
(a)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotope should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.27P
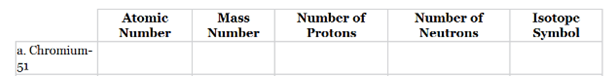
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The atomic number for chromium is 24 and mass number is 51.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the number of protons in chromium is 24 and the number of neutrons in chromium can be calculated by simply subtracting number of protons from mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Chromium is
(b)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotopes should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.27P
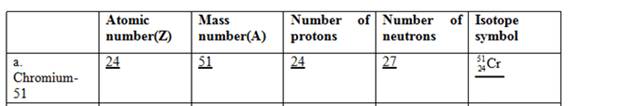
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Palladium-103 | 46 | 103 | 46 | 57 |
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons.
The atomic number for the element listed in b option is given which is equal to 46 and the mass number is 103. So, the element is Palladium (Pd).
Since atomic number = number of protons.
Thus, the number of protons in palladium is 46 and the number of neutrons in palladium can be calculated by simply subtracting number of protons from the mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Palladium is
(c)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotopes should be completed.
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.27P
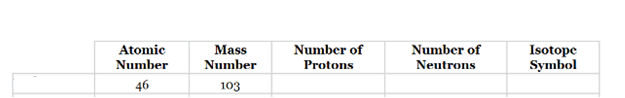
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Potassium-19 | 19 | 42 | 19 | 23 |
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The number of protons in element listed in option c is 19 and the number of neutrons is 23.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the atomic number of this element is 19 and the element will be Potassium (K) and the mass number will be calculated as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Palladium is
(d)
Interpretation:
The given table of isotopes should be completed.

Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.27P
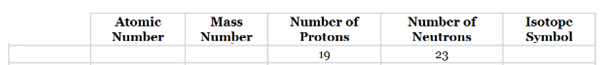
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Xenon-133 | 54 | 133 | 54 | 79 |
Explanation of Solution
Atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The number of protons for element listed in d option are 54 and mass number is 133.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, atomic number for this element will be 54 and the element is Xenon (Xe) and the number of neutrons in xenon can be calculated by simply subtracting number of protons from mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Xenon is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM
- Please help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forwardSelect the stronger base from each pair of compounds. (a) H₂CNH₂ or EtzN (b) CI or NH2 NH2 (c) .Q or EtzN (d) or (e) N or (f) H or Harrow_forward
- 4. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. 2. 1. LDA 3. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





