
Concept explainers
You stand in a flat meadow and observe two cows (Fig. P1.73). Cow A is due north of you and 15.0 m from your position. Clow B is 25.0111 from your position. From your point of view, the angle between cow A and cow H is 20.0°, with cow B appearing to the right of cow A. (a) How far apart are cow A and cow B? (b) Consider the view seen by cow A. According to this cow, what is the angle between you and cow B? (c) Consider the view seen by cow B. According to this cow, what is the angle between you and cow A? Hint: What does the situation look like to a hummingbird hovering above the meadow? (d) Two stars in the sky appear to be 20.0° apart. Star A is 15.0 ly from the Earth, and star B. appearing to the right of star A. is 25.0 ly from the Earth. To an inhabitant of a planet orbiting star A. what is the angle in the sky between star B and our Sun?

Figure P1.73 Your view of two cows in a meadow. Cow A U due north of you. You must rotate your eyes through an angle of 20.0° to look from cow A to cow B.
(a)
The distance between cow
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The distance between cow
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The Cow
Consider the following figure.
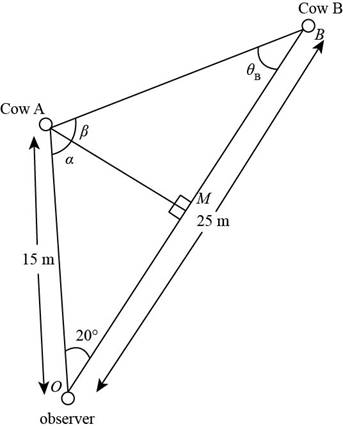
Figure (1)
The expression for the distance between cow
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the distance between cow
(b)
The angle between observer and the cow B.
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The angle between observer and the cow B is
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The Cow
From figure (1),
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
In triangle
Substitute
The value of the
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
The expression for the angle between observer and the cow
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the angle between observer and the cow B is
(c)
The angle between the observer and cow
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The angle between the observer and cow
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The Cow
The expression for the angle between the observer and cow
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the angle between the observer and cow
(d)
The angle between the star
Answer to Problem 1.73AP
The angle between the star
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The star
Consider the following figure.
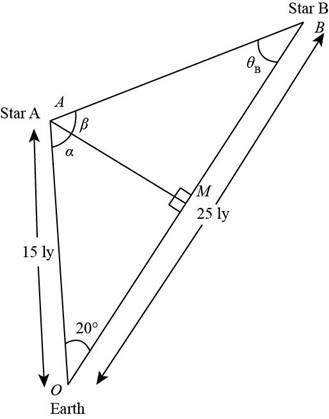
Figure (2)
The expression for the distance between star
Substitute
Thus the value of
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
In triangle
Substitute
The value of the
In triangle
Substitute
Thus the value of the
The expression for the angle between earth and the star
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle between the star
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 1
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
HUMAN ANATOMY
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- Please solve this problem correctly please and be sure to provide explanation on each step so I can understand what's been done thank you. (preferrably type out everything)arrow_forwardUse a calculation to determine how far the fishing boat is from the water level .Determine distance Yarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward
- 2. 1. Tube Rating Charts Name: Directions: For the given information state if the technique is safe or unsafe and why. 60 Hertz Stator Operation Effective Focal Spot Size- 0.6 mm Peak Kilovolts MA 2 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 2501 60 50 40 30 .01 .02 .04.06 .1 .2 .4.6 1 8 10 Maximum Exposure Time In Seconds Is an exposure of 80 kVp, 0.1 second and 200 mA within the limits of the single phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above? Is an exposure of 100 kVp, 0.9 second and 150 mA within the limits of the single phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above?arrow_forwardQ: You have a CO2 laser resonator (λ = 10.6 μm). It has two curved mirrors with R₁=10m, R2= 8m, and mirror separation /= 5m. Find: R2-10 m tl Z-O 12 R1-8 m 1. Confocal parameter. b= 21w2/2 =√1 (R1-1)(R2-1)(R1+R2-21)/R1+R2-21) 2. Beam waist at t₁ & t2- 3. Waist radius (wo). 4. 5. The radius of the laser beam outside the resonator and about 0.5m from R₂- Divergence angle. 6. Radius of curvature for phase front on the mirrors R₁ & R2-arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





