
The following calendar year-end information is taken from the December 31, 2015, adjust
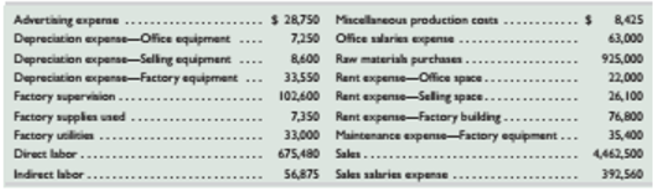
Required
- Identity and classify each of the costs above as either a product or period cost.
- Classify each of the product costs as either direct materials, direct labor, or factory
overhead. - Classify each of the period costs as either selling or general and administrative expenses.
Concept introduction:
Product cost:
The costs are incurred when the product is acquired or produced and are considered in the inventory valuation. It includes costs of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overheads. Rents on factory building, factory maintenance, and depreciation on factory equipment are some of its examples.
Period cost:
These costs are associated with the passage of time, i.e. when the business has no production or inventory purchasing activities, this cost would still be incurred. Mostly, these costs are associated with selling or general and administrative activities. Depreciation on office equipment, advertising expense and office manager salaries are some of its examples.
Requirement 1:
Identification and Classification of costs of Leone Company as either product or period.
Answer to Problem 2PSA
Classification of costs of Leone Company (Amount in $):
| Particulars | Product cost | Period cost |
| Advertising expense | 28, 750 | |
| Depreciation expense- Office equipment | 7, 250 | |
| Depreciation expense- Selling equipment | 8, 600 | |
| Depreciation expense- Factory equipment | 33, 550 | |
| Factory supervision | 1, 02, 600 | |
| Factory supplies used | 7, 350 | |
| Factory utilities | 33, 000 | |
| Direct labor | 6, 75, 480 | |
| Indirect labor | 56, 875 | |
| Miscellaneous production costs | 8, 425 | |
| Office salaries expense | 63, 000 | |
| Raw materials purchases | 9, 25, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Office space | 22, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Selling space | 26, 100 | |
| Rent expense- Factory building | 76, 800 | |
| Maintenance expense- Factory equipment | 35, 400 | |
| Sales salaries expense | 3, 92, 560 |
Explanation of Solution
The costs of Leone Company can be classified into product or period based on their nature as explained below:
Product costs are incurred when the product is acquired or produced and are considered in the inventory valuation. It includes costs of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overheads. Therefore, following costs would be classified as Product:
- Depreciation expense- Factory equipment: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Factory supervision: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Factory supplies used: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Factory utilities: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Direct labor: as it is cost of direct labor
- Indirect labor: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Miscellaneous production costs: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Raw material purchases: as it relates to direct materials
- Rent expense- Factory building: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
- Maintenance expense- Factory equipment: as it relates to manufacturing overheads
Period costs are associated with the passage of time, i.e. when the business has no production or inventory purchasing activities, this cost would still be incurred. Mostly, these costs are associated with selling or general and administrative activities. Following would be classified as Period costs:
- Advertising expense: : as it relates to selling activity
- Depreciation expense- Office equipment: as it relates to general and administrative activity
- Depreciation expense- Selling equipment: as it relates to selling activity
- Office salaries expense: as it relates to general and administrative activity
- Rent expense- Office space: as it relates to general and administrative activity
- Rent expense- Selling space: as it relates to selling activity
- Sales salaries expense: as it relates to selling activity
Therefore, identification and classification of costs of Leone Company, as asked in the given problem is shown below:
Classification of costs of Leone Company (Amount in $):
| Particulars | Product cost | Period cost |
| Advertising expense | 28, 750 | |
| Depreciation expense- Office equipment | 7, 250 | |
| Depreciation expense- Selling equipment | 8, 600 | |
| Depreciation expense- Factory equipment | 33, 550 | |
| Factory supervision | 1, 02, 600 | |
| Factory supplies used | 7, 350 | |
| Factory utilities | 33, 000 | |
| Direct labor | 6, 75, 480 | |
| Indirect labor | 56, 875 | |
| Miscellaneous production costs | 8, 425 | |
| Office salaries expense | 63, 000 | |
| Raw materials purchases | 9, 25, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Office space | 22, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Selling space | 26, 100 | |
| Rent expense- Factory building | 76, 800 | |
| Maintenance expense- Factory equipment | 35, 400 | |
| Sales salaries expense | 3, 92, 560 |
Concept introduction:
Product cost:
The costs are incurred when the product is acquired or produced and are considered in the inventory valuation. It includes costs of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overheads. Rents on factory building, factory maintenance, depreciation on factory equipment are some of its examples.
Direct materials:
These are the cost of materials used for production of the product. The cost of all the materials integral to finished product and having a physical presence that is readily traced to that finished product is included in direct materials.
Direct labor:
These consist of wages paid to labor who have physically and directly work on the goods being produced other than administrative and selling activities.
Factory overheads:
All other costs remaining other than direct materials and direct labor relating to factory comes under Factory overheads.
Requirement 2:
Identification and Classification of product costs of Leone Company as direct materials, direct labor and factory overheads.
Answer to Problem 2PSA
Classification of product costs of Leone Company (Amount in $):
| Particulars | Direct materials | Direct labor | Factory overheads |
| Depreciation expense- Factory equipment | 33, 550 | ||
| Factory supervision | 1, 02, 600 | ||
| Factory supplies used | 7, 350 | ||
| Factory utilities | 33, 000 | ||
| Direct labor | 6, 75, 480 | ||
| Indirect labor | 56, 875 | ||
| Miscellaneous production costs | 8, 425 | ||
| Raw materials purchases | 9, 25, 000 | ||
| Rent expense- Factory building | 76, 800 | ||
| Maintenance expense- Factory equipment | 35, 400 |
Explanation of Solution
The product costs of Leone Company can be classified into direct materials, direct labor and factory overheads based on their nature as explained below:
Direct materials are the cost of materials used for production of the product. Therefore, costs of Raw material purchases would be classified under direct materials.
Direct labor includes wages paid to labor who have physically and directly work on the goods being produced other than administrative and selling activities. Only cost of direct labor would be covered under direct labor.
All other costs remaining other than direct materials and direct labor relating to factory comes under Factory overheads. Therefore, following costs would factory overheads:
- Depreciation expense- Factory equipment
- Factory supervision
- Factory supplies used
- Factory utilities
- Indirect labor
- Miscellaneous production costs
- Rent expense- Factory building
- Maintenance expense- Factory equipment
Therefore, identification and classification of product costs of Leone Company, as asked in the given problem is shown below:
Classification of product costs of Leone Company (Amount in $):
| Particulars | Direct materials | Direct labor | Factory overheads |
| Depreciation expense- Factory equipment | 33, 550 | ||
| Factory supervision | 1, 02, 600 | ||
| Factory supplies used | 7, 350 | ||
| Factory utilities | 33, 000 | ||
| Direct labor | 6, 75, 480 | ||
| Indirect labor | 56, 875 | ||
| Miscellaneous production costs | 8, 425 | ||
| Raw materials purchases | 9, 25, 000 | ||
| Rent expense- Factory building | 76, 800 | ||
| Maintenance expense- Factory equipment | 35, 400 |
Concept introduction:
Period cost:
These costs are associated with the passage of time, i.e. when the business has no production or inventory purchasing activities, this cost would still be incurred. Mostly, these costs are associated with selling or general and administration activities. Depreciation on office equipment, advertising expense and office manager salaries are some of its examples.
Selling expenses:
These are the expenses incurred for making sales. These include direct and indirect cost associated with selling a product.
General and administrative expenses:
These are basically the overheads of the company. These are the costs a company incurs to keep its business operational.
Requirement 3:
Identification and Classification of period costs of Leone Company as selling and general or administration expenses.
Answer to Problem 2PSA
Classification of period costs of Leone Company (Amount in $):
| Particulars | Selling expenses | General or administration expenses |
| Advertising expense | 28, 750 | |
| Depreciation expense- Office equipment | 7, 250 | |
| Depreciation expense- Selling equipment | 8, 600 | |
| Office salaries expense | 63, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Office space | 22, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Selling space | 26, 100 | |
| Sales salaries expense | 3, 92, 560 |
Explanation of Solution
The period costs of Leone Company can be classified into product or period based on their nature as explained below:
Period costs are associated with the passage of time and are associated with selling and general or administration activities.
Selling expenses are incurred for making sales and include direct and indirect cost associated with selling a product. Following would be covered under selling expenses:
- Advertising expense:
- Depreciation expense- Selling equipment
- Rent expense- Selling space
- Sales salaries expense
General or administrative expenses are the overheads a company incurs to keep its business operational. Following are classified under them:
- Depreciation expense- Office equipment
- Office salaries expense
- Rent expense- Office space
Therefore, identification and classification of period costs of Leone Company, as asked in the given problem is shown below:
Classification of period costs of Leone Company (Amount in $):
| Particulars | Selling expenses | General or administration expenses |
| Advertising expense | 28, 750 | |
| Depreciation expense- Office equipment | 7, 250 | |
| Depreciation expense- Selling equipment | 8, 600 | |
| Office salaries expense | 63, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Office space | 22, 000 | |
| Rent expense- Selling space | 26, 100 | |
| Sales salaries expense | 3, 92, 560 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- A business purchased machinery for $210,000 on January 1, 2023.arrow_forwardAn asset owned by Shahidi Technologies has a book value of $36,750 on June 30, Year 5. The asset has been depreciated at an annual rate of $8,200 using the straight-line method. Assuming the asset is sold on June 30, Year 5 for $41,500, how should the company record the transaction? a. Neither a gain nor a loss is recognized on this type of transaction. b. A gain on sale of $4,750. c. A gain on sale of $4,000. d. A loss on sale of $4,750. e. A loss on sale of $4,000.arrow_forwardTaylor Technologies purchased a server system for its data center at a cost of $124,800. The server system has an estimated residual value of $9,200 and an estimated useful life of 8 years. What is the amount of the annual depreciation computed by the straight-line method?arrow_forward
- Can you please help me solve this General accounting problem using accurate methodsarrow_forwardPeralta Distillery has estimated budgeted costs of $134,500, $155,000, and $175,500 for the manufacture of 5,000, 7,000, and 9,000 liters of spirits, respectively, next quarter. What are the variable and fixed manufacturing costs in the flexible budget for Peralta Distillery?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forward
- Please provide correct answerarrow_forwardGaulle Metal Industries manufactures a single product that sells for $75 per unit. Variable costs are $42 per unit, and fixed costs total $168,000 per month. Calculate the operating income if the selling price is raised to $82 per unit, maintenance expenditures are increased by $22,000 per month, and monthly unit sales volume becomes 6,200 units.arrow_forwardCompute the cost should be allocated to the warehouse.arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College




