
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305856240
Author: Pytel
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.73P
Resolve the force
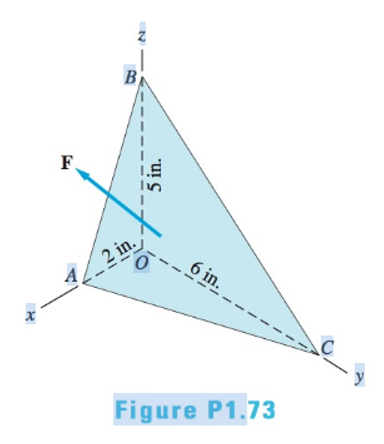
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please answer
Oxygen at 300 kPa and 90°C flowing at an average velocity of 3 m/s is expanded in an adiabatic nozzle. What is the maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle when the outlet pressure is 60 kPa? Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases.
The maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle is 532.5 Numeric ResponseEdit Unavailable. 532.5 incorrect.m/s.
A container filled with 70 kg of liquid water at 95°C is placed in a 90-m3 room that is initially at 12°C. Thermal equilibrium is established after a while as a result of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room. Assume the room is at the sea level, well sealed, and heavily insulated.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Determine the amount of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room.
The amount of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room is kJ.
A strain gauge rosette that is attached to the surface of a stressed component
gives 3 readings (ɛa = A, b = B, &c = C). If the strain gauge rosette is of the D°
type (indicating the angle between each of the gauges), construct a Mohr's Strain
Circle overleaf. You should assume that gauge A is aligned along the x-axis.
Using the Mohr's Strain Circle calculate the:
(i) principal strains (ε1, 2)?
(ii) principal angles (1, 2)?
You should measure these anticlockwise from the y-axis.
(iii) maximum shear strain in the plane (ymax)?
Chapter 1 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics 4th Edition
Ch. 1 - A person weighs 30 lb on the moon, where...Ch. 1 - The radius and length of a steel cylinder are 40...Ch. 1 - Convert the following: (a) 400lbft to knm; (b)...Ch. 1 - A compact car travels 30 mi on one gallon of gas....Ch. 1 - The kinetic energy of a car of mass m moving with...Ch. 1 - In a certain application, the coordinate a and the...Ch. 1 - When a force F acts on a linear spring, the...Ch. 1 - In some applications dealing with very high...Ch. 1 - A geometry textbook gives the equation of a...Ch. 1 - A differential equation is d2ydt2=Ay2+Byt where y...
Ch. 1 - The position coordinate x of a particle is...Ch. 1 - A differential equation encountered in the...Ch. 1 - Determine the dimensions of constants A and B far...Ch. 1 - The typical power output of a compact car engine...Ch. 1 - Two 12-kg spheres are placed 400 mm apart. Express...Ch. 1 - Two identical spheres of radius 8 in. and weighing...Ch. 1 - A man weighs 170 lb on the surface of the earth....Ch. 1 - Use Eq. (1.4) to show that the weight of an object...Ch. 1 - Plot the earths gravitational acceleration g(m/s2)...Ch. 1 - Find the elevation h (km) where the weight of an...Ch. 1 - Calculate the gravitational force between the...Ch. 1 - The magnitudes of the two velocity vectors are...Ch. 1 - Determine the magnitudes of vectors v1 and v2 so...Ch. 1 - The pole AB is held up by the rope attached to B....Ch. 1 - Resolve the 20-kN force into components along the...Ch. 1 - The velocity vector of the boat has two...Ch. 1 - Two members of a truss apply the forces shown to...Ch. 1 - Two members of a truss apply the forces shown to...Ch. 1 - Determine the resultant of the position vectors A...Ch. 1 - Resolve the position vector A of the car (measured...Ch. 1 - Resolve the 360-lb force into components along the...Ch. 1 - The supporting cables AB and AC are oriented so...Ch. 1 - The two forces shown act on the structural member...Ch. 1 - The resultant of the two forces has a magnitude of...Ch. 1 - The forces acting on the bob of the pendulum are...Ch. 1 - A surveyor sights a target at C from points A and...Ch. 1 - Knowing that the resultant of the two forces is...Ch. 1 - To move the oil drum, the resultant of the three...Ch. 1 - The resultant of the 50-Ib and 30-lb forces is R....Ch. 1 - Obtain the rectangular representation of the force...Ch. 1 - The length of the position vector r is 240 mm....Ch. 1 - Determine the rectangular components of the 560-lb...Ch. 1 - The coordinates of points A and B are (-3, 0, 2)...Ch. 1 - The slider travels along the guide rod AB with the...Ch. 1 - Find the rectangular representation of the force...Ch. 1 - The magnitude of the force F is 160 lb. Find its...Ch. 1 - A rifle at A is fired at a target at B. If the...Ch. 1 - The pole OB is subjected to the 6004b force at B....Ch. 1 - The cables AB and AC are attached to the frame...Ch. 1 - The two forces are applied to the end of the boom...Ch. 1 - The magnitudes of the three forces are...Ch. 1 - Given that P=120lb and Q=130lb, find the...Ch. 1 - Knowing that P=90lb and that the resultant of P...Ch. 1 - If R is the resultant of the forces P and Q, find...Ch. 1 - The force R is the resultant of P and 0. Determine...Ch. 1 - The vertical post is secured by three cables. The...Ch. 1 - Compute the dot product A - B for each of the...Ch. 1 - Compute the cross product C=AB for each of the...Ch. 1 - Given r=4i6j+2km (position vector) F=20i+40j30kN...Ch. 1 - Compute AB and CB for the position vectors shown.Ch. 1 - Use the dot product to find the angle between the...Ch. 1 - Use the dot product to find the angle between the...Ch. 1 - Let A and B be two nonparallel vectors that lie in...Ch. 1 - Determine (a) the angle between the position...Ch. 1 - Find a unit vector that is perpendicular to both...Ch. 1 - The three points A(0,2,2),B(1,4,1), and C(3,0,0)...Ch. 1 - For the position vectors P and Q shown, determine...Ch. 1 - Compute the orthogonal Component of F=6i+20j12klb...Ch. 1 - Compute the value of the scalar a for which the...Ch. 1 - Resolve A=3i+5j4k in. into two vector...Ch. 1 - The force F=5i+12j+4k lb is applied to the handle...Ch. 1 - Determine the value of the scalar a if the...Ch. 1 - Resolve the force F=20i+30j+50klb into two...Ch. 1 - It can be show that a plane area may he...Ch. 1 - The coordinates of the corners of a triangle ABC...Ch. 1 - Show that |abc| equals the volume of a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1. If the yield stress (σy) of a material is 375MPa, determine whether yield is predicted for the stresses acting on both the elements shown below using: (a) Tresca Criterion (b) Von Mises Criterion P Element A R S Element B Note: your values for P (vertical load on Element A) should be negative (i.e. corresponding to a compressive vertical load).arrow_forwardQ. After a puncture a driver is attempting to remove a wheel nut by applying a force of P KN to one end of a wheel brace as shown in Fig. 1. In cross-section the brace is a hollow steel tube (see section aa) of internal diameter r mm and external diameter q mm. wheel nut n Position S P m r q Section aa Fig, 1 (a) Calculate (i) the twisting moment, (ii) the bending moment, and (iii) the shear force in the brace at position S due to the applied load P. (b) Calculate (i) the shear stress due to twisting, and (ii) the bending stress at position S. Note that the shear force will not produce any shear stress at S. (c) Calculate the maximum shearing stress in the brace at position S using the Maximum Shear Stress Criterion. 2 Mechanics of Materials 2 Tutorials Portfolio: Exercise 5 (d) If the maximum permissible shear stress in the steel is 200 MPa, determine the maximum torque that can be applied by the brace without the risk of failure at S.arrow_forwardCalculate the first 5 Fourier series coefficients (A0-4 and B1-5 ) for the estimated R wave.arrow_forward
- Refrigerant-134a is expanded isentropically from 600 kPa and 70°C at the inlet of a steady-flow turbine to 100 kPa at the outlet. The outlet area is 1 m2, and the inlet area is 0.5 m2. Calculate the inlet and outlet velocities when the mass flow rate is 0.65 kg/s. Use the tables for R-134a. The inlet velocity is m/s. The outlet velocity is m/s.arrow_forwardA container filled with 70 kg of liquid water at 95°C is placed in a 90-m3 room that is initially at 12°C. Thermal equilibrium is established after a while as a result of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room. Assume the room is at the sea level, well sealed, and heavily insulated. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final equilibrium temperature. Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases. The final equilibrium temperature is °C.arrow_forwardSteam at 100 psia and 650°F is expanded adiabatically in a closed system to 10 psia. Determine the work produced, in Btu/lbm, and the final temperature of steam for an isentropic expansion efficiency of 80 percent. Use steam tables. The work produced is Btu/lbm. The final temperature of steam is °F.arrow_forward
- Complet the solution : Vavg Ti Te Ts Q hexp Nuexp htheo Re Nutheo Error (m/s) (*C) (*C) (*C) (W) 2.11 18.8 21.3 45.8 2.61 18.5 20.8 46.3arrow_forwardA 48-kg iron block and a 76-kg copper block, both initially at 80°C, are dropped into a large lake at 15°C. Thermal equilibrium is established after a while as a result of heat transfer between the blocks and the lake water. Determine the total entropy change for this process. The specific heat of iron at room temperature is cp = 0.45 kJ/kg·K. The specific heat of copper at 27°C is cp = 0.386 kJ/kg·K. The total entropy change for this process is kJ/K.arrow_forwardPlease help Air at 4.4 MPa and 500°C is expanded in an adiabatic gas turbine to 0.2 MPa. Calculate the maximum work that this turbine can produce in kJ/kg. Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases. The maximum work that this turbine can produce is kJ/kg.arrow_forward
- Saturated water vapor at 150°C is compressed in a reversible steady-flow device to 1150 kPa while its specific volume remains constant. Determine the work required in kJ/kg. Use steam tables. The work required is kJ/kg.arrow_forwardThree lbm of R-134a is expanded isentropically in a closed system from 100 psia and 100°F to 10 psia. Determine the total heat transfer and the work production for this process. Use the tables for R-134a. The total heat transfer is Btu. The work production for this process is Btu. Three lbm of R-134a is expanded isentropically in a closed system from 100 psia and 100°F to 10 psia. Determine the total heat transfer and the work production for this process. Use the tables for R-134a. The total heat transfer is Btu. The work production for this process is Btu.arrow_forwardOxygen at 300 kPa and 90°C flowing at an average velocity of 3 m/s is expanded in an adiabatic nozzle. What is the maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle when the outlet pressure is 60 kPa? Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases. The maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle is m/s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY