
Concept explainers
You stand in a flat meadow and observe two cows (Fig. P1.73). Cow A is due north of you and 15.0 m from your position. Clow B is 25.0111 from your position. From your point of view, the angle between cow A and cow H is 20.0°, with cow B appearing to the right of cow A. (a) How far apart are cow A and cow B? (b) Consider the view seen by cow A. According to this cow, what is the angle between you and cow B? (c) Consider the view seen by cow B. According to this cow, what is the angle between you and cow A? Hint: What does the situation look like to a hummingbird hovering above the meadow? (d) Two stars in the sky appear to be 20.0° apart. Star A is 15.0 ly from the Earth, and star B. appearing to the right of star A. is 25.0 ly from the Earth. To an inhabitant of a planet orbiting star A. what is the angle in the sky between star B and our Sun?

Figure P1.73 Your view of two cows in a meadow. Cow A U due north of you. You must rotate your eyes through an angle of 20.0° to look from cow A to cow B.
(a)
The distance between cow
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The distance between cow
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The Cow
Consider the following figure.
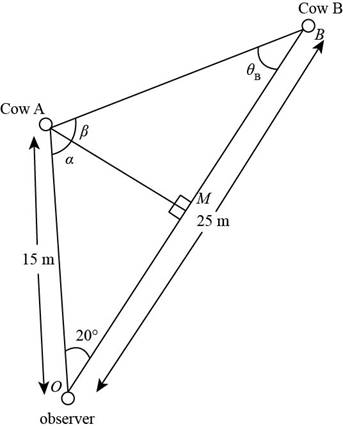
Figure (1)
The expression for the distance between cow
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the distance between cow
(b)
The angle between observer and the cow B.
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The angle between observer and the cow B is
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The Cow
From figure (1),
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
In triangle
Substitute
The value of the
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
The expression for the angle between observer and the cow
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the angle between observer and the cow B is
(c)
The angle between the observer and cow
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The angle between the observer and cow
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The Cow
The expression for the angle between the observer and cow
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the angle between the observer and cow
(d)
The angle between the star
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The angle between the star
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The star
Consider the following figure.
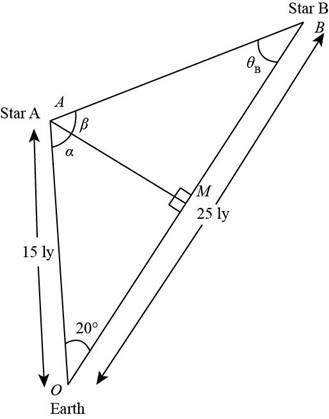
Figure (2)
The expression for the distance between star
Substitute
Thus the value of
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
In triangle
Substitute
The value of the
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
The expression for the angle between earth and the star
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle between the star
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 1, Chapters 1-22
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
HUMAN ANATOMY
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Iarrow_forwardHow would partial obstruction of an air intake port of an air-entrainment mask effect FiO2 and flow?arrow_forward14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forwardCheckpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forward
- What is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





