(a)
Interpretation: The shortest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order, shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.68P
The shortest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
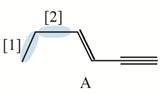
Figure 1
Both
The shortest
(b)
Interpretation: The longest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.68P
The longest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
The longest
(c)
Interpretation: The shortest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.68P
The shortest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
The shortest
(d)
Interpretation: The weakest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.68P
The weakest
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
Both
The weakest
(e)
Interpretation: The strongest
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.68P
The strongest
Explanation of Solution
The length and strength of a
Triple bond is formed by
The strongest
(f)
Interpretation: Bond
Concept introduction: There is an inverse relationship between bond length and bond strength. Shorter bonds are stronger bonds or higher the bond order shorter is the bond length.
Answer to Problem 1.68P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
In hybridization, one
Bond
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward

 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





