
Concept explainers
Classify each example of molecular art as a pure element, a pure compound, or a mixture.
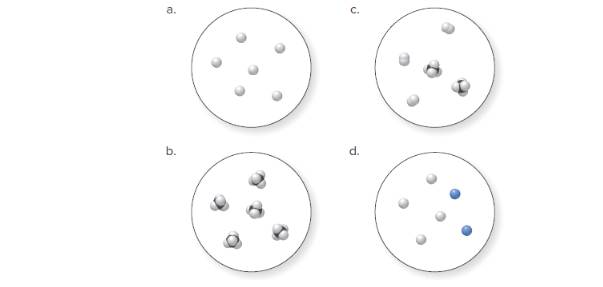
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given molecular art is a pure compound, mixture, or a pure element needs to be classified.

Concept Introduction:
An element is known as the pure substance that cannot be broken down further using chemical methods. The methods are such as electrolysis, cooling, heating, and reactions with other chemical substances.
A compound is known as the pure substance which is made up of more than two different atoms that are bonded chemically to one another. Using chemical methods, a compound can be destroyed. It can be broken down into simpler compounds or into its elements.
A mixture is the combination of more than two dissimilar elemental substances or compounds. The mixture is not a pure substance, but it is the combination of different atoms of elements. Mixtures are of two kinds, Heterogenous and Homogeneous.
Answer to Problem 1.33P
Molecular art 'a' − Pure element.
Explanation of Solution
As per the definitions of element, compound and mixture:
The pure element is the substance that doesn't separate into simple substances through the chemical procedures.
A pure compound is a substance formed by combinations of two or more elements.
A mixture is made up of the combination of one or more components with several compositions.
Now, based on these definitions, molecular art (a) signifies pure elements.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the below molecular art is pure compound, mixture, or a pure element needs to be determined.
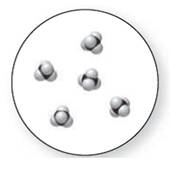
Concept Introduction:
An element is known as the pure substance that cannot be broken down further using chemical methods. The methods are such as electrolysis, cooling, heating, and reactions with other chemical substances.
A compound is known as the pure substance which is made up of more than two different atoms that are bonded chemically to one another. Using chemical methods, a compound can be destroyed. It can be broken down into simpler compounds or into its elements.
A mixture is the combination of more than two dissimilar elemental substances or compounds. The mixture is not a pure substance, but it is the combination of different atoms of elements. Mixtures are of two kinds, Heterogenous and Homogeneous.
Answer to Problem 1.33P
Molecular art 'b' − Pure compounds
Explanation of Solution
As per the definitions of element, compound and mixture:
The pure element is the substance that doesn't separate into simple substances through the chemical procedures.
A pure compound is a substance formed by combinations of two or more elements.
A mixture is made up of the combination of one or more components with several compositions.
Now based on these definitions, molecular art (b) signifies pure compounds.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the below compound is a pure compound, mixture, or a pure element needs to be determined.
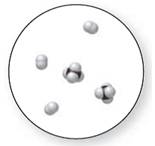
Concept Introduction:
An element is known as the pure substance that cannot be broken down further using chemical methods. The methods are such as electrolysis, cooling, heating, and reactions with other chemical substances.
A compound is known as the pure substance which is made up of more than two different atoms that are bonded chemically to one another. Using chemical methods, a compound can be destroyed. It can be broken down into simpler compounds or into its elements.
A mixture is the combination of more than two dissimilar elemental substances or compounds. The mixture is not a pure substance, but it is the combination of different atoms of elements. Mixtures are of two kinds, Heterogenous and Homogeneous.
Answer to Problem 1.33P
Molecular art 'c' − Mixture
Explanation of Solution
As per the definitions of element, compound and mixture:
The pure element is the substance that doesn't separate into simple substances through the chemical procedures.
A pure compound is a substance formed by combinations of two or more elements.
A mixture is made up of the combination of one or more components with several compositions.
Now based on these definitions, molecular art (c) signifies mixture.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the below compound is a pure compound, mixture, or a pure element needs to be determined.
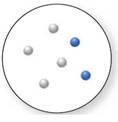
Concept Introduction:
An element is known as the pure substance that cannot be broken down further using chemical methods. The methods are such as electrolysis, cooling, heating, and reactions with other chemical substances.
A compound is known as the pure substance which is made up of more than two different atoms that are bonded chemically to one another. Using chemical methods, a compound can be destroyed. It can be broken down into simpler compounds or into its elements.
A mixture is the combination of more than two dissimilar elemental substances or compounds. The mixture is not a pure substance, but it is the combination of different atoms of elements. Mixtures are of two kinds, Heterogenous and Homogeneous.
Answer to Problem 1.33P
Mixture
Explanation of Solution
As per the definitions of element, compound and mixture:
The pure element is the substance that doesn't separate into simple substances through the chemical procedures.
A pure compound is a substance formed by combinations of two or more elements.
A mixture is made up of the combination of one or more components with several compositions.
Now, based on these definitions, molecular art (d) signifies mixture.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- (a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





