
Nike: Somewhere between a Swoosh and a Slam Dunk
Nike, Inc.’s principal business activity involves the design, development, and worldwide marketing of high-quality footwear, apparel, equipment, and accessory products for serious and recreational athletes. Almost 25,000 employees work for the firm as of 2009. Nike boasts the largest worldwide market share in the athletic footwear industry and a leading market share in sports and athletic apparel.
This case uses Nike’s financial statements and excerpts from its notes to review important concepts underlying the three principal financial statements (
Industry Economics
Product Lines
Industry analysts debate whether the athletic footwear and apparel industry is a performancedriven industry or a fashion-driven industry. Proponents of the performance view point to Nike’s dominant market position, which results in part from continual innovation in product development. Proponents of the fashion view point to the difficulty of protecting technological improvements from competitor imitation, the large portion of total expenses comprising advertising, the role of sports and other personalities in promoting athletic shoes, and the fact that a high percentage of athletic footwear and apparel consumers use the products for casual wear rather than the intended athletic purposes (such as playing basketball or running).
Growth
There are only modest growth opportunities for footwear and apparel in the United States. Concern exists with respect to volume increases (how many pairs of athletic shoes will consumers tolerate in their closets) and price increases (will consumers continue to pay prices for innovative athletic footwear that is often twice as costly as other footwear).
Athletic footwear companies have diversified their revenue sources in two directions in recent years. One direction involves increased emphasis on international sales. With dress codes becoming more casual in Europe and East Asia and interest in American sports such as basketball becoming more widespread, industry analysts view international markets as the major growth markets during the next several years. Increased emphasis on soccer (European football) in the United States aids companies such as Adidas that have reputations for quality soccer footwear.
The second direction for diversification is sports and athletic apparel. The three leading athletic footwear companies capitalize on their brand name recognition and distribution channels to create a line of sportswear that coordinates with their footwear. Team uniforms and matching apparel for coaching staffs and fans have become a major growth avenue. For example, to complement Nike’s footwear sales, Nike acquired Umbro, a major brand-name line of jerseys, shorts, jackets, and other apparel in the soccer market.
Production
Essentially all athletic footwear and most apparel are produced in factories in Asia, primarily China (40%), Indonesia (31%), Vietnam, South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand. The footwear companies do not own any of these manufacturing facilities. They typically hire manufacturing representatives to source and oversee the manufacturing process, helping to ensure quality control and serving as a link between the design and the manufacture of products. The manufacturing process is labor-intensive, with sewing machines used as the primary equipment. Footwear companies typically price their purchases from these factories in U.S. dollars.
Marketing
Athletic footwear and sportswear companies sell their products to consumers through various independent department, specialty, and discount stores. Their sales forces educate retailers on new product innovations, store display design, and similar activities. The market shares of Nike and the other major brand-name producers dominate retailers’ shelf space, and slower growth in sales makes it increasingly difficult for the remaining athletic footwear companies to gain market share. The slower growth also has led the major companies to increase significantly their advertising and payments for celebrity endorsements. Many footwear companies, including Nike, have opened their own retail stores, as well as factory outlet stores for discounted sales of excess inventory.
Athletic footwear and sportswear companies have typically used independent distributors to market their products in other countries. With increasing brand recognition and anticipated growth in international sales, these companies have recently acquired an increasing number of their distributors to capture more of the profits generated in other countries and maintain better control of international marketing.
Financing
Compared to other apparel firms, the athletic footwear firms generate higher profit margins and
Nike Strategy
Nike targets the serious athlete with performance-driven footwear and athletic wear, as well as the recreational athlete. The firm has steadily expanded the scope of its product portfolio from its primary products of high-quality athletic footwear for running, training, basketball, soccer, and casual wear to encompass related product lines such as sports apparel, bags, equipment, balls, eyewear, timepieces, and other athletic accessories. In addition, Nike has expanded its scope of sports, now offering products for swimming, baseball, cheerleading, football, golf, lacrosse, tennis, volleyball, skateboarding, and other leisure activities. In recent years, the firm has emphasized growth outside the United States. Nike also has grown by acquiring other apparel companies, including Cole Haan (dress and casual footwear), Converse (athletic and casual footwear and apparel), Hurley (apparel for action sports such as surfing, skateboarding, and snowboarding), and Umbro (footwear, apparel, and equipment for soccer). The firm sums up the company’s philosophy and driving force behind its success as follows:
Nike designs, develops, and markets high quality footwear, apparel, equipment and accessory products worldwide. We are the largest seller of athletic footwear and apparel in the world. Our strategy is to achieve long-term revenue growth by creating innovative, “must-have” products; building deep, personal consumer connections with our brands; and delivering compelling retail presentation and experiences.
To maintain its technological edge, Nike engages in extensive research at its research facilities in Beaverton, Oregon. It continually alters its product line to introduce new footwear, apparel, equipment, and evolutionary improvements in existing products.
Nike maintains a reputation for timely delivery of footwear products to its customers, primarily as a result of its “Futures” ordering program. Under this program, retailers book orders five to six months in advance. Nike guarantees delivery of the order within a set time period at the agreed price at the time of ordering. Approximately 89% of the U.S. footwear orders received by Nike during 2009 came through its Futures program. This program allows the company to improve production scheduling, thereby reducing inventory risk. However, the program locks in selling prices and increases Nike’s risk of increased raw materials and labor costs. Independent contractors manufacture virtually all of Nike’s products. Nike sources all of its footwear and approximately 95% of its apparel from other countries.
The following exhibits present information for Nike:
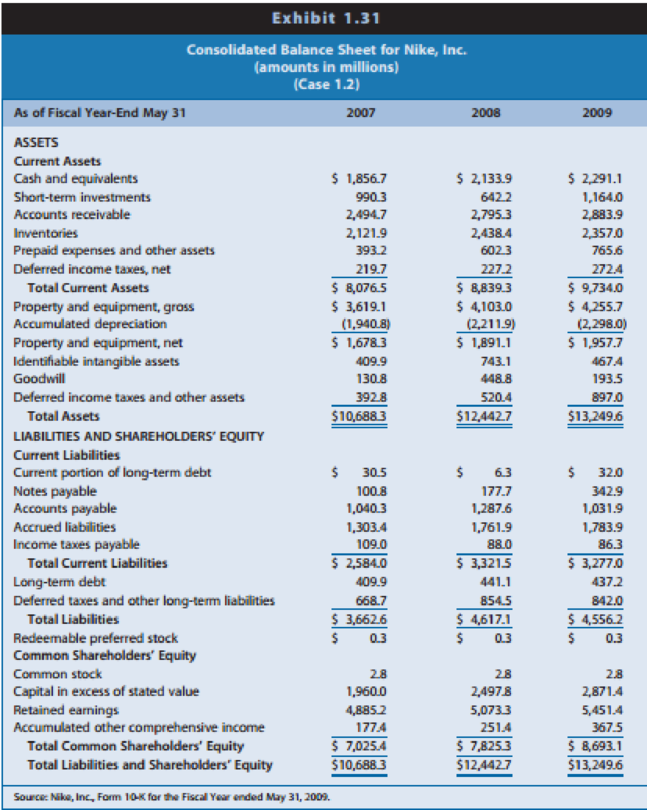
Exhibit 1.31: Consolidated balance sheets for 2007, 2008, and 2009
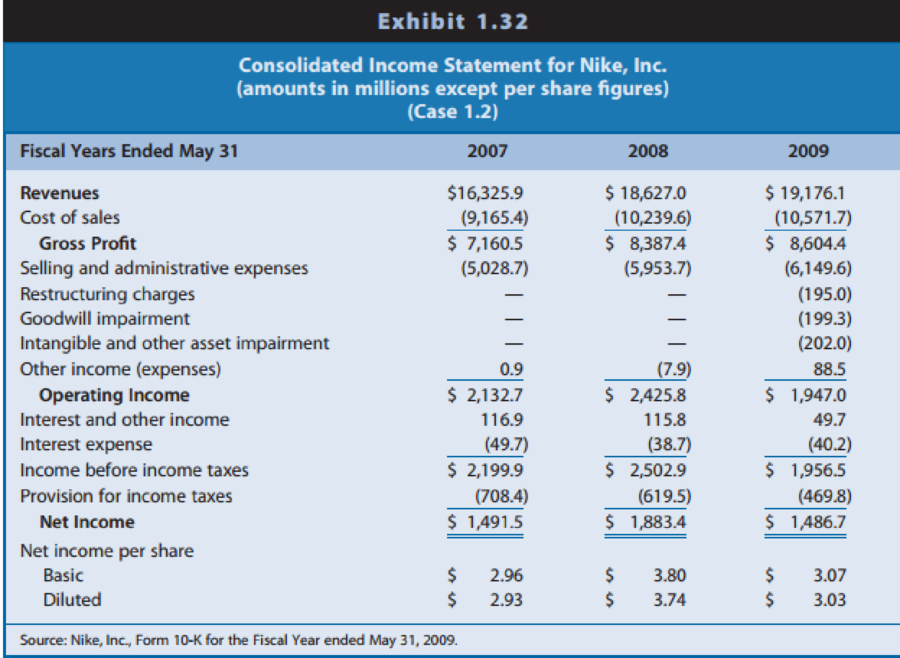
Exhibit 1.32: Consolidated income statements for 2007,2008, and 2009
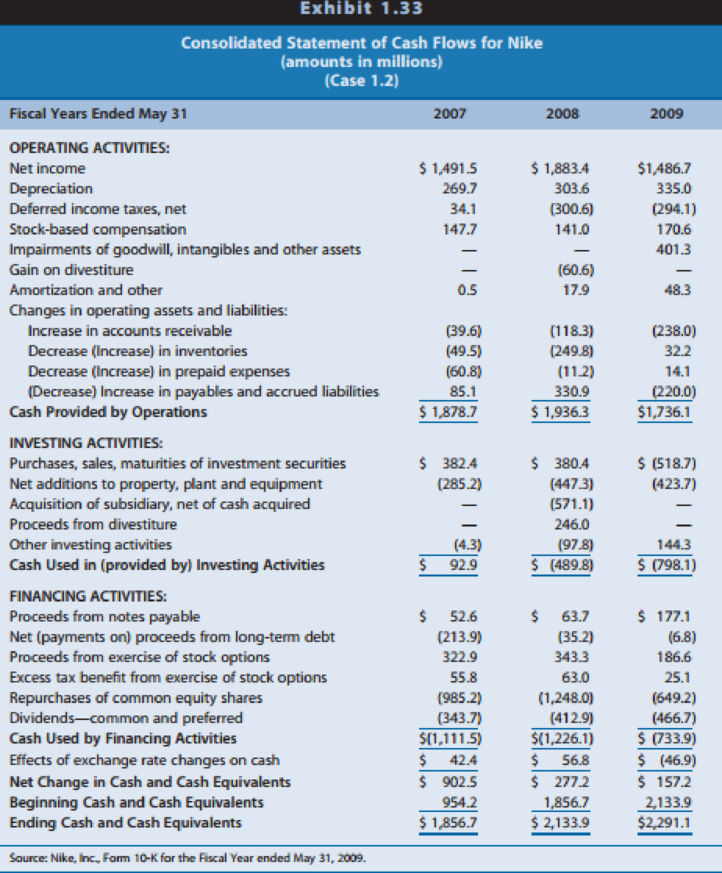
Exhibit 1.33: Consolidated statements of cash flows 2007, 2008, and 2009
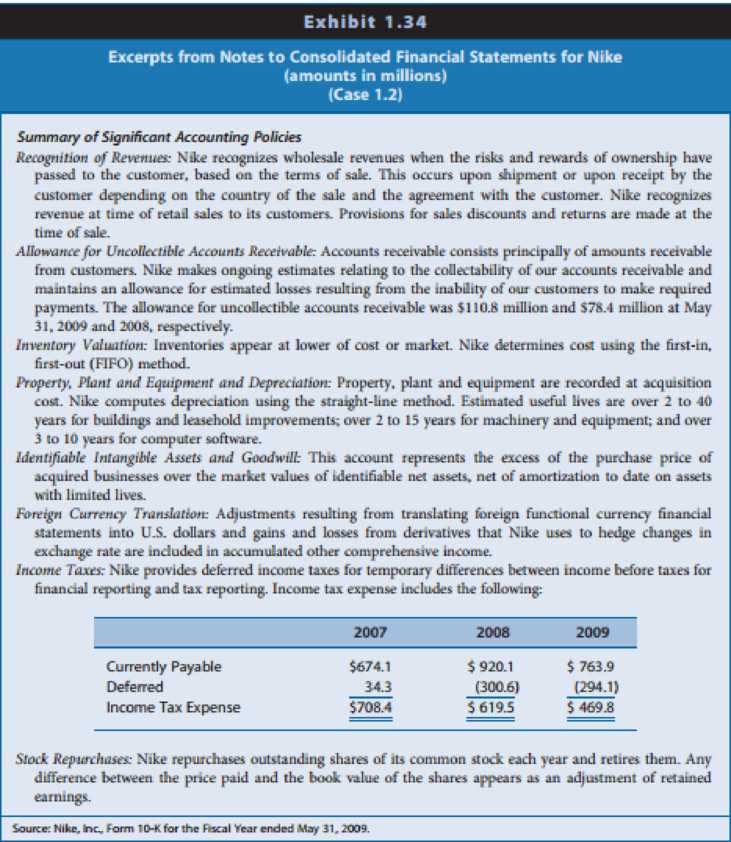
Exhibit 1.34: Excerpts from the notes to Nike’s financial statements
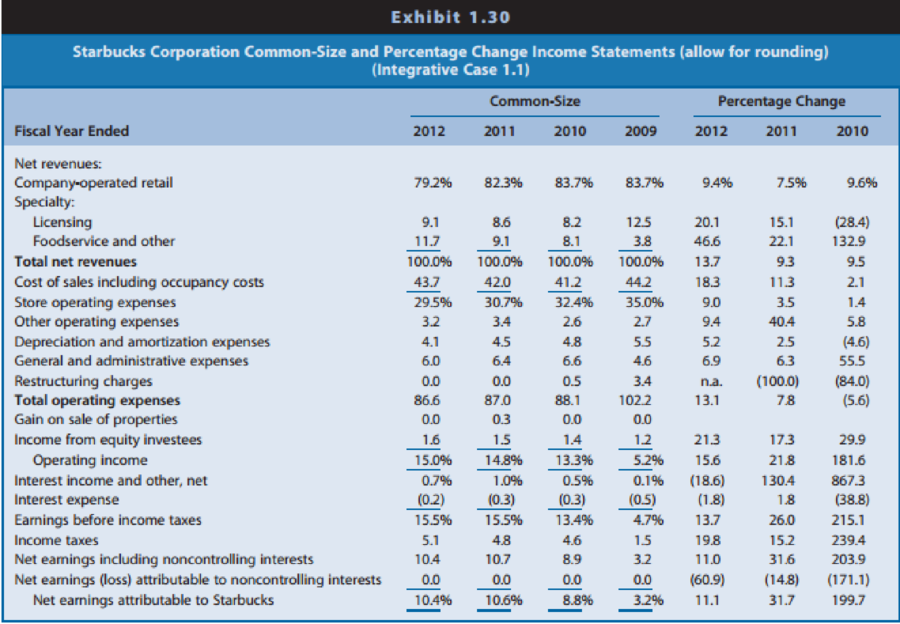
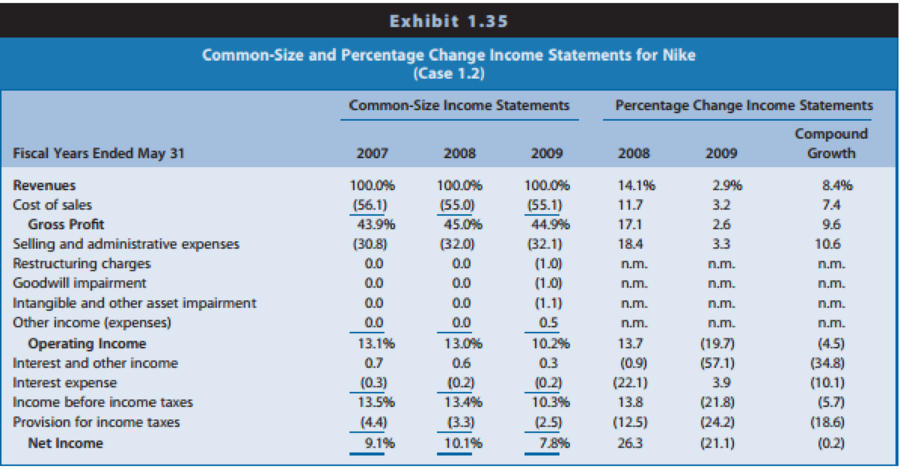
Exhibit 1.35: Common-size and percentage change income statements
Exhibit 1.36: Common-size and percentage change balance sheets
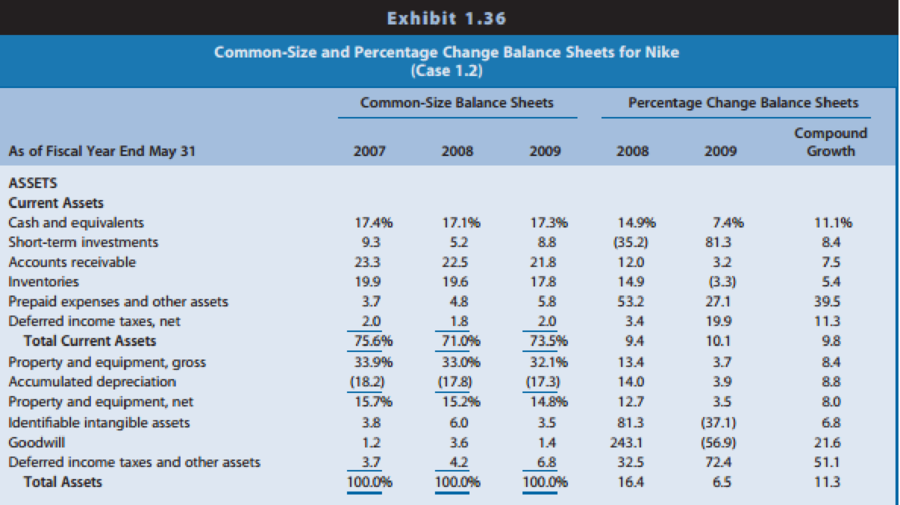
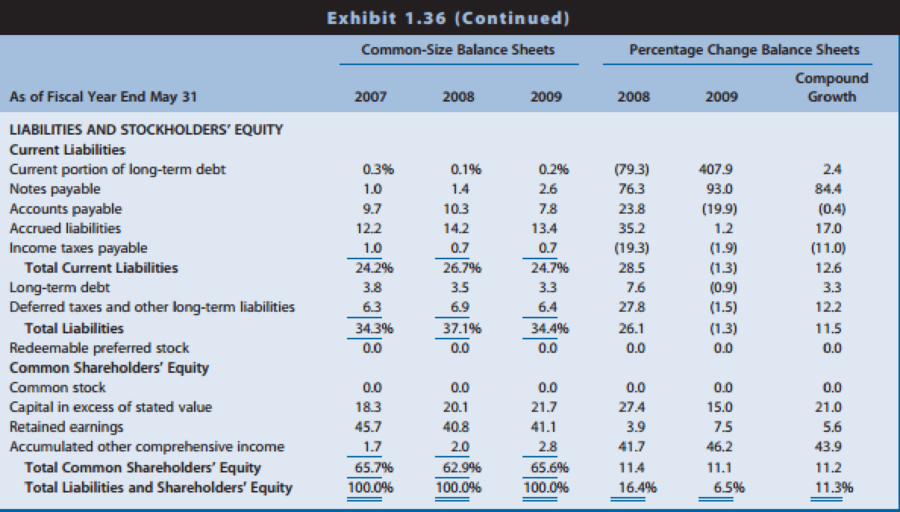
REQUIRED
Study the financial statements and notes for Nike and respond to the following questions.
Nike reports property, plant, and equipment on its balance sheet and discloses the amount of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK FINANCIAL REPORTING, FINANCIAL STAT
- if image is blurr or data is not clear in image please comment i will write data or upload new image. Don't use chatgpt. confirm i will give unhelpful if answer with using incorrect data .arrow_forwardBright wood Seating sells reclining chairs for $55.00 per unit. The variable cost is 322 per unit. Each reclining chair requires 5 direct labor hours and 3 machine hours to produce. atribution margin pegmachine home* Wrightwood Manufacturing has a break-even point of 1,500 units. The sales price per unit is $18, and the variable cost per u 13. If the company sells 3,500 units, what will its net income be? Creatwood Industries provides the following budget data for its Processing Department for the year 2022: ⚫ Manufacturing Overhead Costs=$250,400 . Direct Labor Costs $1,234,500 Determine the manufacturing overhead application rate underthe base of Direct Labor Costs. Modesto Accessories manufactures two types of wallets leather and canvas. The company allocates manufacturing overhead using a single plant wide rate with direct labor cost as the allocation base. $48 Estimated Overhead Costs = 30,600 Direct Labor Cost per Leather Wallet Direct Labor Cost per Canvas Wallet = $52 Number of…arrow_forwardPlease don't use AI . Chatgpt giving wrong answer . confirm i will give unhelpharrow_forward
- Anti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information inits income statement:Sales = $5,250,000;Costs = $2, 173,000;Other expenses = $187,400;Depreciation expense = $79,000;Interest expense= $53,555;Taxes = $76,000;Dividends = $69,000.$136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year andlong-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed.a) Compute the cash flow from assetsb) Compute the net change in working capital Show all calculations. Please no spreadsheet so that I can clearly understandarrow_forwardAnswer this question Using the Google drive liink below it hhas the case study In the scenario, Sharp’s employer has been putting more emphasis on controlling costsfor the various businesses. With the slowing of overall spending in the construction sector,Travolta had ordered managers to closely monitor expenses. He had sold several companiesand has given vice presidents greater responsibility for statements of financial positions. Whatpositive and negative consequences might this pose to the company in future fraud prevention?Outline at least three of each type. Please use sources and insert intext citiations Apa 7 format in the answer and provide the links and references below. https://docs.google.com/document/d/1MpthrFl3eAnMKR-EprYRP9sMo8Ll0WtbhxhpGtLbdcw/edit?usp=sharingarrow_forwardfile:///C:/Users/rafan/Downloads/Assignment%201%20Paving%20Company%20Case%20S2%202024%20to%202025.pdf Using the link for the fraud case answer only this question below. b) As discussed in units 1 to 4, all frauds involve key elements. Identify and describe usingexamples, the elements of Sharp’s fraud.arrow_forward
- Option should be match experts are giving incorrect answer they are using AI /Chatgpt that is generating wrong answer. i will give unhelpful if answer will not match in option. dont use AI alsoarrow_forwardOption should be match. please don't use ai if option will not match means answer is incorrect . Ai giving incorrect answerarrow_forwardOption should be match. please don't use ai if option will not match means answer is incorrect . Ai giving incorrect answerarrow_forward
- all frauds involve key elements. Identify and describe usingexamples the elements of fraudarrow_forwardSolve for maturity value, discount period, bank discount, and proceeds. Assume a bank discount rate of 9%. Use the ordinary interest method. (Use Days in a year table.) Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest cent. face value(principal) $50000rate interest:11%length of note: 95 days maturity value: ?date of note: june 10date note discounted: July 18discount period:?bank discount:?proceeds:?arrow_forwardWhat are the different types of audits and different types of auditors? WHat is an example of each type of audit? What is the significance of each from the perspective of different stakeholders?arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...AccountingISBN:9781305080577Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...AccountingISBN:9781305080577Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub





