
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the alcohols is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the alcohols is given below.
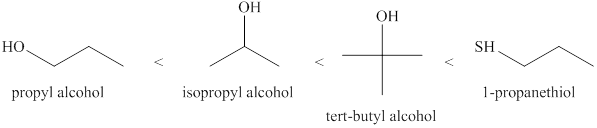
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing hydrogen ion.
Sulfur atom present in
Order of the acidity is shown below in Figure 1.

Figure 1
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is
(b)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is given below.
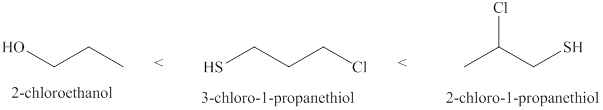
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing hydrogen ion. Sulfur atom present in
Therefore, increasing order of the given molecules is shown below in Figure 2.
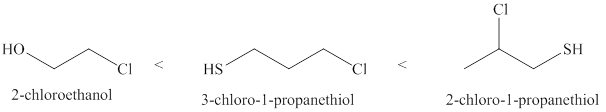
Figure 2
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is
(c)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is stated below.
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing hydrogen ion. Nitrogen atom which is positively charged, stabilizes the negative charge which is generated after releasing the hydrogen ion. Therefore, structure 3 is the most stable structure with most acidic character. Position of the electronegative atom also determines the strength of an acid. Closer the electronegative atom to the generated negative charge after releasing the hydrogen ion, more is the strength of the acid.
Therefore, increasing order of the given molecules is stated below.
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is
(d)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is stated below.
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing the hydrogen ion. In structure
Therefore, increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is stated below.
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is
(e)
Interpretation:
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidity of a molecule is dependent on the value of
Answer to Problem 10.46AP
The increasing order of acidity of the molecules is stated below.
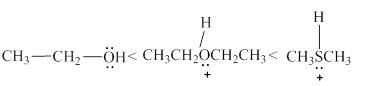
Explanation of Solution
Acidity of the molecules is dependent upon the stability of the ion formed after releasing the hydrogen ion. In structure
Therefore, increasing order of the given molecules is stated below in Figure 3.
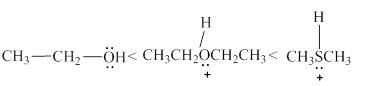
Figure 3
The increasing order of acidity of the given molecules is shown above in Figure 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions
- answer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forward
- answer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardC app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Drawingarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following reaction sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. H O 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CHзBr Drawingarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


