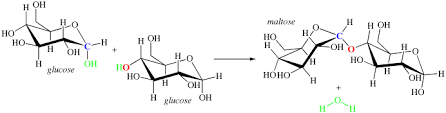
What is the name of the process shown below and how does it work (be specific about what happens to the molecules involved)? Which class of biomolecules (protein, lipid, carbohydrate, nucleic acid) are involved in this particular reaction example? List at least 2 types of functions this class of macromolecules might be involved in biologically. 2 H-C-OH a to H OH H-C-OH H H H O H .H H-C-OH H O H it H LOH H + H₂0
Catalysis and Enzymatic Reactions
Catalysis is the kind of chemical reaction in which the rate (speed) of a reaction is enhanced by the catalyst which is not consumed during the process of reaction and afterward it is removed when the catalyst is not used to make up the impurity in the product. The enzymatic reaction is the reaction that is catalyzed via enzymes.
Lock And Key Model
The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity, based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the particular active site of the enzyme. This is significant in understanding the intermolecular interaction between proteins and plays a vital role in drug interaction.
21

In this reaction, 2 monosaccharides are joined together to form a disaccharides by a glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage. The hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a monosaccharide reacts with OH (hydroxyl) group of monosaccharide (with the elimination of a H2O molecule, i.e. dehydration) to form a disaccharide.
In this reaction, 2 glucose molecules link up together to form the sugar known as Maltose. Maltose is one of the most common disaccharide carbohydrates.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









