
(This serial problem begins in this chapter and continues through most Of the book. It is helpful, but not necessary, to use the Working papers that accompany the book.)
SP 1 Santana Rey, owner of Business Solutions, decides to diversify her business by also manufacturing computer workstation furniture.
Required
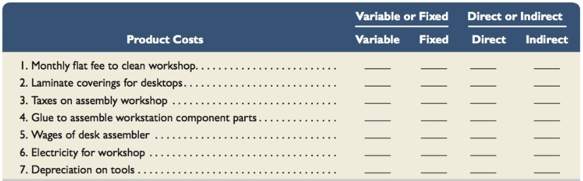
- Classify the following
manufacturing costs of Business Solutions as either (a) variable or fixed and (b) direct or indirect.
- Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for Business Solutions for the month ended January 31, 2016. Assume the following manufacturing costs:
Direct materials: $2,2000
Beginning work in process: none (December 31, 2015)
Ending work in process: $540 (January 31, 2016)
- Prepare the cost of goods sold section of a partial income statement for Business Solutions for the month ended January 31, 2016.
Concept introduction:
Variable cost:
The costs which are associated with the amount of goods produced or services provided. These vary directly with the production level i.e. company’s variable cost increases as the production increases and vice-a-versa.
Fixed cost:
These costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. They remain same even if the company does not produce any product or provide any service during an accounting period.
Direct cost:
These costs, as the name specifies, are traceable to the production of specific product or service. These are connected to specific cost object which can be a product, department or project.
Indirect cost:
These costs are necessary for production but not traceable to act of production. These costs are necessary to keep business operational. They go beyond the costs associated with creating a product to include the costs of maintaining the entire company.
Requirement 1:
Classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solutions as (a) variable or fixed and (b) direct or indirect.
Answer to Problem 1SP
Classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solutions:
| Particulars | Variable or Fixed cost | Direct or Indirect cost |
| Monthly flat fee to clean workshop | Fixed | Indirect |
| Laminate coverings for desktops | Variable | Direct |
| Taxes on assembly workshops | Fixed | Indirect |
| Glue to assemble workstation component parts | Variable | Indirect |
| Wages of desk assembler | Variable | Direct |
| Electricity for workshop | Variable | Indirect |
| Depreciation on tools | Fixed | Indirect |
Explanation of Solution
The manufacturing costs of Business Solutions can be classified into variable or fixed and direct or indirect costs based on their nature i.e. on the basis of their behavior and traceability as explained below:
Variable costs vary directly with the production level i.e. company’s variable cost increases as the production increases and vice-a-versa. Therefore, following costs would be classified as Variable:
- Laminate coverings for desktops: The number of desktops held by Business Solutions would determine the costs for their laminate coverings which would vary
- Glue to assemble workstation component parts: Component parts held by Business Solutions at its workstation would determine the costs for glue required for their assembly
- Wages of desk assembler: Number of desk assembler may vary at different periods, thereby leading to variation in their wages
- Electricity for workshop: Electricity cost for workshop would vary in proportion of number of units consumed
Fixed costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. Therefore, those costs which are fixed in nature would be covered under fixed costs as given below:
- Monthly flat fee to clean workshop: The cost that would be incurred for cleaning of workshop monthly is fixed in nature
- Taxes on assembly workshops: Taxes incurred on assembly workshops are fixed irrespective of the level of production
- Depreciation on tools: The depreciation charge on tools would remain fixed and would not change with the level of production
Direct costs are traceable to the production of specific product or service. These are connected to specific cost object which can be a product, department or project. Following would be classified as direct costs:
- Laminate coverings for desktops: These costs are traceable to the production of specific product
- Wages of desk assembler: These costs are traceable to the production of specific product
Indirect costs are necessary for production but not traceable to act of production. These costs are necessary to keep business operational. They go beyond the costs associated with creating a product to include the costs of maintaining the entire company. Following are the indirect cost given in the problem:
- Monthly flat fee to clean workshop are associated with costs of maintenance
- Taxes on assembly workshops are not traceable to act of production
- Glue to assemble workstation component parts are not traceable to act of production
- Electricity for workshop are costs necessary to keep business operational
- Depreciation on tools are associated with costs of maintenance
Therefore, classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solution as asked in the given problem is shown below in the tabular manner:
Classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solutions:
| Particulars | Variable or Fixed cost | Direct or Indirect cost |
| Monthly flat fee to clean workshop | Fixed | Indirect |
| Laminate coverings for desktops | Variable | Direct |
| Taxes on assembly workshops | Fixed | Indirect |
| Glue to assemble workstation component parts | Variable | Indirect |
| Wages of desk assembler | Variable | Direct |
| Electricity for workshop | Variable | Indirect |
| Depreciation on tools | Fixed | Indirect |
Concept introduction:
Cost of goods manufactured:
Cost of goods manufactured, also known as cost of goods completed calculates the total value of inventory that was produced during the period and is ready for sale. It is the total amount of expenses incurred to turn work in process into finished goods. It includes total manufacturing costs including all direct materials, direct labor, factory overheads to the beginning work in process inventory and subtracting ending work in process inventory which can be seen below:
Requirement 2:
To calculate:
Cost of goods manufactured for Business Solutions for the month ended January 31, 2016.
Answer to Problem 1SP
Cost of goods manufactured = $3, 050
Explanation of Solution
To calculate cost of goods manufactured, following formula would be used:
In the given problem, following information is given:
Direct materials = $2, 200
Direct labor = $900
Factory overheads = $490
Beginning work in process inventory = Nil
Ending work in process inventory = $540
Therefore, schedule of cost of goods manufactured as asked in the given problem is given below:
Schedule of cost of goods manufactured of Business Solutions (Amount in $):
| Particulars | (Amount in $) | (Amount in $) |
| Direct materials | 2, 200 | |
| Add: Direct labor | 900 | |
| Add: Factory overheads | 490 | |
| Total manufacturing costs | 3, 590 | |
| Add: Beginning work in process inventory | 0 | |
| Less: Ending work in process inventory | (540) | |
| Cost of goods manufactured | 3, 050 |
Thus, cost of goods manufactured = $3, 050.
Concept introduction:
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the costs incurred for manufacturing or acquiring the products sold by a company in a given year. It includes all the direct costs incurred for the products sold. It can be calculated using the following formula:
Requirement 3:
Cost of goods sold section of partial income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016.
Answer to Problem 1SP
Cost of goods sold = $2, 700
Explanation of Solution
For calculating cost of goods sold, following formula would be used:
We have already calculated cost of goods manufactured as $3, 050. In the given problem, it is given that Beginning finished goods inventory is Nil and Ending finished goods inventory are $350.
Therefore, Cost of goods sold section of partial income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016 would be:
Cost of goods sold section of partial income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016 of Business Solutions (Amount in $):
| Particulars | (Amount in $) | (Amount in $) |
| Cost of goods manufactured | 3, 050 | |
| Add: Beginning finished goods inventory | 0 | |
| Total manufacturing costs | 3, 050 | |
| Less: Ending finished goods inventory | (350) | |
| Cost of goods sold | 2, 700 |
Thus, Cost of goods sold = $2, 700.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Can you explain the correct approach to solve this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning


