
a.
To draw: To draw a square that has sides that are twice the length of the given square.
a.
Answer to Problem 13E
The length of the new square is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Square that has sides that are twice the length of the given square.
Expiations:
Suppose the length of the given square is ‘x’.
Therefore, the length of the new square is
Given square:
New square:

b.
To draw: To draw a square that has sides are change as given.
b.
Answer to Problem 13E
The perimeter of the squares are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Square is 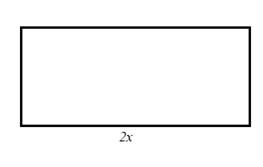
Suppose the length of the given square is ‘x’.
Therefore, the length of the new squares are
Perimeter: The sum of all sides is called perimeter.
New squares:
| Side Length | Perimeter |
c.
To calculate: Analyze the perimeter of the square.
c.
Answer to Problem 13E
The perimeter of the square is also increases.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Suppose the length of the given square is ‘x’.
Therefore, the length of the new squares are
Explantion:
Perimeter: The sum of all sides is called perimeter.
| Side Length | Perimeter |
d.
To calculate: Calculate the perimeter of the square.
d.
Answer to Problem 13E
The perimeter of the square is
Explanation of Solution
Suppose the length of the given square is
When length of the square is multiply by 8, the length of the square become
Perimeter: The sum of all sides is called perimeter.
Perimeter
Chapter 0 Solutions
Pre-Algebra, Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Precalculus
Introductory Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
- There were 426 books sold in one week. The number of biology books sold was 5 times that of the number of psychology books. How many books each were sold?arrow_forwardPopulation decreases 5% each year. Starts with a starting population of 3705. Find that population after 5 years.arrow_forwardsolve using substitution -2x-3y=-15 -3x+9y=12arrow_forward
- Suppose that 7000 is placed in an accout that pays 4% interest. Interest compunds each year. Assume that no withdraws are made. How much would the account have after 1 year? And how much would the account have after 2 years?arrow_forwardUse substitution to solve the equations -2x+5y=18 x=2y-8arrow_forward5) For each function represented by an equation, make a table and plot the corresponding points to sketch the graph of the function. (a) y = 75 ()* 220 X y 200- -2 180 160 -1 140 0 120 100 1 60 80 2 3 4 x (b) y = 20 ()* 1 60 40 20 20 0 2 3 65- -1 X y 60 -2 55- 50 45 44 40 0 35- 30 1 25 2 20 20 15 3 10 5 LO 4 3-2 T -1 0 5- 4- -3- 2-arrow_forward
- A system of inequalities is shown. y 5 3 2 1 X -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 -1- Which system is represented in the graph? Oy>-x²-x+1 y 2x²+3 -2 -3 тarrow_forwardWhich set of systems of equations represents the solution to the graph? -5 -4 -3 -2 Of(x) = x² + 2x + 1 g(x) = x²+1 f(x) = x²+2x+1 g(x) = x²-1 f(x) = −x² + 2x + 1 g(x) = x²+1 f(x) = x² + 2x + 1 g(x) = x²-1 -1 5 y 4 3 2 1 0 -1- -2 -3- -4. -5 1 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardWhich of the graphs below correctly solves for x in the equation -x² - 3x-1=-x-4? о 10 8 (0,2) -10 -8 -6 -2 2 4 6 8 10 (-4,-2) -2 + (0,2) (4,6) -10-8-6-4-2 -2 2 4 6 8 10 (-3, -1) -2 2 (1-5) -6 -8 -10 10 -10-8-6-4-2 2 6 8 10 (2,0)arrow_forward
- 1) Express these large and small numbers from the Read and Study section in scientific notation: (a) 239,000 miles (b) 3,800,000,000,000 sheets of paper (c) 0.0000000000000000000000167 grams 2) Find all values for the variable x that make these equations true. (a) 5x = 1 (b) 3x = 1/1 9 (c) 4* = 11/ 4 (e) 4* = 64 (g) 10x = 1,000,000 (d) 3x=-3 (f) 2x = = 8 (h) 10x = 0.001arrow_forward(b) 4) Find an equation to fit each of the following graphs: (a) 20 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 16 A 2 -3 -2 -1-0 2 3 4. -1 0 1 2 3. -2 -2arrow_forward3) Which of the following are equivalent to 3? (There may be more than one that is equivalent!) -1 (a) (9)¯¹ 3. (b) (-3)-1 (c) (-3) -1 (d) -(¯3) (e) 11 3-1 (f) 3-4arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





