||
| Cash | 9,900 | |||
| (To record the paid semiannual interest and record amortization) |
Table (5)
- Bonds interest account is an expense account. Interest has been paid by the company which increases the liabilities of the company. So, debit the bonds interest expense account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increases the liabilities of company. Now premium on bonds payable has been paid which decrease the liability. So, debit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Cash is an asset account. Since the cash is paid, the value of assets is decreased. So, credit the cash account.
5.
Journal entry at retirement for 2%.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Retirement of bonds on January 1, 2019 at 98%
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 1, 2019 | Bonds payable | 180,000 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 1,670 | |||
| Gain on retirement of bonds | 176,400 | |||
| Cash | 5,270 | |||
| (to record retirement of bonds at premium) |
Table (6)
- Bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Bonds have been retired, which decreases the liabilities of the company. So, debit the bonds payable account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increases the liabilities of company. Now premium on bonds payable has been paid which decrease the liability. So, debit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Gain on retirement of bond is a nominal account. Retirement of bond is an gain for the company which increase the income of the company. So, credit the gain on retirement of bond account.
- Cash is an asset account. Since the cash is paid, the value of assets is decreased. So, credit the cash account.
6.
Change in interest rate will affect the amount reported in financial statement account.
6.
Explanation of Solution
- If the bonds are issued at the 12% instead of the 10%, then bonds will be issued at discount. As the rate of interest on account for 11% which is less than
rate of return in the new market. - The change in the market rate of interest decreases the bond liability of the company in the
balance sheet . But, the bond liability increases gradually with amortization of the premium. - In this case, the
cash flow statement will show greater amount of bond interest expense till the maturity period of the bond
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Gen Combo Ll Financial Accounting Fundamentals; Connect Access Card
- Consolidation after Several Years On January 1, 2016, Adams Corporation acquired all of the stock of Baker Company. The fair value of Adams’ shares used in the exchange was $37,500,000. At the time of acquisition, the book value of Baker’s shareholders’ equity was $5,000,000, and the book value of Baker’s building (25-year life) exceeded its fair value by $1,000,000. From the date of acquisition to December 31, 2021, Baker had cumulative net income of $1,300,000. For 2022, Baker reported net income of $300,000. Adams uses the complete equity method to account for its investment in Baker. There is no goodwill impairment loss for the period 2016 through 2021, but there is impairment loss of $100,000 in 2022. Baker declared no dividends during the period 2016–2022. Required Prepare the working paper eliminating entries necessary to consolidate the financial statements of Adams and Baker at December 31, 2022. Enter numerical answers using all zeros (do not abbreviate in thousands or in…arrow_forwardGive me the answer in a clear organized table please. Thank you!arrow_forwardGive me the answer in a clear organized table please. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Assess the role of the Conceptual Framework in financial reporting and its influence on accounting theory and practice. Discuss how the qualitative characteristics outlined in the Conceptual Framework enhance financial reporting and contribute to decision-usefulness. Provide examplesarrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress Cullumber Corporation has income from continuing operations of $464,000 for the year ended December 31, 2025. It also has the following items (before considering income taxes). 1. An unrealized loss of $128,000 on available-for-sale securities. 2. A gain of $48,000 on the discontinuance of a division (comprised of a $16,000 loss from operations and a $64,000 gain on disposal). Assume all items are subject to income taxes at a 20% tax rate. Prepare a partial income statement, beginning with income from continuing operations. Income from Continuing Operations Discontinued Operations Loss from Operations Gain from Disposal Net Income/(Loss) CULLUMBER CORPORATION Income Statement (Partial) For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Prepare a statement of comprehensive income. Net Income/(Loss) $ CULLUMBER CORPORATION Statement of Comprehensive Income For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 = Other Comprehensive Income Unrealized Loss of Available-for-Sale Securities ✰…arrow_forwardPlease make a trial balance, adjusted trial balance, Income statement. end balance ,owners equity statement, Balance sheet , Cash flow statement ,Cash end balancearrow_forward
- Activity Based Costing - practice problem Fontillas Instrument, Inc. manufactures two products: missile range instruments and space pressure gauges. During April, 50 range instruments and 300 pressure gauges were produced, and overhead costs of $89,500 were estimated. An analysis of estimated overhead costs reveals the following activities. Activities 1. Materials handling 2. Machine setups Cost Drivers Number of requisitions Number of setups Total cost $35,000 27,500 3. Quality inspections Number of inspections 27,000 $89.500 The cost driver volume for each product was as follows: Cost Drivers Instruments Gauge Total Number of requisitions 400 600 1,000 Number of setups 200 300 500 Number of inspections 200 400 600 Insructions (a) Determine the overhead rate for each activity. (b) Assign the manufacturing overhead costs for April to the two products using activity-based costing.arrow_forwardBodhi Company has three cost pools and two doggie products (leashes and collars). The activity cost pool of ordering has the cost drive of purchase orders. The activity cost pool of assembly has a cost driver of parts. The activity cost pool of supervising has the cost driver of labor hours. The accumulated data relative to those cost drivers is as follows: Expected Use of Estimated Cost Drivers by Product Cost Drivers Overhead Leashes Collars Purchase orders $260,000 70,000 60,000 Parts 400,000 300,000 500,000 Labor hours 300,000 15,000 10,000 $960,000 Instructions: (a) Compute the activity-based overhead rates. (b) Compute the costs assigned to leashes and collars for each activity cost pool. (c) Compute the total costs assigned to each product.arrow_forwardTorre Corporation incurred the following transactions. 1. Purchased raw materials on account $46,300. 2. Raw Materials of $36,000 were requisitioned to the factory. An analysis of the materials requisition slips indicated that $6,800 was classified as indirect materials. 3. Factory labor costs incurred were $55,900, of which $51,000 pertained to factory wages payable and $4,900 pertained to employer payroll taxes payable. 4. Time tickets indicated that $50,000 was direct labor and $5,900 was indirect labor. 5. Overhead costs incurred on account were $80,500. 6. Manufacturing overhead was applied at the rate of 150% of direct labor cost. 7. Goods costing $88,000 were completed and transferred to finished goods. 8. Finished goods costing $75,000 to manufacture were sold on account for $103,000. Instructions Journalize the transactions.arrow_forward
- Chapter 15 Assignment of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead Stine Company uses a job order cost system. During May, a summary of source documents reveals the following. Job Number Materials Requisition Slips Labor Time Tickets 429 430 $2,500 3,500 $1,900 3,000 431 4,400 $10,400 7,600 $12,500 General use 800 1,200 $11,200 $13,700 Stine Company applies manufacturing overhead to jobs at an overhead rate of 60% of direct labor cost. Instructions Prepare summary journal entries to record (i) the requisition slips, (ii) the time tickets, (iii) the assignment of manufacturing overhead to jobs,arrow_forwardSolve accarrow_forwardSolve fastarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





