
(a)
Bonds
Bonds are a kind of interest bearing notes payable, usually issued by companies, universities and governmental organizations. It is a debt instrument used for the purpose of raising fund of the corporations or governmental agencies. If selling price of the bond is equal to its face value, it is called as par on bond. If selling price of the bond is lesser than the face value, it is known as discount on bond. If selling price of the bond is greater than the face value, it is known as premium on bond.
Redemption of Bonds
The process of repaying the sale amount of bonds to bondholders at the time of maturity or before the maturity period is called as redemption of bonds. It is otherwise called as retirement of bonds.
To prepare: The
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of bonds for Corporation K on October 1as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| October 1, 2016 | Cash | $700,000 | |
| Bonds payable | $700,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of 5% bonds payable at face value for Corporation K) |
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
- Cash is a current asset and increased. Therefore, debit Cash account for $396,000.
- Bonds payable is a long-term liability and increased. Therefore, credit bonds payable account for $700,000.
(b)
To prepare: The
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
The adjusting entry to record the accrual of interest for Corporation K on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2016 | Interest expense (1) | $8,750 | |
| Interest payable | $8,750 | ||
| (To record the accrual interest expense for Corporation K) |
Table (2)
Working note:
Calculation of Interest expense for Corporation K is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Interest expense is a component of
stockholders’ equity and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $8,750. - Interest payable is a current liability and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $8,750.
(c)
To prepare: The
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
Prepare the balance sheet presentation of bonds payable and bond interest payable of Incorporation K as shown below:
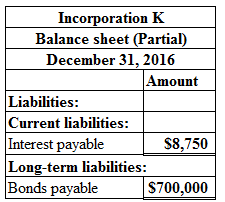
Figure (1)
Explanation of Solution
The balance sheet presentation of interest payable ($8,750) comes under the current liability section and the balance sheet presentation of bonds payable ($700,000) comes under long-term liability section.
(d)
To prepare: The journal entry to record the payment of interest for Corporation K on October 1, 2017.
(d)
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the payment of interest for Corporation K on October 1, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| October 1, 2017 | Interest expense (1) | $26,250 | |
| Interest payable (3) | $8,750 | ||
| Cash (2) | $35,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of interest expense for Corporation K) |
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculation of interest expense for Corporation K on 1st October 2017 is shown below:
Calculation of cash paid for bonds payable of Corporation K 1st October 2017 is shown below:
Calculation of Interest expense for Corporation K is shown below:
Calculation of Interest payable of Corporation K 1st October 2017 is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Interest expense is a stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $26,250.
- Interest payable is a current liability and decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $8,750.
- Cash is a current asset account, and decreased. Therefore, cash account for $35,000.
(e)
To prepare: The adjusting entry to record the accrual of interest for Corporation K on December 31, 2017.
(e)
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
The adjusting entry to record the accrual of interest for Corporation K on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2017 | Interest expense (1) | $8,750 | |
| Interest payable | $8,750 | ||
| (To record the accrual interest expense for Corporation K) |
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculation of Interest expense for Corporation K is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $8,750.
- Interest payable is a current liability and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $8,750.
(f)
To prepare: The journal entry to record the payment of interest for Corporation K on January 1, 2018.
(f)
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the payment of interest for Corporation K on January 1, 2018 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2018 | Interest payable | $8,750 | |
| Cash | $8,750 | ||
| (To record the payment of interest expense for Corporation K) |
Table (5)
Explanation of Solution
Interest payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, interest payable account for $8,750
Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, cash account for $8,750.
To prepare: The journal entry to record the redemption of bonds for Corporation K on January 1, 2018.
Answer to Problem 10.4AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the redemption of bonds for Corporation K on January 1, 2018 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2018 | Bonds payable | $700,000 | |
| Loss on redemption of bonds (2) | $28,000 | ||
| Cash (1) | $728,000 | ||
| (To record the redemption of bonds before the maturity period for Corporation K) |
Table (6)
Working notes:
Calculation of cash paid for redemption of bonds payable is shown below:
Calculation of loss on redemption of bonds payable is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Bonds payable is a long-term liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit bonds payable account for $700,000
Loss on redemption of bonds is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased. Therefore, debit loss on redemption of bonds for $28,000.
Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $728,000
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting 8th Edition
- please give me true answer accounting questionarrow_forwardplease give me true answerarrow_forwardSharon Mars, a recent graduate of Bell's accounting program, evaluated the operating performance of Carla Vista Company's six divisions. Sharon made the following presentation to Carla Vista's board of directors and suggested the Percy Division be eliminated. "If the Percy Division is eliminated," she said, "our total profits would increase by $25,300." The Other Five Divisions Percy Division Total Sales $1,663,000 $100,900 $1,763,900 Cost of goods sold 978,400 76,500 1,054,900 Gross profit 684,600 24,400 709,000 Operating expenses 528,500 49,700 578,200 Net income $156,100 $(25,300 ) $130,800 In the Percy Division, cost of goods sold is $60,100 variable and $16,400 fixed, and operating expenses are $29,100 variable and $20,600 fixed. None of the Percy Division's fixed costs will be eliminated if the division is discontinued. Is Sharon right about eliminating the Percy Division? Prepare a schedule to support your answer. (Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding…arrow_forward
- managerial accountingarrow_forwardi need correct optionarrow_forwardMark purchased 200 shares of stock for $40 per share. During the year, he received $500 in dividends. He recently sold the stock for $55 per share. What was Mark's return on the stock? a) $3,500 b) $4,000 c) $3,900 d) $4,500arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning



