
General Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780073402758
Author: Chang, Raymond/ Goldsby
Publisher: McGraw-Hill College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.19QP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: In the increasing order of dipole moment, the given molecules have to be listed.
Concept Introduction: The term dipole moment refers to the quantitative measure of polarity of a bond. It is represented as
For example:
The diatomic molecule
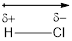
The crossed arrow represents the direction of the shift of electrons towards the highly electronegative chlorine atom form the least electronegative hydrogen atom.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the following two half-reactions, determine the pH range in which $NO_2^-\ (aq)$ cannot be found as the predominant chemical species in water.* $NO_3^-(aq)+10H^+(aq)+8e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+3H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=14.88$* $NO_2^-(aq)+8H^+(aq)+6e^-\rightarrow NH_4^+(aq)+2H_2O(l),\ pE^{\circ}=15.08$
Indicate characteristics of oxodec acid.
What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.
Chapter 10 Solutions
General Chemistry
Ch. 10.1 - Practice Exercise Use the VSEPR model to predict...Ch. 10.1 - Review of Concepts
Which of the following...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 1PECh. 10.2 - Prob. 1RCCh. 10.3 - Prob. 1RCCh. 10.4 - Prob. 1PECh. 10.4 - Prob. 2PECh. 10.4 - Prob. 1RCCh. 10.5 - Prob. 1PECh. 10.5 - Prob. 1RC
Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 1RCCh. 10.6 - Prob. 2RCCh. 10.6 - Prob. 1PECh. 10 - Prob. 10.1QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.2QPCh. 10 - 10.3 How many atoms arc directly bonded to the...Ch. 10 - 10.4 Discuss the basic features of the VSEPR...Ch. 10 - 10.5 In the trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, why...Ch. 10 - 10.6 The geometry of CH4 could be square planar,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.7QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.8QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.9QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.10QPCh. 10 - 10.11 Describe the geometry around each of the...Ch. 10 - 10.12 Which of these species are tetrahedral?...Ch. 10 - 10.13 Define dipole moment. What are the units and...Ch. 10 - 10.14 What is the relationship between the dipole...Ch. 10 - 10.15 Explain why an atom cannot have a permanent...Ch. 10 - 10.16 The bonds in beryllium hydride (BeH2)...Ch. 10 - 10.17 Referring to Table 10.3. arrange the...Ch. 10 - 10.18 The dipole moments of the hydrogen halides...Ch. 10 - 10.19 List these molecules in order of increasing...Ch. 10 - 10.20 Docs the molecule OCS have a higher or lower...Ch. 10 - 10.21 Which of these molecules has a higher dipole...Ch. 10 - 10.22 Arrange these compounds in order of...Ch. 10 - 10.23 What is valence bond theory? How does it...Ch. 10 - 10.24 Use valence bond theory to explain the...Ch. 10 - 10.25Draw a potential energy curve for the bond...Ch. 10 - 10.26 What is the hybridization of atomic...Ch. 10 - 10.27 How does a hybrid orbital differ from a pure...Ch. 10 - 10.28 What is the angle between these two hybrid...Ch. 10 - 10.29 How would you distinguish between a sigma...Ch. 10 - 10.30 Which of these pairs of atomic orbitals of...Ch. 10 - 10.31 The following potential energy curve...Ch. 10 - 10.32 What is the hybridization state of Si in...Ch. 10 - 10.33 Describe the change in hybridization (if...Ch. 10 - 10.34 Consider the reaction
Describe the changes...Ch. 10 - 10.35 What hybrid orbitals are used by nitrogen...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.36QPCh. 10 - 10.37 Specify which hybrid orbitals are used by...Ch. 10 - 10.38 What is the hybridization state of the...Ch. 10 - 10.39 The allene molecule H2C=C=CH2 is linear (the...Ch. 10 - 10.40 Describe the hybridization of phosphorus in...Ch. 10 - 10.41 How many sigma bonds and pi bonds are there...Ch. 10 - 10.42 How many pi bonds and sigma bonds are there...Ch. 10 - 10.43 Give the formula of a cation comprised of...Ch. 10 - 10.44 Give the formula of an anion comprised of...Ch. 10 - 10.45 What is molecular orbital theory? How does...Ch. 10 - 10.46 Define these terms: bonding molecular...Ch. 10 - 10.47 Sketch the shapes of these molecular...Ch. 10 - 10.48 Explain the significance of bond order. Can...Ch. 10 - 10.49 Explain in molecular orbital terms the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.50QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.51QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.52QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.53QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.54QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.55QPCh. 10 - 10.56 Compare the Lewis and molecular orbital...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.57QPCh. 10 - 10.58 Compare the relative stability of these...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.59QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.60QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.61QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.62QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.63QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.64QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.65QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.66QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.67QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.68QPCh. 10 - 10.69 Draw Lewis structures and give the other...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.70QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.71QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.72QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.73QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.74QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.75QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.76QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.77QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.78QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.79QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.80QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.81QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.82QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.83QPCh. 10 - 10.84 The ionic character of the bond in a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.85QPCh. 10 - 10.86 Aluminum trichloride (AlCl3) is an...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.87QPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.88QPCh. 10 - 10.90 Progesterone is a hormone responsible for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.91SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.92SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.93SPCh. 10 - 10.94 The molecule benzyne (C6H4) is a very...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.95SPCh. 10 - 10.96 As mentioned in the chapter, the Lewis...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.97SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.98SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.99SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.100SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.101SPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.102SP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY