
(a)
Notes payable
Notes Payable is a written promise to pay a certain amount on a future date, with certain percentage of interest. Companies use to issue notes payable to meet short-term financing needs.
Sales tax payable
The Company collects the tax from the customer when the sale is made on cash or on account, and periodically pays the collections to the state’s department of revenue. Many states are implementing sales taxes on purchases made on the internet also. Sales taxes are stated as percentage of the sales price.
Unearned revenue
It is an advance made by the buyer before receiving the product or service. In upcoming period seller will have an obligation to provide goods or perform the services to the buyer for the payment already received. It is a current liability until the goods are delivered or the service is performed.
Salaries and wages payable
Salaries and wages payable is a payment made to an employee for completion of work allocated by the company. Gross pay is computed by using normal hours worked by the employee with hourly wages rate.
Payroll tax
The costs incurred by an employer to pay the employee for his labor, including other employee benefits, plus the payroll taxes the employer pays to the government, are called payroll tax.
Current liability
Current liability is an obligation that the companies need to pay from the remaining current assets or creation of other current liabilities within a fiscal year or the operating cycle whichever is higher.
To prepare: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of 5% notes payable from bank A on January 1, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2017 | Cash | $18,000 | |
| 5% Notes payable | $18,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of 5%Notes payable from Bank A) |
Table (1)
Description:
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit Cash account for $18,000.
- 5% Notes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit 5% notes payable account for $18,000.
To prepare: The journal entry to record the cash proceeds from sales revenue of $6,254 that includes sales tax on January 5, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the cash proceeds from sales revenue of $6,254 that includes sales tax on January 5, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| January 5, 2017 | Cash | $6,254 | |
| Sales taxes payable (2) | $354 | ||
| Sales revenue (1) | $5,900 | ||
| (To record sales revenue and sales tax of Company R) |
Table (2)
Working notes:
Calculation of sales amount of Company C is shown below:
Calculation of Sales taxes of Company C is shown below:
Description:
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit Cash account for $6,254.
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore credit sales taxes payable for $354.
- Sales revenue is a component of
stockholders’ equity , and increased. Therefore, credit sales revenue account for $5,900.
To prepare: The journal entry to record performed service for customers who had made advance payments for $10,000.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record performed service for customers who had made advance payments for $10,000 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| January 12, 2017 | Unearned service revenue | $10,000 | |
| Service revenue | $10,000 | ||
| (To record service revenue earned that was collected in advance for Company R) |
Table (3)
Description:
Unearned service revenue is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit unearned service revenue account for $10,000.
Service revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, service revenue account for $10,000.
To prepare: The sales taxes collected from state treasurer’s department on 14th January 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the sales taxes collected from state treasurer’s department of Company R on January 14, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| January 14, 2017 | Sales taxes payable | $6,600 | |
| Cash | $6,600 | ||
| (To record cash payment for sales taxes payable for Company R) |
Table (4)
Description:
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit sales taxes payable account for $6,600.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $6,600.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record sale of 500 units of new product on credit at $48 per unit, plus 6% sales taxes on 20th January 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record sale of 500 units of new product on credit at $48 per unit, plus 6% sales taxes on 20th January 2017 as on below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| January 20, 2017 | $25,440 | ||
| Sales taxes payable (2) | $1,440 | ||
| Sales revenue (1) | $24,000 | ||
| (To record sale on account and sales taxes of Company R) |
Table (5)
Working note:
Calculation of sale revenue of Company R is shown below:
Calculation of Sales taxes payable of Company R is shown below:
Description:
- Accounts receivable is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit accounts receivable account for $25,440.
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit sales taxes payable account for $1,440.
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit sales revenue account for $24,000.
(b)
To prepare: The
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjusting entry to record 5% notes payable of Company R on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2017 | Interest expense (1) | $75 | |
| Interest payable | $75 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expense of 5% notes payable for Company R) |
Table (6)
Working note:
Calculation of interest expense for the company R is shown below:
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $75.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $75.
To prepare: The adjusting journal entry to record salaries and wages expense of Company R on 31st December 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjusting journal entry to record salaries and wages expense of Company R on 31st December 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2017 | Salaries and wages expense | $70,000 | |
| FICA taxes payable | $5,355 | ||
| State income taxes payable | $1,500 | ||
| Federal income taxes payable | $5,000 | ||
| Salaries and wages payable | $58,145 | ||
| (To record the salaries and wages expenses for company R) |
Table (7)
Description:
- Salaries and wages expense is a stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit salaries and wages expense account for $70,000.
- FICA taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit FICA taxes payable account for $5,355.
- State income taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit state income taxes payable account for $1,500.
- Federal income taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit federal income taxes payable account for $5,000.
- Salaries and wages payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit salaries and wages payable account for $58,145.
To prepare: The adjusting entry to record payroll tax expenses for Company R on 31st December 2017 as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account title and Description | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2017 | Payroll taxes expense | $5,355 | |
| FICA taxes payable | $5,355 | ||
| (To record the salaries and wages expenses for company R) |
Table (8)
Description:
- Payroll taxes expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit payroll taxes expense account for $5,355.
- FICA taxes payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, credit FICA taxes payable account for $5,335.
(c)
To prepare: The current liabilities section of the balance sheet for Company R on January 31, 2017.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the current liabilities section of the balance sheet for Company R on January 31, 2017 as shown below:
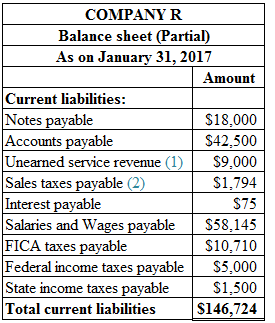
Figure (1)
Working note:
Calculation of unearned service revenue for Company R is shown below:
Calculation of Sales taxes payable for Company R is shown below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting, Binder Ready Version: Tools for Business Decision Making
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
