
Bonds:
Bonds are a kind of the security which an investor invests in an entity for a specific period at a fixed interest rate. These bonds are issued at that time when entity needs huge amount of fund.
1.
To prepare:
Explanation of Solution
Issue of bonds at discount on January 30, 2017
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 30 | Cash | 493,608 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 43,608 | |||
| Bonds payable | 450,000 | |||
| (To record the issue bonds at premium) |
Table (1)
- Cash account is the assets account. Since the cash is received, the value of assets is increased. So, debit the credit the cash account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increase the liabilities of the company. So, credit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Bonds has been sold, which increases the liabilities of the company. So, credit the bonds payable account.
2.
Net expense of interest on bond
2.
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | Amounts($) |
| Amount repaid: | |
| Interest payment | 234,000 |
| Add: Maturity value | 450,000 |
| Repaid amount | 684,000 |
| Less: Borrowed amount | 493,608 |
| Net expense of interest on bond | 190,392 |
Table (2)
Hence, net expense interest on bond is $190,392.
Working notes:
Given,
Rate of interest is 13%.
Time period is 0.5.
Calculation of amount of the interest paid at semiannual period,
Calculation of amount of interest repaid,
3.
Effective interest amortization method.
3.
Explanation of Solution
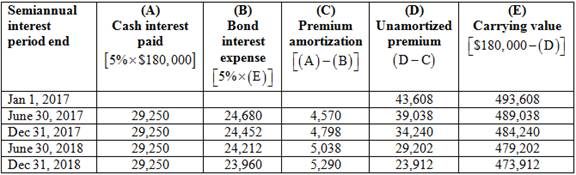
Table (3)
4.
To prepare: Journal entry.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Payment of interest on June 30, 2017
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| June 30 | Bonds interest expense | 24,980 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 4,570 | |||
| Cash | 29,250 | |||
| (To record the paid semiannual interest and record premium amortization) |
Table (4)
- Bonds interest account is an expense account. Interest has been paid by the company which increases the liabilities of the company. So, debit the bonds interest expense account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increases the liabilities of company. Now premium on bonds payable has been paid which decrease the liability. So, debit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Cash is an asset account. Since the cash is paid, the value of assets is decreased. So, credit the cash account.
Payment of interest on December 31, 2017
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Dec 31 | Bonds interest expense | 24,980 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 4,570 | |||
| Cash | 29,250 | |||
| (To record the paid semiannual interest and record amortization) |
Table (5)
- Bonds interest account is an expense account. Interest has been paid by the company which increases the liabilities of the company. So, debit the bonds interest expense account
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increases the liabilities of company. Now premium on bonds payable has been paid which decrease the liability. So, debit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Cash is an asset account. Since the cash is paid, the value of assets is decreased. So, credit the cash account.
5.
To prepare: Journal entry at retirement for 2%.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Retirement of bonds on January 1, 2019 at 98%
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post.Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 1, 2019 | Bonds payable | 180,000 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | 23,912 | |||
| Loss on retirement of bonds | 3,088 | |||
| Cash | 477,000 | |||
| (to record retirement of bonds at premium) |
Table (6)
- Bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Bonds have been retired, which decreases the liabilities of the company. So, debit the bonds payable account.
- Premium on bonds payable account is the liabilities account. Here, at the time of issue of the bonds premium has been given which increases the liabilities of company. Now premium on bonds payable has been paid which decrease the liability. So, debit the premium on bonds payable account.
- Loss on retirement of bond is a nominal account. Retirement of bond is a loss for the company which decreases the income of the company. So, debit the loss on retirement of bond account.
- Cash is an asset account. Since the cash is paid, the value of assets is decreased. So, credit the cash account.
6.
Change in interest rate will affect the amount reported in financial statement account.
6.
Explanation of Solution
- If the bonds are issued at the 14% instead of the 10%, then bonds will be issued at discount. As the rate of interest on account for 13% which is less than
rate of return in the new market. - The change in the market rate of interest decreases the bond liability of the company in the
balance sheet . But, the bond liability increases gradually with amortization of the premium. - In this case, the
cash flow statement will show greater amount of bond interest expense till the maturity period of the bond
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Gen Combo Ll Financial Accounting Fundamentals; Connect Access Card
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning





