-Z +Z -27 Three charges are on a line as shown. An electron (charge -e, mass m) is released from rest at point A. We want to determine how fast the electron is A B --- --- W W W W moving at point B. a. A common mistake is to calculate the electric force on the electron at point A and then use Newton's 2nd law and constant acceleration kinematics to find the speed of the electron at point B. Why won't this work? b. Use conservation of energy to determine the speed of the electron a point B.
-Z +Z -27 Three charges are on a line as shown. An electron (charge -e, mass m) is released from rest at point A. We want to determine how fast the electron is A B --- --- W W W W moving at point B. a. A common mistake is to calculate the electric force on the electron at point A and then use Newton's 2nd law and constant acceleration kinematics to find the speed of the electron at point B. Why won't this work? b. Use conservation of energy to determine the speed of the electron a point B.
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:-Z
+Z
-27
2. Three charges are on a line as shown. An electron
(charge -e, mass m) is released from rest at point
A
В
A. We want to determine how fast the electron is
W
W
W
W
moving at point B.
A common mistake is to calculate the electric force on the electron at point A and then use Newton's 2nd law
and constant acceleration kinematics to find the speed of the electron at point B. Why won't this work?
а.
b. Use conservation of energy to determine the speed of the electron a point B.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Part (a)
In the given arrangement, at point A the net force on the electron can be written as below,
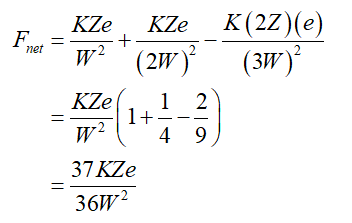
Here it is assumed that the force towards the positive x-axis is a positive direction and that towards the negative x-axis is the negative direction.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images
