
Concept explainers
(a)
Liabilities
Liabilities are an obligation of the business to pay to the creditors in future for the goods and services purchased on account or any for other financial benefit received. It can be current liabilities or a non-current liabilities depending upon the time period in which it is paid.
Current liability
Current liability is an obligation that the companies need to pay from the remaining current assets or creation of other current liabilities within a fiscal year or the operating cycle whichever is higher.
Notes payable
Notes Payable is a written promise to pay a certain amount on a future date, with certain percentage of interest. Companies use to issue notes payable to meet short-term financing needs.
To Prepare: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of 6% notes payable to purchase of an inventory on September 1, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Sept. 1, 2017 | Inventory | $12,000 | |
| 6% Notes payable | $12,000 | ||
| (To record the 6% notes payable for purchases of an inventory of Corporation E) |
Table (1)
Description:
- Inventory is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit inventory account for $12,000.
- 6% Notes payable is a current liability and increased. Therefore, credit 6% notes payable account for $12,000.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable on September 30, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable on September 30, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Sept. 30, 2017 | Interest expense (1) | $60 | |
| Interest payable | $60 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable for Corporation E) |
Table (2)
Working note:
Calculate interest expense on 30th September 2017 of Corporation E as shown below:
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of
stockholders’ equity , and decreased it. Therefore, debit inventory account for $60. - Interest payable is a current liability and decreased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $60.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the issuance of 8% notes payable to purchase equipment on October 1, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the issuance of 8% notes payable to purchases equipment on October 1, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Oct. 1, 2017 | Equipment | $16,500 | |
| 8% Notes payable | $16,500 | ||
| (To record the 8% notes payable to purchase of an equipment for Corporation E) |
Table (3)
Description:
- Equipment is a fixed asset, and increased. Therefore, debit equipment account for $16,500.
- 8% Notes payable is a current liability and increased. Therefore, credit 8% notes payable account for $16,500.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable and 8% notes payable on October 31, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable and 8% notes payable on October 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Oct. 31, 2017 | Interest expense (3) | $170 | |
| Interest payable | $170 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable for Corporation E) |
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculate interest expense on 31st October 2017 of Corporation E as shown below:
Calculate interest expense on 31st October 2017 of Corporation E as shown below:
Calculate total interest expenses as on 31st October 2017 of Corporation E as shown below:
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit inventory account for $170.
- Interest payable is a current liability and decreased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $170.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the issuance of 6% notes payable to purchases Vehicle on November 1, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the issuance of 8% notes payable to purchase vehicle on November 1, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Nov. 1, 2017 | Vehicle | $34,000 | |
| 6% Notes payable | $26,000 | ||
| Cash | $8,000 | ||
| (To record the 8% notes payable to purchase of an equipment for Corporation E) |
Table (5)
Description:
- Vehicle is a fixed asset, and increased. Therefore, debit Vehicle account for $34,000.
- 6% Notes payable is a current liability and increased. Therefore, credit 6% notes payable account for $26,000.
- Cash is a current asset and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $8,000.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable on November 31, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the accrued interest expense of 6% notes payable on November 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Nov. 31, 2017 | Interest expense (5) | $300 | |
| Interest payable | $300 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expense for Corporation E) |
Table (6)
Working note:
Calculate interest expense on 31st October 2017 of Corporation E as shown below:
Calculate total interest expenses as on 31st November 2017 using working note (3) and (4) of Corporation E as shown below:
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit inventory account for $300.
- Interest payable is a current liability and decreased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $300.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the payment of principal and interest on December 1, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of principal and interest on December 1, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Dec. 1, 2017 | 6% Notes payable | $12,000 | |
| Interest payable (6) | $180 | ||
| Cash | $12,180 | ||
| (To record the 6% notes payable to purchase of an equipment for Corporation E) |
Table (7)
Working note:
Calculate interest payable for Corporation E as shown below:
Description:
- 6% notes payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account for $12,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability and decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $180.
- Cash is a current asset and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $12,180.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the payment of principal and interest on December 31, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of principal and interest on December 31, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| Dec. 31, 2017 | Interest expense (7) | $240 | |
| Interest payable | $240 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expenses for Corporation E) |
Table (8)
Working note:
Calculate interest expenses for Corporation E on 31st December 2017 using working note (2) and (4) as shown below:
(b)
To Compute: The T-Accounts of Notes payable, Interest payable and Interest expense of Corporation E.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the T-Accounts of Notes payable, Interest payable and Interest expense of Corporation E as shown below:
| Notes Payable | |||||
| 12/1 | $12,000 | 9/1 | $12,000 | ||
| 10/1 | $16,500 | ||||
| 11/1 | $26,000 | ||||
| 12/31 | Bal. | $42,500 | |||
Table (1)
| Interest Payable | |||||
| 12/1 | $180 | 9/30 | $60 | ||
| 10/31 | $170 | ||||
| 11/30 | $300 | ||||
| 12/31 | $240 | ||||
| 12/31 | Bal. | $590 | |||
Table (2)
| Interest Expense | |||||
| 9/30 | $60 | ||||
| 10/31 | $170 | ||||
| 11/30 | $300 | ||||
| 12/31 | $240 | ||||
| 12/31 | Bal. | $770 | |||
Table (3)
Description:
Normal balance of assets account, expenses, and losses account are debit balance. Hence, a debit increases these accounts and credit decreases these accounts.
Normal balance of liabilities account, capital account, revenue account and gains are credit balance. Hence, a debit decreases these accounts and credit increases these accounts.
(c)
To Compute: The balance sheet presentation of notes payable and interest payable of Corporation E on December 31, 2017.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the balance sheet presentation of notes payable and interest payable of Corporation E on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
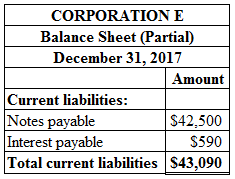
Figure (1)
(d)
To Identify: The total interest expense of Corporation E using T-Accounts.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate total interest expense of Corporation E using T-Accounts as shown below:
| Interest Expense | |||||
| 9/30 | $60 | ||||
| 10/31 | $170 | ||||
| 11/30 | $300 | ||||
| 12/31 | $240 | ||||
| 12/31 | Bal. | $770 | |||
Table (3)
Therefore, total interest expense of Corporation E is $770.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting 8th Edition
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning


