
(a)
Balance Sheet
This is a financial statement that shows the assets owned, and the liabilities owed to the creditors and the owners (
To Prepare: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
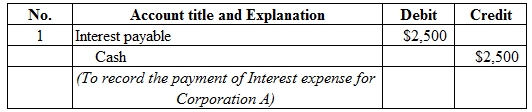
Figure (1)
Description:
- Interest payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $2,500.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $2,500.

Figure (2)
Description:
- Inventory is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit inventory account for $241,100.
- Accounts payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit accounts payable account for $241,100.
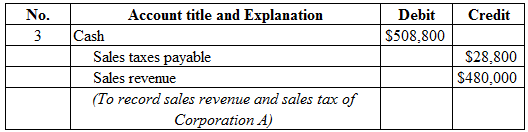
Figure (3)
Description:
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash is a current asset account for $508,800.
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit sales taxes payable account for $28,800.
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit sales revenue account for $480,000.
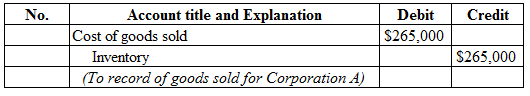
Figure (4)
Description:
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold account for $265,000.
- Inventory is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit inventory account for $265,000.

Figure (5)
Description:
- Accounts payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit accounts payable account for $230,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $230,000.
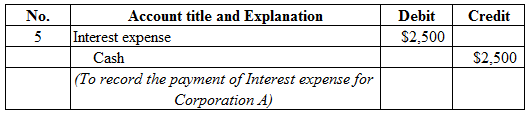
Figure (6)
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $2,500.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $2,500.
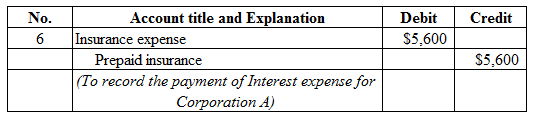
Figure (7)
Description:
- Insurance expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit insurance expense account for $5,600.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $5,600.

Figure (8)
Description:
- Prepaid insurance is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit prepaid insurance account for $10,200.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $10,200.
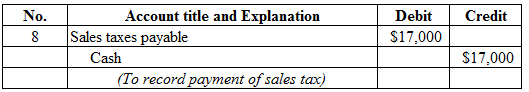
Figure (9)
Description:
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit sales taxes payable account for $17,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $17,000.
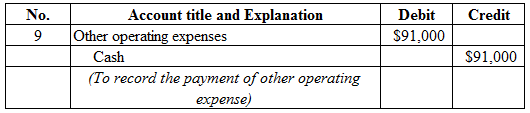
Figure (10)
Description:
- Other operating expenses are a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit other operating expenses account for $91,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $91,000.
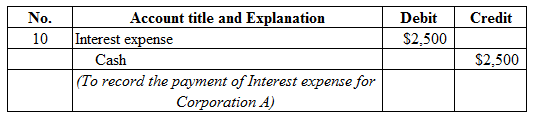
Figure (11)
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $2,500.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $2,500.
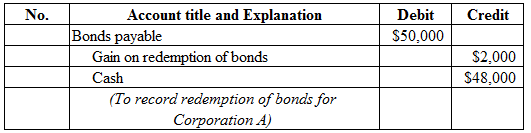
Figure (12)
Description:
- Bonds payable is a liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit bonds payable account for $50,000.
- Gain on redemption of bonds is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit gain on redemption of bonds account for $2,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $48,000.
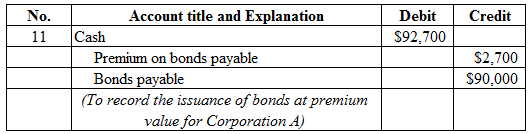
Figure (13)
Description:
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $92,700.
- Premium on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit premium on bonds payable for $2,700.
- Bonds payable is a long-term liability, and increased. Therefore, credit bonds payable account for $90,000.
To Prepare: The
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjustment entries of Corporation as shown below:
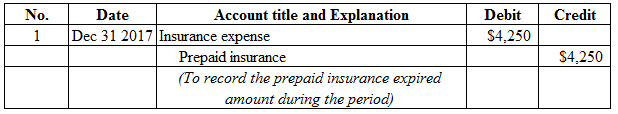
Figure (14)
Working note:
Calculate interest expense as shown below:
Description:
Insurance expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit insurance expense account for $4,250.
Prepaid insurance is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $4,250.
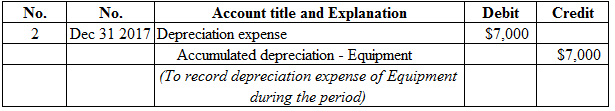
Figure (15)
Description:
Depreciation expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit depreciation expense account for $7,000.Accumulated depreciation – equipment is a contra asset, and increased. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation - equipment account for $7,000.
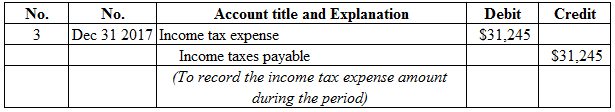
Figure (16)
Working note:
Calculate income tax expense as shown below:
Description:
- Income tax expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit income tax expense account for $31,245.
- Income taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit income taxes payable account for $31,245.
To Prepare: The T-Accounts of Corporation A.
Answer to Problem 10.1CACR
| Cash | |||
| Bal. | $30,000 | $2,500 | |
| $508,800 | $230,000 | ||
| $92,700 | $2,500 | ||
| $10,200 | |||
| $17,000 | |||
| $91,000 | |||
| $2,500 | |||
| $48,000 | |||
| Bal. | $227,800 | ||
Table (1)
| Inventory | |||
| Bal. | $30,750 | $265,000 | |
| $241,100 | |||
| Bal. | $6,850 | ||
Table (2)
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| Bal. | $5,600 | $5,600 | |
| $10,200 | $4,250 | ||
| Bal. | $5,950 | ||
Table (3)
| Equipment | |||
| Bal. | $38,000 | ||
Table (4)
| Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment | |||
| $7,000 | |||
Table (5)
| Accounts Payable | |||
| $230,000 | Bal. | $13,750 | |
| $241,100 | |||
| Bal. | $24,850 | ||
Table (6)
| Other Operating Expenses | |||
| $91,000 | |||
Table (7)
| Interest Expense | |||
| $2,500 | |||
| $2,500 | |||
| Bal. | $5,000 | ||
Table (8)
| Income Tax Expense | |||
| $31,245 | |||
Table (9)
| Interest Payable | |||
| $2,500 | Bal. | $2,500 | |
| Bal. | $0 | ||
Table (10)
| Sales Taxes Payable | |||
| $17,000 | $28,800 | ||
| Bal. | $11,800 | ||
Table (11)
| Income Taxes Payable | |||
| $31,245 | |||
Table (12)
| Bonds Payable | |||
| $50,000 | Bal. | $50,000 | |
| $90,000 | |||
| Bal. | $90,000 | ||
Table (13)
| Premium on Bonds Payable | |||
| $2,700 | |||
Table (14)
| Common Stock | |||
| Bal. | $25,000 | ||
Table (15)
| Bal. | $13,100 | ||
Table (16)
| Sales Revenue | |||
| $480,000 | |||
Table (17)
| Cost of Goods sold | |||
| $265,000 | |||
Table (18)
| Depreciation Expense | |||
| $7,000 | |||
Table (19)
| Insurance Expense | |||
| $5,600 | |||
| $4,250 | |||
| Bal. | $9,850 | ||
Table (20)
| Gain on Redemption of Bonds | |||
| Bal. | $2,000 | ||
Table (21)
Explanation of Solution
Normal balance of assets account, expenses, losses account is debit balance. Hence, a debit increases these accounts and credit decreases these accounts.
Normal balance of liabilities account, capital account, revenue account and gains is credit balance. Hence, a debit decreases these accounts and credit increases these accounts.
(b)
To Prepare: The adjusted trail balance of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjusted trail balance of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
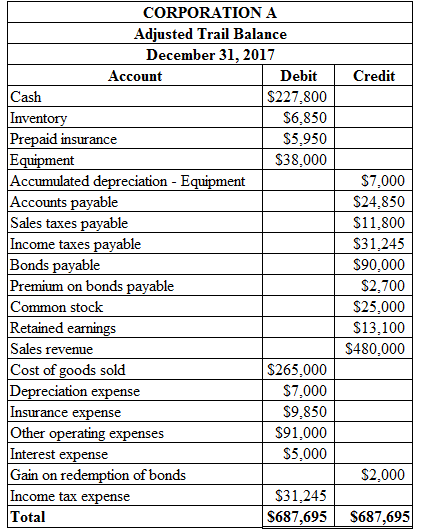
Figure (17)
(c)
To Prepare: The income statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.1CACR
Prepare the income statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
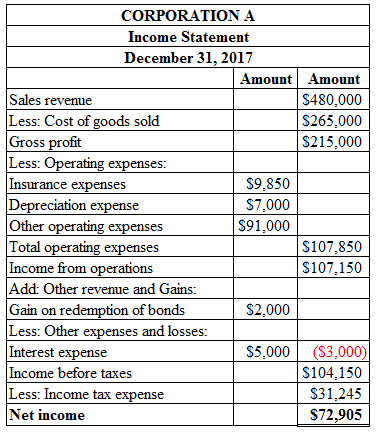
Figure (18)
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is calculated by deducting cost of goods sold from sales revenue. Total operating expenses are calculated by adding insurance expense, depreciation expense, and other operating expenses. Income from operations is calculated by deducting total operating expenses from gross profit. Income before taxes is calculated by deducting interest expenses and adding gain on redemption of bonds from income from operations. Income tax expense is calculated by multiplying income from operations with tax rate. Net income is calculated by deducting income tax expense from income before taxes.
To Prepare: The retained earnings statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
Answer to Problem 10.1CACR
Prepare retained earnings statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
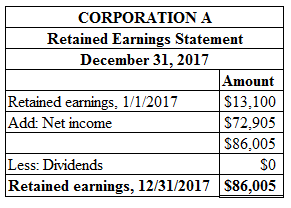
Figure (19)
Explanation of Solution
Ending retained earnings is calculated by adding opening retained earnings and net income and then deducting the dividends. Therefore, ending retained earnings is $86,005.
To Prepare: The classified balance sheet statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare classified balance sheet statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
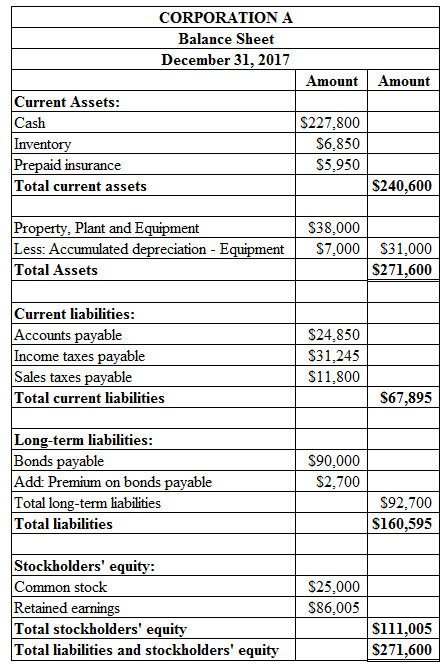
Figure (20)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting 8th Edition
- Questin 5arrow_forwardBelle Garments manufactures customized T-shirts for football teams. The business uses a perpetual inventory system and has a highly labour-intensive production process, so it assigns manufacturing overhead based on direct labour cost. The business operates at a profit margin of 33% on sales. Belle Garments expects to incur $2,205,000 of manufacturing overhead costs and estimated direct labour costs of $3,150,000 during 2025. At the end of December 2024, Belle Line Garments reported work in process inventory of $93,980 - Job FBT 101 - $51,000 & Job FBT 102 - $42,980 The following events occurred during January 2025. i) Purchased materials on account, $388,000. The purchase attracted freight charges of $4,000 ii) Incurred manufacturing wages of $400,000 iii) Requisitioned direct materials and used direct labour in manufacturing. Job # FBT 101 FBT 102 FBT 103 FBT 104 Direct Materials $70,220 97,500 105,300 117,000 iv) Issued indirect materials to production, $30,000. Direct Labour $61,200…arrow_forwardThe trial balance for K and J Nursery, Incorporated, listed the following account balances at December 31, 2024, the end of its fiscal year: cash, $27,000; accounts receivable, $22,000; inventory, $36,000; equipment (net), $91,000; accounts payable, $25,000; salaries payable, $10,500; interest payable, $6,500; notes payable (due in 18 months), $41,000; common stock, $72,000. Determine the year-end balance in retained earnings for K and J Nursery, Incorporated.arrow_forward
- Brun Company produces its product through two processing departments: Mixing and Baking. Information for the Mixing department follows. Direct Materials Conversion Unit Percent Complete Percent Complete Beginning work in process inventory 7.500 Units started this period 104,500 Units completed and transferred out 100.000 Ending work in process inventory 12.000 100% 25% Beginning work in process inventory Direct materials Conversion $6.800 14.500 $21.300 Costs added this period Drect materials 116,400 Conversion Total costs to account for 1.067,000 1.183.400 $1.204.700 Required 1. Prepare the Mixing department's production cost report for November using the weighted average method Check (1) C$1.000 2. Prepare the November 30 journal entry to transfer the cost of completed units from Mixing to Bakingarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardNot need ai solution please solve this general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





